Illegal Drugs
... Illegal drugs are abused because they produce a euphoric effect Euphoria – a deep sense of well-being Why do many people take illegal drugs? It makes them feel good!!! ...
... Illegal drugs are abused because they produce a euphoric effect Euphoria – a deep sense of well-being Why do many people take illegal drugs? It makes them feel good!!! ...
Certified Medication Technician Student Manual
... The metric system is the international standard of measurement for weight, volume, length, and temperature. It has replaced the apothecary system which is no longer used in formal drug literature or health care applications. The use of roman numerals (HO 9) has also been discontinued in healthcare s ...
... The metric system is the international standard of measurement for weight, volume, length, and temperature. It has replaced the apothecary system which is no longer used in formal drug literature or health care applications. The use of roman numerals (HO 9) has also been discontinued in healthcare s ...
Controlled drug release
... is to administer the drug at a constant (zeroorder) rate over the entire dosing interval. ...
... is to administer the drug at a constant (zeroorder) rate over the entire dosing interval. ...
Controlled drug release
... is to administer the drug at a constant (zeroorder) rate over the entire dosing interval. ...
... is to administer the drug at a constant (zeroorder) rate over the entire dosing interval. ...
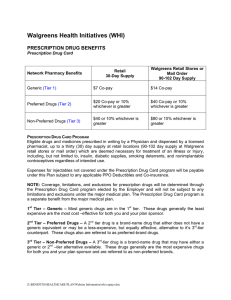
Walgreens Health Initiatives (WHI)
... under this Plan subject to any applicable PPO Deductibles and Co-insurance. NOTE: Coverage, limitations, and exclusions for prescription drugs will be determined through the Prescription Drug Card program elected by the Employer and will not be subject to any limitations and exclusions under the maj ...
... under this Plan subject to any applicable PPO Deductibles and Co-insurance. NOTE: Coverage, limitations, and exclusions for prescription drugs will be determined through the Prescription Drug Card program elected by the Employer and will not be subject to any limitations and exclusions under the maj ...
Prescribing in the Elderly - Benton Franklin County Medical Society
... Drug-disease interactions? Is the drug indicated? Is the drug effective? Unnecessary drug duplication? ...
... Drug-disease interactions? Is the drug indicated? Is the drug effective? Unnecessary drug duplication? ...
vol.13 No.2 - TU Teaching Hospital
... Meals and medicines Understanding the possible clinical implications of taking medicines with or without a meal is important for achieving quality use of medicines. Although the effect of food is not clinically important for many drugs, there are food-drug interactions which may have adverse consequ ...
... Meals and medicines Understanding the possible clinical implications of taking medicines with or without a meal is important for achieving quality use of medicines. Although the effect of food is not clinically important for many drugs, there are food-drug interactions which may have adverse consequ ...
Toxicology: Drugs and Poisons Forensic Science
... • Effects of toxins do not cause VISIBLE changes in the body in living people or during an autopsy. • Medical Examiner will collect fluids and tissues for testing – Toxins are sneaky! Biotransformation can change one chemical into another within the body due to metabolism. – The toxicologist may hav ...
... • Effects of toxins do not cause VISIBLE changes in the body in living people or during an autopsy. • Medical Examiner will collect fluids and tissues for testing – Toxins are sneaky! Biotransformation can change one chemical into another within the body due to metabolism. – The toxicologist may hav ...
教案编写基本格式与要求
... with a cellular component called receptor. Some drugs act through simple physical or chemical reactions without interacting with any receptor. • Receptors are protein molecules present either on the cell surface or with in the cell e.g. adrenergic receptors, cholinoceptors, insulin receptors, etc. • ...
... with a cellular component called receptor. Some drugs act through simple physical or chemical reactions without interacting with any receptor. • Receptors are protein molecules present either on the cell surface or with in the cell e.g. adrenergic receptors, cholinoceptors, insulin receptors, etc. • ...
Background PLASMA PROTEIN BINDING Protocol
... candidates by working in close partnership with clients and other departments within Sygnature to provide successful optimisation ...
... candidates by working in close partnership with clients and other departments within Sygnature to provide successful optimisation ...
N204
... as response physiologically to med. Culturally competent care involves knowledge not only of pt’s beliefs and values about health care and illness, but also of their responses to treatment ...
