Physics 51
... not necessarily zero). 23.29.(a) IDENTIFY and SET UP: The electric field on the ring’s axis is calculated in Example 21.9. The force on the electron exerted by this field is given by Eq. (21.3). EXECUTE: When the electron is on either side of the center of the ring, the ring exerts an attractive for ...
... not necessarily zero). 23.29.(a) IDENTIFY and SET UP: The electric field on the ring’s axis is calculated in Example 21.9. The force on the electron exerted by this field is given by Eq. (21.3). EXECUTE: When the electron is on either side of the center of the ring, the ring exerts an attractive for ...
Chapter 9.7 - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... pedal). When a car brakes, the work is the friction force (supplied by the brakes) multiplied by the distance over which the friction force acts. KE is transformed by work (friction) into thermal energy, sound energy and larger-scale vibrations. ...
... pedal). When a car brakes, the work is the friction force (supplied by the brakes) multiplied by the distance over which the friction force acts. KE is transformed by work (friction) into thermal energy, sound energy and larger-scale vibrations. ...
Lecture XVIII_XIX
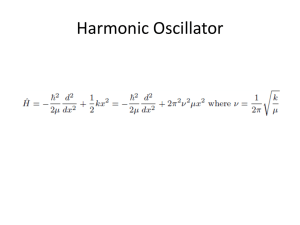
... be approximated by a parabola near the bottom of the well. The parabolic potential leads to harmonic oscillations. • At high excitation energies the parabolic approximation is poor (the true potential is less confining), and does not apply near the dissociation limit. • Must therefore use a asymmetr ...
... be approximated by a parabola near the bottom of the well. The parabolic potential leads to harmonic oscillations. • At high excitation energies the parabolic approximation is poor (the true potential is less confining), and does not apply near the dissociation limit. • Must therefore use a asymmetr ...
Name: Chapter 14: Changing Forms of Energy Words to Know
... A sand castle being hit by a beach ball vs. a basketball At any particular SPEED a moving object with more MASS has more kinetic energy Friction can cause kinetic energy to turn into thermal energy (rubbing hands together) Potential energy (or ‘stored’ energy) is energy that is not causing any chang ...
... A sand castle being hit by a beach ball vs. a basketball At any particular SPEED a moving object with more MASS has more kinetic energy Friction can cause kinetic energy to turn into thermal energy (rubbing hands together) Potential energy (or ‘stored’ energy) is energy that is not causing any chang ...
energy
... exerting a force through a distance. – This force is usually against something and there are five main groups of resistance. • Work against inertia –Since inertia is an object’s resistance to change of motion, it naturally follows that this would resist forces acting upon it. ...
... exerting a force through a distance. – This force is usually against something and there are five main groups of resistance. • Work against inertia –Since inertia is an object’s resistance to change of motion, it naturally follows that this would resist forces acting upon it. ...
Homework No. 05 (2014 Fall) PHYS 320: Electricity and Magnetism I
... 3. (20 points.) Consider an infinite chain of equidistant alternating point charges +q and −q on the x-axis. Calculate the electric potential at the site of a point charge due to all other charges. This is equal to the work per point charge required to assemble such a cofiguration. In terms of the d ...
... 3. (20 points.) Consider an infinite chain of equidistant alternating point charges +q and −q on the x-axis. Calculate the electric potential at the site of a point charge due to all other charges. This is equal to the work per point charge required to assemble such a cofiguration. In terms of the d ...
Stored Energy
... using sun energy: carbon dioxide + water is changed to stored energy in plants. ...
... using sun energy: carbon dioxide + water is changed to stored energy in plants. ...
Midterm I Solutions ρ
... Newton’s 2nd Law applied to this case: total force in direction of motion = T – f = ma, where f = µ mg. Thus T =f + ma=m(µg + a). Plug in m=5 kg, a = 2 m/s2, µ = 0.2 and g = 9.8 m/s2, you get the value for T. ...
... Newton’s 2nd Law applied to this case: total force in direction of motion = T – f = ma, where f = µ mg. Thus T =f + ma=m(µg + a). Plug in m=5 kg, a = 2 m/s2, µ = 0.2 and g = 9.8 m/s2, you get the value for T. ...
Quantum Mechanics Potential energy
... physical entities.[1] The SI unit for measuring work and energy is the joule (symbol J). The term potential energy was introduced by the 19th century Scottish engineer and physicist William Rankine,[2][3] although it has links to Greek philosopher Aristotle's concept of potentiality. Potential energ ...
... physical entities.[1] The SI unit for measuring work and energy is the joule (symbol J). The term potential energy was introduced by the 19th century Scottish engineer and physicist William Rankine,[2][3] although it has links to Greek philosopher Aristotle's concept of potentiality. Potential energ ...
File
... Mechanical energy – ability to do work (sum of potential & kinetic energy) Form of energy involved in the operation of simple machines Potential energy – stored energy in an object due to its position (energy at rest) Kinetic energy – energy in motion Amount of kinetic energy depends on mass & s ...
... Mechanical energy – ability to do work (sum of potential & kinetic energy) Form of energy involved in the operation of simple machines Potential energy – stored energy in an object due to its position (energy at rest) Kinetic energy – energy in motion Amount of kinetic energy depends on mass & s ...
New Energy Powerpoint (Power Point)
... investigated; the resulting velocity and/or height of the object can then be predicted from energy information. ...
... investigated; the resulting velocity and/or height of the object can then be predicted from energy information. ...