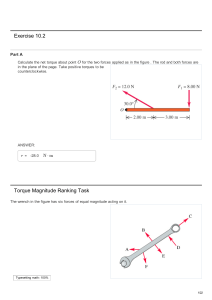
1. (a) Torque and moment are to do with `distance multiplied by force
... Torque and moment are to do with ‘distance multiplied by force’ B1 ...
... Torque and moment are to do with ‘distance multiplied by force’ B1 ...
File
... 3. Determine the magnitude of any known forces and label on the freebody diagram. (For example, if the mass is given, then the Fgrav can be determined) 4. Use circular motion equations to determine any unknown information. (For example, if the speed and the radius are known, then the acceleration ca ...
... 3. Determine the magnitude of any known forces and label on the freebody diagram. (For example, if the mass is given, then the Fgrav can be determined) 4. Use circular motion equations to determine any unknown information. (For example, if the speed and the radius are known, then the acceleration ca ...
Rotary Motion
... 7. Choose New Data Set from the Data menu. Enter your values for the hanging mass and angular acceleration for the stacked disks. As you did in Step 2, create a new calculated column finding the values of the net torque the hanging mass applied to the disks. 8. Plot a graph of net torque, , vs. ang ...
... 7. Choose New Data Set from the Data menu. Enter your values for the hanging mass and angular acceleration for the stacked disks. As you did in Step 2, create a new calculated column finding the values of the net torque the hanging mass applied to the disks. 8. Plot a graph of net torque, , vs. ang ...
true or false questions
... If a bicycle and a parked car have a head-on collision, the force of impact is greater on the bicycle. A quantity that has both magnitude and direction is called a scalar. When all forces acting on an object are balanced, the object is said to be in equilibrium. Momentum is defined as an object's ma ...
... If a bicycle and a parked car have a head-on collision, the force of impact is greater on the bicycle. A quantity that has both magnitude and direction is called a scalar. When all forces acting on an object are balanced, the object is said to be in equilibrium. Momentum is defined as an object's ma ...
Review - Hingham Schools
... Be able to identify and diagram the forces on an object. Be able to break forces at angles into components. Know an object is in equilibrium when the forces acting on the object are balanced. Know an object in equilibrium will move at a constant speed or not at all. Be able to identify forces that a ...
... Be able to identify and diagram the forces on an object. Be able to break forces at angles into components. Know an object is in equilibrium when the forces acting on the object are balanced. Know an object in equilibrium will move at a constant speed or not at all. Be able to identify forces that a ...
conceptual physics c#39AC39
... What is rotational inertia, and how does it compare to inertia as studied in previous chapters? Ans. Rotational inertia, often called moment of inertia, is the sum of the products of an object’s mass multiplied by their distance to the center of rotation squared. Inertia is the resistance an object ...
... What is rotational inertia, and how does it compare to inertia as studied in previous chapters? Ans. Rotational inertia, often called moment of inertia, is the sum of the products of an object’s mass multiplied by their distance to the center of rotation squared. Inertia is the resistance an object ...