Presentation2 Equilibrium Conditions
... The uniform 400-kg drum is mounted on a line of rollers at A and a line of rollers at B. An 80-kg man moves slowly a distance of 700 mm from the vertical centerline before the drum begins to rotate. All rollers are perfectly free to rotate, except one of them at B which must overcome appreciable fri ...
... The uniform 400-kg drum is mounted on a line of rollers at A and a line of rollers at B. An 80-kg man moves slowly a distance of 700 mm from the vertical centerline before the drum begins to rotate. All rollers are perfectly free to rotate, except one of them at B which must overcome appreciable fri ...
Unipolar induction: a neglected topic in the teaching of
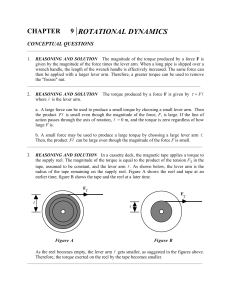
... These considerations are important in the unipolar generator, because one can see from figure 2 that the field has an angular momentum directed along the axis of rotation, given by equation (18). In figure 7 the engine exerts a torque +0 on the magnet, so that it exerts a torque −0 on the framework. ...
... These considerations are important in the unipolar generator, because one can see from figure 2 that the field has an angular momentum directed along the axis of rotation, given by equation (18). In figure 7 the engine exerts a torque +0 on the magnet, so that it exerts a torque −0 on the framework. ...
work - cloudfront.net
... the infield dirt. In such instances, the force acts in the direction opposite the objects motion in order to slow it down. The force doesn't cause the displacement but rather hinders it. These situations involve what is commonly called negative work. The negative of negative work refers to the numer ...
... the infield dirt. In such instances, the force acts in the direction opposite the objects motion in order to slow it down. The force doesn't cause the displacement but rather hinders it. These situations involve what is commonly called negative work. The negative of negative work refers to the numer ...
Vector Practice
... of the other vector on the vector. a. b is called the dot product of the two vectors. a. b = a b cos . If the two vectors are parallel, then a. b = a b And if the two vectors are perpendicular to each other, then a. b = 0 Cross Product of any two vectors is defined by a b= c = a b sin n̂ , wher ...
... of the other vector on the vector. a. b is called the dot product of the two vectors. a. b = a b cos . If the two vectors are parallel, then a. b = a b And if the two vectors are perpendicular to each other, then a. b = 0 Cross Product of any two vectors is defined by a b= c = a b sin n̂ , wher ...
Study Guide - Chapter 5
... ----------------------------------------Time it takes to change velocity ...
... ----------------------------------------Time it takes to change velocity ...
Study Guide - Chapter 5
... ----------------------------------------Time it takes to change velocity ...
... ----------------------------------------Time it takes to change velocity ...
Exam I - Physics
... pages for scratch work. PARTIAL CREDIT POSSIBLE: Select one (1), two (2), or three (3) answers 6 points if you mark the single correct answer 4 points if the correct answer is among your two choices 2 points if the correct answer is among your three choices 10 problems, 6 pts each =60 pts = 50% of e ...
... pages for scratch work. PARTIAL CREDIT POSSIBLE: Select one (1), two (2), or three (3) answers 6 points if you mark the single correct answer 4 points if the correct answer is among your two choices 2 points if the correct answer is among your three choices 10 problems, 6 pts each =60 pts = 50% of e ...
Physics 1401 Chapter 6 Review-New
... 28. A 45-N brick is suspended by a light string from a 2.0-kg pulley. The brick is released from rest and falls to the floor below as the pulley rotates through 5.0 rad. The pulley may be considered a solid disk of radius 1.5 m. What is the angular speed of the pulley? (a) 7.3 rad/s (d) 15 rad/s (b ...
... 28. A 45-N brick is suspended by a light string from a 2.0-kg pulley. The brick is released from rest and falls to the floor below as the pulley rotates through 5.0 rad. The pulley may be considered a solid disk of radius 1.5 m. What is the angular speed of the pulley? (a) 7.3 rad/s (d) 15 rad/s (b ...
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION AND BASIC CONCEPTS
... Newton’s laws: Relations between motions of bodies and the forces acting on them. Newton’s first law: A body at rest remains at rest, and a body in motion remains in motion at the same velocity in a straight path when the net force acting on it is zero. Therefore, a body tends to preserve its state ...
... Newton’s laws: Relations between motions of bodies and the forces acting on them. Newton’s first law: A body at rest remains at rest, and a body in motion remains in motion at the same velocity in a straight path when the net force acting on it is zero. Therefore, a body tends to preserve its state ...