document
... previously… A force is conservative if the work done on an object when moving from A to B does not depend on the path followed. Consequently, work was defined as: ...
... previously… A force is conservative if the work done on an object when moving from A to B does not depend on the path followed. Consequently, work was defined as: ...
Physical Science
... the quantity of energy before the transfer is equal to the quantity of energy after the transfer. P.CM.M.1 Changes in State – Matter changing from state to state can be explained by using models, which show that matter is composed of tiny particles in motion. When changes of state occur, the atoms a ...
... the quantity of energy before the transfer is equal to the quantity of energy after the transfer. P.CM.M.1 Changes in State – Matter changing from state to state can be explained by using models, which show that matter is composed of tiny particles in motion. When changes of state occur, the atoms a ...
tut8_q
... 15 Interactive Solution 18.15 provides a model for solving this type of problem. Two small objects, A and B, are fixed in place and separated by 3.00 cm in a vacuum. Object A has a charge of +2.00 µC, and object B has a charge of –2.00 µC. How many electrons must be removed from A and put onto B to ...
... 15 Interactive Solution 18.15 provides a model for solving this type of problem. Two small objects, A and B, are fixed in place and separated by 3.00 cm in a vacuum. Object A has a charge of +2.00 µC, and object B has a charge of –2.00 µC. How many electrons must be removed from A and put onto B to ...
Name: Period: _____ Date
... A. closed system B. efficiency C. elastic potential energy D. gravitational potential energy E. kinetic energy F. Joules G. Law of conservation of energy H. nuclear energy I. open system J. power K. radiant energy L. thermal energy M. Watts N. work O. energy ...
... A. closed system B. efficiency C. elastic potential energy D. gravitational potential energy E. kinetic energy F. Joules G. Law of conservation of energy H. nuclear energy I. open system J. power K. radiant energy L. thermal energy M. Watts N. work O. energy ...
Electrical potentials on surfaces, Debye length, and transmembrane
... o In order for a cell to develop a transmembrane potential by pumping ions out of the cell it needs to charge the capacitator o The amount of charge that needs to be pumped depends on membrane thickness, surface area and the polarizability (0)of the membrane o The thickness and 0 are essent ...
... o In order for a cell to develop a transmembrane potential by pumping ions out of the cell it needs to charge the capacitator o The amount of charge that needs to be pumped depends on membrane thickness, surface area and the polarizability (0)of the membrane o The thickness and 0 are essent ...
Mechanical Energy = Potential Energy + Kinetic Energy
... mechanical energy. Before it leaves his hands it has stored energy (potential), and once he throws the ball it has kinetic energy. It is important to understand that all other types of energy involve potential and kinetic energy also. Most of the other forms of energy are associated with the particl ...
... mechanical energy. Before it leaves his hands it has stored energy (potential), and once he throws the ball it has kinetic energy. It is important to understand that all other types of energy involve potential and kinetic energy also. Most of the other forms of energy are associated with the particl ...
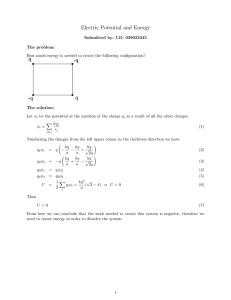
Electric Potential and Energy
... An infinite wire is placed on the z-axis and homogeneously charged with linear charge density λ. An electric dipole p~ = pb y is positioned at (x, 0, 0). 1. What is the torque acting on the dipole? 2. What is the energy of the dipole in the field of the wire? 3. What is the energy of the wire in the ...
... An infinite wire is placed on the z-axis and homogeneously charged with linear charge density λ. An electric dipole p~ = pb y is positioned at (x, 0, 0). 1. What is the torque acting on the dipole? 2. What is the energy of the dipole in the field of the wire? 3. What is the energy of the wire in the ...