frequency modulator
... In Figure 6-4, the capacitance of varactor diode D1 and L1 form the parallel tuned circuit of the oscillator. The value of C1 is made very large so its reactance is very low. C1 connects the tuned circuit to the oscillator and blocks the dc bias on the base of Q1 from being shorted to ground through ...
... In Figure 6-4, the capacitance of varactor diode D1 and L1 form the parallel tuned circuit of the oscillator. The value of C1 is made very large so its reactance is very low. C1 connects the tuned circuit to the oscillator and blocks the dc bias on the base of Q1 from being shorted to ground through ...
integration of artificial intelligence control to the unified power quality
... applying a small-signal perturbation technique to obtain its transfer function. In this method of deriving a linear model, the system is assumed to operate in the steady state, and the defining equations are linearized for small-signal perturbation. The relation between the input (ac side) and outpu ...
... applying a small-signal perturbation technique to obtain its transfer function. In this method of deriving a linear model, the system is assumed to operate in the steady state, and the defining equations are linearized for small-signal perturbation. The relation between the input (ac side) and outpu ...
An Accurate Automatic Quality-Factor Tuning Scheme for Second
... can be identified from (20) and (22). Let us identify its stability behavior using the phase-portrait concept. Fig. 6 shows the phase portrait of the system defined by (20) and (22) using the same filter parameters used in Fig. 5. This figure clearly shows that there has been a change in the nature ...
... can be identified from (20) and (22). Let us identify its stability behavior using the phase-portrait concept. Fig. 6 shows the phase portrait of the system defined by (20) and (22) using the same filter parameters used in Fig. 5. This figure clearly shows that there has been a change in the nature ...
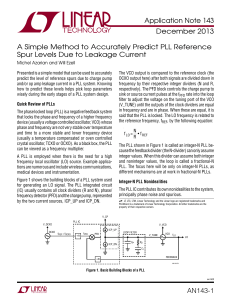
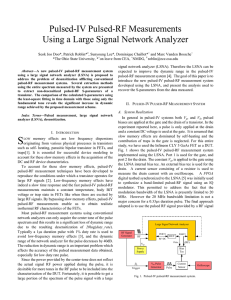
Pulsed-IV Pulsed-RF Measurements Using a Large Signal Network
... S kl (ω 0 ) . As a result of the larger signal amplitude, a reduced noise is expected in the S-parameters. In addition to considering the above three analyses, additional processing steps are required for extracting S-parameters from LSNA measurements. In distinction to a conventional network analyz ...
... S kl (ω 0 ) . As a result of the larger signal amplitude, a reduced noise is expected in the S-parameters. In addition to considering the above three analyses, additional processing steps are required for extracting S-parameters from LSNA measurements. In distinction to a conventional network analyz ...
Chapter 2 - Portal UniMAP
... – Attenuation refers to a loss introduced by a circuit or component. If the output signal is lower in amplitude than the input, the circuit has loss or attenuation. – The letter A is used to represent attenuation – Attenuation A = output/input = Vout/Vin – Circuits that introduce attenuation have a ...
... – Attenuation refers to a loss introduced by a circuit or component. If the output signal is lower in amplitude than the input, the circuit has loss or attenuation. – The letter A is used to represent attenuation – Attenuation A = output/input = Vout/Vin – Circuits that introduce attenuation have a ...
High-accuracy charge-redistribution SC video bandpass filter in
... nominal settling time-constant of 3.5 ns, which is lower than strictly necessary for this design. However, extra margin was built into the design to account for slow process parameters, high die temperatures, slewing, and clock overlap times [9], ...
... nominal settling time-constant of 3.5 ns, which is lower than strictly necessary for this design. However, extra margin was built into the design to account for slow process parameters, high die temperatures, slewing, and clock overlap times [9], ...
Ringing artifacts

In signal processing, particularly digital image processing, ringing artifacts are artifacts that appear as spurious signals near sharp transitions in a signal. Visually, they appear as bands or ""ghosts"" near edges; audibly, they appear as ""echos"" near transients, particularly sounds from percussion instruments; most noticeable are the pre-echos. The term ""ringing"" is because the output signal oscillates at a fading rate around a sharp transition in the input, similar to a bell after being struck. As with other artifacts, their minimization is a criterion in filter design.