... as response physiologically to med. Culturally competent care involves knowledge not only of pt’s beliefs and values about health care and illness, but also of their responses to treatment ...
PHARMACOLOGY Pharmacology is an experimental science
... I.D. (intradermal) – drugs are injected into the skin, the absorption rate is very slow, used e.g. for Tuberculosis skin tests I.P. (intraperitoneal) – drugs are injected directly into the peritoneal cavity, often used in combination with I.V. injections to prolong the availability of the medication ...
... I.D. (intradermal) – drugs are injected into the skin, the absorption rate is very slow, used e.g. for Tuberculosis skin tests I.P. (intraperitoneal) – drugs are injected directly into the peritoneal cavity, often used in combination with I.V. injections to prolong the availability of the medication ...
DRUG PRODUCT DEVELOPMENT
... New Drug defined in section C.0 1A.001(2) of Food and Drug Regulations (HPFB) any agent that has not been generally recognized as safe and effective under the conditions recommended ...
... New Drug defined in section C.0 1A.001(2) of Food and Drug Regulations (HPFB) any agent that has not been generally recognized as safe and effective under the conditions recommended ...
Clinical Trials and Scientific Methods Chapter 0 Enrichment
... evaluate safety, side effects, and a safe dosage range. If Phase I is successful, Phase II will test an expanded group up to 100 people. Phase III studies more than 200 people to further determine safety, effectiveness, and side effects, and also to compare the drug to existing therapies. Phase IV s ...
... evaluate safety, side effects, and a safe dosage range. If Phase I is successful, Phase II will test an expanded group up to 100 people. Phase III studies more than 200 people to further determine safety, effectiveness, and side effects, and also to compare the drug to existing therapies. Phase IV s ...
OTC Plus Slide Presentation
... Choice of Medications • Selection must be based on clinical effectiveness and safety, such as drug to treat illnesses that: – Require limited physical assessment – Can be identified by easily interpreted lab tests ...
... Choice of Medications • Selection must be based on clinical effectiveness and safety, such as drug to treat illnesses that: – Require limited physical assessment – Can be identified by easily interpreted lab tests ...
Nursing Process Focus: Bethanechol (Urecholine)
... (This is due to muscarinic blockade on the problem. tone and motility of intestinal smooth muscle ) Use cautiously with the elderly or very Inform patient and caregivers to report any young. Symptoms that might be more adverse reactions to the health care pronounced in the elderly are urinary pr ...
... (This is due to muscarinic blockade on the problem. tone and motility of intestinal smooth muscle ) Use cautiously with the elderly or very Inform patient and caregivers to report any young. Symptoms that might be more adverse reactions to the health care pronounced in the elderly are urinary pr ...
STUDY GUIDE DRUGS
... 1. isolated from the coca plant, cocaine is a natural alkaloid with an extensive history in South America 2. crack = cocaine + baking soda 3. effects similar to meth F. MDMA also known as ecstasy 1. hallucinogenic stimulant causes euphoria 2. data shows beneficial use to treat certain psychiatric di ...
... 1. isolated from the coca plant, cocaine is a natural alkaloid with an extensive history in South America 2. crack = cocaine + baking soda 3. effects similar to meth F. MDMA also known as ecstasy 1. hallucinogenic stimulant causes euphoria 2. data shows beneficial use to treat certain psychiatric di ...
22Jan2002 PAGE 1
... a. motor vehicle crashes b. value of lost productivity c. direct treatment costs d. crime-related costs e. All of the above contribute to these figures. 9. Which of the following is true about the diagnosis of substance-related dependence and abuse in DSM-IV? a. A person may be diagnosed with both d ...
... a. motor vehicle crashes b. value of lost productivity c. direct treatment costs d. crime-related costs e. All of the above contribute to these figures. 9. Which of the following is true about the diagnosis of substance-related dependence and abuse in DSM-IV? a. A person may be diagnosed with both d ...
Internal Medicine Morning Report
... • Increase in volume of distribution for lipophilic drugs – Protein Binding changes are of modest significance for most drugs, especially at steady-state ...
... • Increase in volume of distribution for lipophilic drugs – Protein Binding changes are of modest significance for most drugs, especially at steady-state ...
NIMESULIDE - Pediatric Oncall
... January, 2002, and the committee felt that as such, fixed dose combinations of NSAIDs like paracetamol, Diclofenec, ibuprofen and with Nimesulide have been in use for considerable period and well accepted. There are no reports of any adverse effects for these formulations which are mostly used on sh ...
