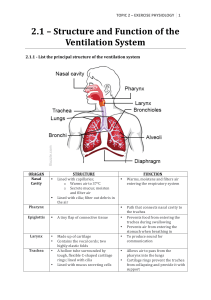
Structure$and$Function$of$the$ Ventilation$System
... •! Oxygen!from!the!inhaled!air!diffuses!through!the!walls!of!the!alveoli!and!adjacent! capillaries!into!the!red!blood!cells! •! The!oxygen!is!then!carried!by!the!blood!to!the!body!tissues! •! Carbon!dioxide!produced!by!the!body’s!metabolism!returns!to!the!lung!via!the!blood! •! It!then!diffuses!acro ...
... •! Oxygen!from!the!inhaled!air!diffuses!through!the!walls!of!the!alveoli!and!adjacent! capillaries!into!the!red!blood!cells! •! The!oxygen!is!then!carried!by!the!blood!to!the!body!tissues! •! Carbon!dioxide!produced!by!the!body’s!metabolism!returns!to!the!lung!via!the!blood! •! It!then!diffuses!acro ...
Introduction to Evolutionary Medicine 2015
... • A. Understanding evolution can improve diagnosis. • B. Understanding evolution can improve preventative or treatment plans. • C. Evolution provides a framework for understanding physiology and pathology ...
... • A. Understanding evolution can improve diagnosis. • B. Understanding evolution can improve preventative or treatment plans. • C. Evolution provides a framework for understanding physiology and pathology ...
SCIENCE STUDY GUIDE
... Produces voice by vibrating. Cords are stretched across the opening of the larynx. ...
... Produces voice by vibrating. Cords are stretched across the opening of the larynx. ...
The Mammalian Body - Walker Elementary
... Specialization – teeth are designed for the food the mammal eats ...
... Specialization – teeth are designed for the food the mammal eats ...
Comparing Animals PPT
... Today there are 6,800 reptile species on earth; the major groups are alligators and crocodiles, turtles, lizards, and snakes. All reptiles are cold-blooded, which is why they warm themselves in the sun, and have bodies covered in dry, horny scales. Some reptiles lay eggs; others give birth to live y ...
... Today there are 6,800 reptile species on earth; the major groups are alligators and crocodiles, turtles, lizards, and snakes. All reptiles are cold-blooded, which is why they warm themselves in the sun, and have bodies covered in dry, horny scales. Some reptiles lay eggs; others give birth to live y ...
Chapter Notes
... When we chew and swallow food, it passes to the stomach and then to the small intestine where it is digested. The walls of the small intestine contain many blood vessels. When it is digested, the food is broken down into very small particles called nutrients. These nutrients (molecules) pass through ...
... When we chew and swallow food, it passes to the stomach and then to the small intestine where it is digested. The walls of the small intestine contain many blood vessels. When it is digested, the food is broken down into very small particles called nutrients. These nutrients (molecules) pass through ...
Basic Molecular Biology Information
... today. The mechanism for the spread of new genes was a slow process of interbreeding between neighboring groups. This theory suggests that many of today’s populations have lived in the same area of the world for a very long time: the Chinese evolved in China, the Africans evolved in Africa, etc. The ...
... today. The mechanism for the spread of new genes was a slow process of interbreeding between neighboring groups. This theory suggests that many of today’s populations have lived in the same area of the world for a very long time: the Chinese evolved in China, the Africans evolved in Africa, etc. The ...
Evolution as Genetic change - Natural selection does not act on
... interbreed, because they have different mating songs. ______________________________ 2. The Kaibab squirrel evolved from the Abert squirrel. The Kaibab squirrels were isolated from the main population by the Colorado River._____________________________________________ 3. The three similar species of ...
... interbreed, because they have different mating songs. ______________________________ 2. The Kaibab squirrel evolved from the Abert squirrel. The Kaibab squirrels were isolated from the main population by the Colorado River._____________________________________________ 3. The three similar species of ...
