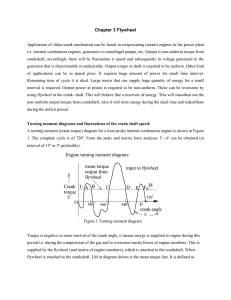
chapter 3 flywheel
... and F are the points where T − θ diagram cuts the mean torque line. These points are transition points from deficit to extra energy or vice versa. So crank starts accelerate from deceleration from such points or vice versa. For example at points: A, C, E → accelerate and at B, D, F → decelerate. At ...
... and F are the points where T − θ diagram cuts the mean torque line. These points are transition points from deficit to extra energy or vice versa. So crank starts accelerate from deceleration from such points or vice versa. For example at points: A, C, E → accelerate and at B, D, F → decelerate. At ...
CHAPTER 9 ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS
... In order to write the torque equation, we must first pick an axis of rotation and determine the lever arms for the forces involved. Since both V and H are unknown, we can eliminate them from the torque equation by picking the rotation axis through the point P (then both V and H have zero lever arms) ...
... In order to write the torque equation, we must first pick an axis of rotation and determine the lever arms for the forces involved. Since both V and H are unknown, we can eliminate them from the torque equation by picking the rotation axis through the point P (then both V and H have zero lever arms) ...
Solutions #9
... These forces are exerted by the rod. Since they are unequal, there would be a net horizontal force on the rod (and hence the axle) due to the masses. This horizontal force would have to be counteracted by the mounting for the rod and axle in order for the rod not to move horizontally. There is also ...
... These forces are exerted by the rod. Since they are unequal, there would be a net horizontal force on the rod (and hence the axle) due to the masses. This horizontal force would have to be counteracted by the mounting for the rod and axle in order for the rod not to move horizontally. There is also ...
posted
... IDENTIFY: Apply the first and second conditions for equilibrium to the ladder. SET UP: Let n2 be the upward normal force exerted by the ground and let n1 be the horizontal normal force exerted by the wall. The maximum possible static friction force that can be exerted by the ground is s n2 . EXECUT ...
... IDENTIFY: Apply the first and second conditions for equilibrium to the ladder. SET UP: Let n2 be the upward normal force exerted by the ground and let n1 be the horizontal normal force exerted by the wall. The maximum possible static friction force that can be exerted by the ground is s n2 . EXECUT ...
Chapter 21 = Electric Charge Lecture
... • Proposaes “conservation of charge” • June 15 1752(?) Franklin flies kite and “collects” electricity • 1839 Michael Faraday proposes “electricity” is all from two opposite types of “charges” • We call “positive” the charge left on glass rubbed with silk • Today we would say ‘electrons” are rubbed o ...
... • Proposaes “conservation of charge” • June 15 1752(?) Franklin flies kite and “collects” electricity • 1839 Michael Faraday proposes “electricity” is all from two opposite types of “charges” • We call “positive” the charge left on glass rubbed with silk • Today we would say ‘electrons” are rubbed o ...
Chapter 13, example problems:
... (ii) The amplitude of the oscillation is still 1.10 m × (8.50° × π radians / 180°) = 0.163 m, independent of the acceleration of the rocket. (13.80) A 40.0 N force stretches a vertical spring 0.250 m. (a) Find m suspended from it to get a period of 1.00 s. Force constant of the spring k = 40.0 N / ...
... (ii) The amplitude of the oscillation is still 1.10 m × (8.50° × π radians / 180°) = 0.163 m, independent of the acceleration of the rocket. (13.80) A 40.0 N force stretches a vertical spring 0.250 m. (a) Find m suspended from it to get a period of 1.00 s. Force constant of the spring k = 40.0 N / ...
Chapter 2 - Dublin City Schools
... and an object in motion will continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a net force. ...
... and an object in motion will continue moving at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a net force. ...
chapter11
... The instantaneous angular momentum of a particle relative to the origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector and its instantaneous linear momentum. ...
... The instantaneous angular momentum of a particle relative to the origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector and its instantaneous linear momentum. ...