thermodynamics - La Salle High School
... Third Law of Thermodynamics If the entropy of each element in its most state is taken as zero at the absolute zero of temperature, every substance has a positive entropy. But at 0K, the entropy of substance may equals to 0, and does become zero in perfect crystalline solids. Implication: all perfec ...
... Third Law of Thermodynamics If the entropy of each element in its most state is taken as zero at the absolute zero of temperature, every substance has a positive entropy. But at 0K, the entropy of substance may equals to 0, and does become zero in perfect crystalline solids. Implication: all perfec ...
Chapter 15 General Science Energy and Matter 15
... * Work is the ability to make something move. Energy is what makes things move. * Without energy, rivers would not move. Cars would not move. Bikes could not move without some energy. The Earth could not go around the sun. You could not move a muscle. Nothing would move at all. * Energy does not hav ...
... * Work is the ability to make something move. Energy is what makes things move. * Without energy, rivers would not move. Cars would not move. Bikes could not move without some energy. The Earth could not go around the sun. You could not move a muscle. Nothing would move at all. * Energy does not hav ...
Chapter Six Outline
... to increase the temperature of that sample by one degree. Specific heat capacity is defined as the quantity of energy needed to increase the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius. Specific heat capacity = the quantity of energy transferred by heating/(sample mass x tempera ...
... to increase the temperature of that sample by one degree. Specific heat capacity is defined as the quantity of energy needed to increase the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius. Specific heat capacity = the quantity of energy transferred by heating/(sample mass x tempera ...
Review 4
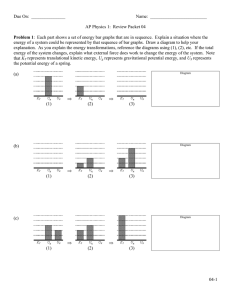
... Big concept: Use energy whenever are given a position and asked for a velocity, OR given a velocity and asked for a position. Example: A block is released from rest at the top of the incline (point A) as shown. If the incline is frictionless, how fast does the block ...
... Big concept: Use energy whenever are given a position and asked for a velocity, OR given a velocity and asked for a position. Example: A block is released from rest at the top of the incline (point A) as shown. If the incline is frictionless, how fast does the block ...
work and energy
... at the bottom of a 40m high hill assuming zero speed at the top of the hill? PE lost = KE gained mgh = ½ mv2 2gh = v2 v = (2gh)1/2 v = (2 x 10 x 40)1/2 = (800)1/2 ...
... at the bottom of a 40m high hill assuming zero speed at the top of the hill? PE lost = KE gained mgh = ½ mv2 2gh = v2 v = (2gh)1/2 v = (2 x 10 x 40)1/2 = (800)1/2 ...
Document
... The vibration and movement of the atoms and molecules; as heat increases, atoms move faster. The flow of thermal energy is called heat. ...
... The vibration and movement of the atoms and molecules; as heat increases, atoms move faster. The flow of thermal energy is called heat. ...
Document
... 1. “Heat is energy that flows between a system and its environment because of a temperature difference between them” We choose our sign convention so that Q is positive in the case that the internal energy of the system tends to be increased. ...
... 1. “Heat is energy that flows between a system and its environment because of a temperature difference between them” We choose our sign convention so that Q is positive in the case that the internal energy of the system tends to be increased. ...
Potential Energy - Sereika Science
... The most basic things I should know after this unit: There are different types of potential energy Types of potential energy are gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, chemical potential energy, electrical potential energy, and magnetic potential energy Potential energy is s ...
... The most basic things I should know after this unit: There are different types of potential energy Types of potential energy are gravitational potential energy, elastic potential energy, chemical potential energy, electrical potential energy, and magnetic potential energy Potential energy is s ...
Types of Energy 1. potential energy – the energy stored in an object
... 1. potential energy – the energy stored in an object or material 2. kinetic energy – the energy of a moving object 3. mechanical energy – energy due to an object’s motion (which is kinetic energy) or an object’s position (which is potential energy) 4. electromagnetic energy – light energy; the energ ...
... 1. potential energy – the energy stored in an object or material 2. kinetic energy – the energy of a moving object 3. mechanical energy – energy due to an object’s motion (which is kinetic energy) or an object’s position (which is potential energy) 4. electromagnetic energy – light energy; the energ ...
Review Package - Work, Energy and Power
... • Is the force in the opposite direction of motion (recall that technically W = Fcosϴ·d) 2) Potential energy: stored energy. Measured in Joules, J. ...
... • Is the force in the opposite direction of motion (recall that technically W = Fcosϴ·d) 2) Potential energy: stored energy. Measured in Joules, J. ...
Conservation of Energy
... Example: A sled and its rider together weigh 800. N. They move down a frictionless hill through a vertical distance of 10.0 m. Use conservation of energy to find the speed of the sled-rider system at the bottom of the hill, assuming the rider pushes off with an initial speed of 5.00 m/s. ...
... Example: A sled and its rider together weigh 800. N. They move down a frictionless hill through a vertical distance of 10.0 m. Use conservation of energy to find the speed of the sled-rider system at the bottom of the hill, assuming the rider pushes off with an initial speed of 5.00 m/s. ...
File - El Paso High School
... useful work, but the rest must be exhausted as waste heat. 3. The entropy of an isolated system never decreases. It can only stay the same or increase. ...
... useful work, but the rest must be exhausted as waste heat. 3. The entropy of an isolated system never decreases. It can only stay the same or increase. ...
Work, Power and Energy Worksheet
... at the top of a loop that is 10.8 m high. 9. A 500.0 kg pig is standing at the top of a muddy hill on a rainy day. The hill is 100.0 m long with a vertical drop of 30.0 m. The pig slips and begins to slide down the hill. What is the pig’s speed at the bottom of the hill? 10. A 50.0 kg gorilla is sit ...
... at the top of a loop that is 10.8 m high. 9. A 500.0 kg pig is standing at the top of a muddy hill on a rainy day. The hill is 100.0 m long with a vertical drop of 30.0 m. The pig slips and begins to slide down the hill. What is the pig’s speed at the bottom of the hill? 10. A 50.0 kg gorilla is sit ...
Energy - Buncombe County Schools
... Media College. COM, How Sound Waves Work, http://www.mediacollege.com/audio/01/soundwaves.html, accessed 12/16/2010 Cool Cosmos, What is Heat?. ...
... Media College. COM, How Sound Waves Work, http://www.mediacollege.com/audio/01/soundwaves.html, accessed 12/16/2010 Cool Cosmos, What is Heat?. ...