File
... 15.) Order of organization in human body Organelle---cell--- tissue---organ--- organ system--- organism 16.) what is pulse? How does it change during exercise? Pulse is the number of times your heart beats in a period of time (BPM’s). When you exercise your muscles need/use more oxygen (and to remov ...
... 15.) Order of organization in human body Organelle---cell--- tissue---organ--- organ system--- organism 16.) what is pulse? How does it change during exercise? Pulse is the number of times your heart beats in a period of time (BPM’s). When you exercise your muscles need/use more oxygen (and to remov ...
A38-Mammals
... • Have various glands, including mammary glands that produce milk • Endothermic (warm-blooded) • Can keep a stable temperature by using energy from food • Hair/fur and fat also provide insulation ...
... • Have various glands, including mammary glands that produce milk • Endothermic (warm-blooded) • Can keep a stable temperature by using energy from food • Hair/fur and fat also provide insulation ...
SI - TEST 1 STUDY GUIDE Bio 203 – Spring 2011 Introductory
... Why should we use parsimony in constructing phylogenetic trees? How do complex traits challenge the principle of parsimony? ...
... Why should we use parsimony in constructing phylogenetic trees? How do complex traits challenge the principle of parsimony? ...
File
... 4.There must be no mutations within the gene pool. 5.There must be no natural selection. ...
... 4.There must be no mutations within the gene pool. 5.There must be no natural selection. ...
Gas exchange
... it becomes harder to exchange substances with their surroundings Stretch; note down four of the main “substances” that need to be exchanged and what process each substance is involved in ...
... it becomes harder to exchange substances with their surroundings Stretch; note down four of the main “substances” that need to be exchanged and what process each substance is involved in ...
www.pandm.prv.pl 1 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Respiratory system
... The bronchi terminate the air bag , called alveoil. The wall of alveoil is rich in capillares. Air enters through the nose and mouth. Then the pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi,bronchioles it passes into the lungs. In the alevole of the lungs oxygen diffuses into the blood stream where is absorbed b ...
... The bronchi terminate the air bag , called alveoil. The wall of alveoil is rich in capillares. Air enters through the nose and mouth. Then the pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi,bronchioles it passes into the lungs. In the alevole of the lungs oxygen diffuses into the blood stream where is absorbed b ...
evolution and speciation ppt
... A cosmic explosion that hurled matter and in all directions created the universe 10-20 billion years ...
... A cosmic explosion that hurled matter and in all directions created the universe 10-20 billion years ...
The Insatiable Appetite
... And then seque into the annual cycle of birds. Because resources are not available at constant levels throughout the year (day length changes, winter, dry & wet seasons in the tropics, etc.), and because they have such insatiable appetites, birds have scheduling conflicts. ...
... And then seque into the annual cycle of birds. Because resources are not available at constant levels throughout the year (day length changes, winter, dry & wet seasons in the tropics, etc.), and because they have such insatiable appetites, birds have scheduling conflicts. ...
The Respiratory System
... • May serve a specific within the function and work together to organism perform a specific activity. • Examples—blood cells, nerve • Examples—blood, nervous, cells, bone cells, etc. bone, etc. Humans have 4 basic tissues: connective, epithelial, muscle, and nerve. Level 3—Organs • Made up of tissue ...
... • May serve a specific within the function and work together to organism perform a specific activity. • Examples—blood cells, nerve • Examples—blood, nervous, cells, bone cells, etc. bone, etc. Humans have 4 basic tissues: connective, epithelial, muscle, and nerve. Level 3—Organs • Made up of tissue ...
Organisms at high altitude
.jpg?width=300)
Organisms can live at high altitude, either on land, or while flying. Decreased oxygen availability and decreased temperature make life at high altitude challenging. Despite these environmental conditions, many species have been successfully adapted at high altitudes. Animals have developed physiological adaptations to enhance oxygen uptake and delivery to tissues which can be used to sustain metabolism. The strategies used by animals to adapt to high altitude depend on their morphology and phylogeny.























