A2
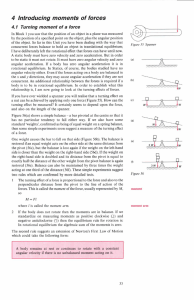
... vector. Here, we are given force vector and need to find position vector so we can determine the x, y and z of the pole. Notice also that F is pointing toward the origin whereas our position vector will need to point away. 1) Find the unit vector in the F direction 2) Negate this vector and scale up ...
... vector. Here, we are given force vector and need to find position vector so we can determine the x, y and z of the pole. Notice also that F is pointing toward the origin whereas our position vector will need to point away. 1) Find the unit vector in the F direction 2) Negate this vector and scale up ...
T072 Q13. Assume that a disk starts from rest and rotates with an
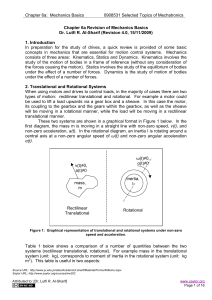
... The angular acceleration of the rod at the moment the rod is in the horizontal position as shown in this figure is: (Ans: 3.35 rad/s2 clockwise) Q19. Force F = (-8.0 N) i+ (6.0 N) j acts on a particle with position vector r = (3.0 m) i+ (4.0 m)j. What is the torque on the particle about the point P ...
... The angular acceleration of the rod at the moment the rod is in the horizontal position as shown in this figure is: (Ans: 3.35 rad/s2 clockwise) Q19. Force F = (-8.0 N) i+ (6.0 N) j acts on a particle with position vector r = (3.0 m) i+ (4.0 m)j. What is the torque on the particle about the point P ...
Electromagnetic force and torque on magnetic and negative
... study optical forces and torques on arbitrary, magnetic objects a numerical approach needs to be formulated. Since in the CDM one represents an arbitrary object as a collection of dipoles, the physics of the opto-mechanical coupling between light and the object must first be understood at the dipol ...
... study optical forces and torques on arbitrary, magnetic objects a numerical approach needs to be formulated. Since in the CDM one represents an arbitrary object as a collection of dipoles, the physics of the opto-mechanical coupling between light and the object must first be understood at the dipol ...
Rotational Motion
... tracks its translational motion. If you took a video of the seagull you would see quite different motion than you would from the ground. The seagull would appear always ahead of you but would rotate and change its “shape” as it flapped its wings (e.g., see the film Winged Migration). You’ve probably ...
... tracks its translational motion. If you took a video of the seagull you would see quite different motion than you would from the ground. The seagull would appear always ahead of you but would rotate and change its “shape” as it flapped its wings (e.g., see the film Winged Migration). You’ve probably ...
Chapter 22 Three Dimensional Rotations and Gyroscopes
... Most of the examples and applications we have considered concerned the rotation of rigid bodies about a fixed axis. However, there are many examples of rigid bodies that rotate about an axis that is changing its direction. A turning bicycle wheel, a gyroscope, the earth’s precession about its axis, ...
... Most of the examples and applications we have considered concerned the rotation of rigid bodies about a fixed axis. However, there are many examples of rigid bodies that rotate about an axis that is changing its direction. A turning bicycle wheel, a gyroscope, the earth’s precession about its axis, ...
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 13: Keeping momentum
... A friend claims that it is safe to go on a car trip with your child without a child seat since he can hold onto your 12kg child even if the car makes a frontal collision (lasting 0.05s and causing the vehicle to stop completely) at v=50 km/h (about 30 miles/h). Is he to be trusted? ...
... A friend claims that it is safe to go on a car trip with your child without a child seat since he can hold onto your 12kg child even if the car makes a frontal collision (lasting 0.05s and causing the vehicle to stop completely) at v=50 km/h (about 30 miles/h). Is he to be trusted? ...
PowerPoint
... and in this case the direction is into the plane of the figure. Expressed as a vector, ...
... and in this case the direction is into the plane of the figure. Expressed as a vector, ...