8.012 Physics I: Classical Mechanics
... the quantities given in the diagram above, in a polar coordinate system centered on the center of the coin’s trajectory. For simplicity, assume that α is very small (i.e., only consider first order terms in α). ...
... the quantities given in the diagram above, in a polar coordinate system centered on the center of the coin’s trajectory. For simplicity, assume that α is very small (i.e., only consider first order terms in α). ...
Ball 1 of mass m moving right with speed v bounces off ball 2 with
... Answer: This one is tricky. The hoop goes faster at the top. Both hoop and puck have the same KEtrans = (1/2)mv2, but , in addition, the hoop has some KErot. In going up the hill, both hoop and puck lose the same amount of KE (KE = –mgh). But for the puck, all of its lost KE was translational KE. W ...
... Answer: This one is tricky. The hoop goes faster at the top. Both hoop and puck have the same KEtrans = (1/2)mv2, but , in addition, the hoop has some KErot. In going up the hill, both hoop and puck lose the same amount of KE (KE = –mgh). But for the puck, all of its lost KE was translational KE. W ...
Mechanics 2 : Revision Notes 1. Kinematics and variable acceleration
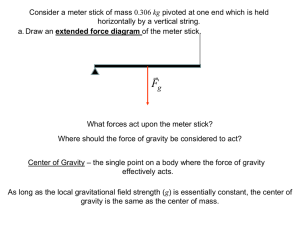
... - draw a diagram to show all the forces – weight – ‘normal’ – tensions …. - by taking moments about a point you can ignore the forces acting at that point - resolve – vertically and horizontally Example A ladder of length 3 m and mass 20 kg, leans against a smooth, vertical wall, so that the angle b ...
... - draw a diagram to show all the forces – weight – ‘normal’ – tensions …. - by taking moments about a point you can ignore the forces acting at that point - resolve – vertically and horizontally Example A ladder of length 3 m and mass 20 kg, leans against a smooth, vertical wall, so that the angle b ...
Angular Momentum
... A rigid body can be treated as a system of particles of infinitesimal mass whose position with respect to the other particles in the system doesn't change. for a particle in circular motion ...
... A rigid body can be treated as a system of particles of infinitesimal mass whose position with respect to the other particles in the system doesn't change. for a particle in circular motion ...
Chapter 5
... Figure 5.4-8 A point mass m and a distributed mass M are rotating at a uniform angular velocity . The linear momentum of a mass m moving in the x direction with a velocity Vx is mVx. The angular momentum (L) of a point mass m rotating with an angular velocity rad/s in an arc having a radius of c ...
... Figure 5.4-8 A point mass m and a distributed mass M are rotating at a uniform angular velocity . The linear momentum of a mass m moving in the x direction with a velocity Vx is mVx. The angular momentum (L) of a point mass m rotating with an angular velocity rad/s in an arc having a radius of c ...
Chapter 5
... object and its direction. -may be a negative depending on direction. Instantaneous speed is the speed of an object at any given ...
... object and its direction. -may be a negative depending on direction. Instantaneous speed is the speed of an object at any given ...
Massive Pulleys Review
... Newton’s 2nd law is always true (for inertial reference frames) Conservation of energy still applies. ...
... Newton’s 2nd law is always true (for inertial reference frames) Conservation of energy still applies. ...
PHYSICS 214 TEST 1 12 February 2008
... momentum conservation work or energy, electrical power, electrical for uniform electric field, where d is distance along the voltage gradient ε = (Thot – Tcold)/Thot Carnot efficiency of an ideal heat engine PV = NkT Ideal gas law where P,V,T are pressure, volume, and Kelvin temperature and k is Bol ...
... momentum conservation work or energy, electrical power, electrical for uniform electric field, where d is distance along the voltage gradient ε = (Thot – Tcold)/Thot Carnot efficiency of an ideal heat engine PV = NkT Ideal gas law where P,V,T are pressure, volume, and Kelvin temperature and k is Bol ...