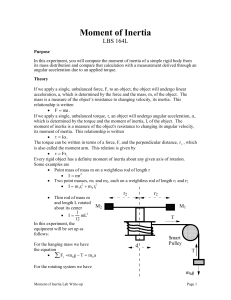
here
... Every object continues either at rest or in constant motion in a straight line, unless it is forced to change that state by forces action on it. An object acted on by no net force moves with constant velocity (which may be zero) and thus with zero acceleration. Zero resultant force is equivalent to ...
... Every object continues either at rest or in constant motion in a straight line, unless it is forced to change that state by forces action on it. An object acted on by no net force moves with constant velocity (which may be zero) and thus with zero acceleration. Zero resultant force is equivalent to ...
Questions and Problems
... not because there is an external force acting on the ball to pull it inward. The moment of inertia and angular speed will, of course, remain the same throughout the process because the ball is rotating in the same plane throughout the motion. 13. •A freely rotating turntable moves at a steady angula ...
... not because there is an external force acting on the ball to pull it inward. The moment of inertia and angular speed will, of course, remain the same throughout the process because the ball is rotating in the same plane throughout the motion. 13. •A freely rotating turntable moves at a steady angula ...
Instructions Grading Scheme
... 3. Two solid balls with different masses and different radii are released from rest simultaneously at the top of a ramp. The balls then roll down the ramp without slipping (neglect air resistance). The two balls reach the bottom of the ramp at the same time. a. True b. False 4. Before a collision, t ...
... 3. Two solid balls with different masses and different radii are released from rest simultaneously at the top of a ramp. The balls then roll down the ramp without slipping (neglect air resistance). The two balls reach the bottom of the ramp at the same time. a. True b. False 4. Before a collision, t ...
File
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=A05n32Bl0aY When the length of an arrow is scaled to represent the amount (magnitude) the arrow is called a vector ...
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=A05n32Bl0aY When the length of an arrow is scaled to represent the amount (magnitude) the arrow is called a vector ...
Conservation of Angular Momentum
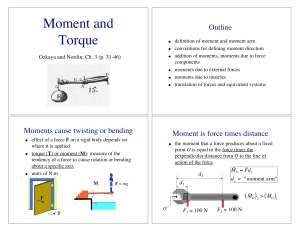
... The torque produced by the external force f ext about some reference point is equal to product of the perpendicular moment arm "d" and the force, i.e. T d f ext . Or, in vector form, the torque is the cross product position vector r from the reference point and f ext , i.e. T r f ext . These ...
... The torque produced by the external force f ext about some reference point is equal to product of the perpendicular moment arm "d" and the force, i.e. T d f ext . Or, in vector form, the torque is the cross product position vector r from the reference point and f ext , i.e. T r f ext . These ...
specimen
... At a particular airport, the length of the runway for the same take-off speed is less than your answer in (b)(iii). State and explain what change could be made to the aircraft to enable it to reach the required take-off speed on this shorter runway. ...
... At a particular airport, the length of the runway for the same take-off speed is less than your answer in (b)(iii). State and explain what change could be made to the aircraft to enable it to reach the required take-off speed on this shorter runway. ...
Questions and Solutions - Physics and Engineering Physics
... The speed of the satellite depends on the radius of the orbit. The speed of the satellite depends on the universal gravitational constant. The speed of the satellite depends on the acceleration due to gravity at its location. ...
... The speed of the satellite depends on the radius of the orbit. The speed of the satellite depends on the universal gravitational constant. The speed of the satellite depends on the acceleration due to gravity at its location. ...
Motion and Forces Study Guide
... First law of motion (law of inertia) An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion at constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Inertia is the property of matter that tends to resist any change in motion. The more massive an object is, the ...
... First law of motion (law of inertia) An object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion at constant velocity unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Inertia is the property of matter that tends to resist any change in motion. The more massive an object is, the ...