... January, 2002, and the committee felt that as such, fixed dose combinations of NSAIDs like paracetamol, Diclofenec, ibuprofen and with Nimesulide have been in use for considerable period and well accepted. There are no reports of any adverse effects for these formulations which are mostly used on sh ...
CHRONOPHARMACOKINETICS: AN OVERVIEW Review Article VINEY CHAWLA
... dose. A circadian time dependency was also found in nifedipineinduced effects on blood pressure and heart rate as monitored by 24 hr. ambulatory blood pressure measurementsl9. Lemmer and Holle20 investigated the chronopharmacokinetics of imipramine and desipramine in rat forebrain and plasma after s ...
... dose. A circadian time dependency was also found in nifedipineinduced effects on blood pressure and heart rate as monitored by 24 hr. ambulatory blood pressure measurementsl9. Lemmer and Holle20 investigated the chronopharmacokinetics of imipramine and desipramine in rat forebrain and plasma after s ...
McCainMay99resp - Lupron Victims Hub
... voluntary system of reporting. The information received from a report of an adverse drug experience is added to the existing data in our Adverse Event Reporting System (AERS) database. The collected reports are monitored and observed for emerging patterns. In the event it appears there may be a pote ...
... voluntary system of reporting. The information received from a report of an adverse drug experience is added to the existing data in our Adverse Event Reporting System (AERS) database. The collected reports are monitored and observed for emerging patterns. In the event it appears there may be a pote ...
Pharmacokinetics

Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK (from Ancient Greek pharmakon ""drug"" and kinetikos ""moving, putting in motion""; see chemical kinetics), is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determining the fate of substances administered externally to a living organism. The substances of interest include pharmaceutical agents, hormones, nutrients, and toxins. It attempts to discover the fate of a drug from the moment that it is administered up to the point at which it is completely eliminated from the body.Pharmacokinetics describes how the body affects a specific drug after administration through the mechanisms of absorption and distribution, as well as the chemical changes of the substance in the body (e.g. by metabolic enzymes such as cytochrome P450 or glucuronosyltransferase enzymes), and the effects and routes of excretion of the metabolites of the drug. Pharmacokinetic properties of drugs may be affected by elements such as the site of administration and the dose of administered drug. These may affect the absorption rate. Pharmacokinetics is often studied in conjunction with pharmacodynamics, the study of a drug's pharmacological effect on the body.A number of different models have been developed in order to simplify conceptualization of the many processes that take place in the interaction between an organism and a drug. One of these models, the multi-compartment model, gives the best approximation to reality; however, the complexity involved in using this type of model means that monocompartmental models and above all two compartmental models are the most-frequently used. The various compartments that the model is divided into are commonly referred to as the ADME scheme (also referred to as LADME if liberation is included as a separate step from absorption): Liberation - the process of release of a drug from the pharmaceutical formulation. See also IVIVC. Absorption - the process of a substance entering the blood circulation. Distribution - the dispersion or dissemination of substances throughout the fluids and tissues of the body. Metabolization (or biotransformation, or inactivation) – the recognition by the organism that a foreign substance is present and the irreversible transformation of parent compounds into daughter metabolites. Excretion - the removal of the substances from the body. In rare cases, some drugs irreversibly accumulate in body tissue.The two phases of metabolism and excretion can also be grouped together under the title elimination.The study of these distinct phases involves the use and manipulation of basic concepts in order to understand the process dynamics. For this reason in order to fully comprehend the kinetics of a drug it is necessary to have detailed knowledge of a number of factors such as: the properties of the substances that act as excipients, the characteristics of the appropriate biological membranes and the way that substances can cross them, or the characteristics of the enzyme reactions that inactivate the drug.All these concepts can be represented through mathematical formulas that have a corresponding graphical representation. The use of these models allows an understanding of the characteristics of a molecule, as well as how a particular drug will behave given information regarding some of its basic characteristics. Such as its acid dissociation constant (pKa), bioavailability and solubility, absorption capacity and distribution in the organism.The model outputs for a drug can be used in industry (for example, in calculating bioequivalence when designing generic drugs) or in the clinical application of pharmacokinetic concepts. Clinical pharmacokinetics provides many performance guidelines for effective and efficient use of drugs for human-health professionals and in veterinary medicine.