ESO201A: Thermodynamics
... isothermal process, entropy change for an adiabatic nozzle, Bernoulli's equation derivation. Lecture #25 Isentropic efficiency of steady flow systems - gas turbine, steam turbine, nozzle, detailed analysis of a compressor, comparison of reversible adiabatic and reversible isothermal processes to get ...
... isothermal process, entropy change for an adiabatic nozzle, Bernoulli's equation derivation. Lecture #25 Isentropic efficiency of steady flow systems - gas turbine, steam turbine, nozzle, detailed analysis of a compressor, comparison of reversible adiabatic and reversible isothermal processes to get ...
Work and Power
... Using several pulleys increases the distance the of the input force causing a larger output force. The mechanical advantage is equal to the number of ropes sharing the load. MA = # of ropes-1 or MA = # of pulleys ...
... Using several pulleys increases the distance the of the input force causing a larger output force. The mechanical advantage is equal to the number of ropes sharing the load. MA = # of ropes-1 or MA = # of pulleys ...
Food and Fuels
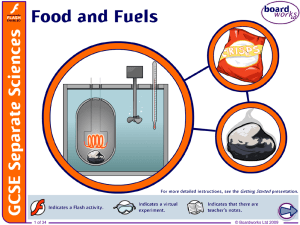
... called calorimetry. Calorimetry involves burning a known mass of food and measuring the energy released. This is done by transferring the energy to a measured volume of water and working out the temperature change. Knowing the temperature change and the specific heat capacity of water, it is possibl ...
... called calorimetry. Calorimetry involves burning a known mass of food and measuring the energy released. This is done by transferring the energy to a measured volume of water and working out the temperature change. Knowing the temperature change and the specific heat capacity of water, it is possibl ...
141S13-NotesCh5b-May28
... 5.3 Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem: Kinetic Energy Think back to Problem #2 from the last lecture. We found that when an object is thrown vertically upward, the force of gravity does negative work on the object on the way up (since force and displacement are in opposite directions) and positive work o ...
... 5.3 Work-Kinetic Energy Theorem: Kinetic Energy Think back to Problem #2 from the last lecture. We found that when an object is thrown vertically upward, the force of gravity does negative work on the object on the way up (since force and displacement are in opposite directions) and positive work o ...
Chapter 6
... • While the total internal energy of a system (E) cannot be determined, changes in internal energy (E) can be determined. • The change in internal energy will be the amount of energy exchanged between a system and its surroundings during a physical or chemical change. ...
... • While the total internal energy of a system (E) cannot be determined, changes in internal energy (E) can be determined. • The change in internal energy will be the amount of energy exchanged between a system and its surroundings during a physical or chemical change. ...
Kinetic Energy
... What is conservation of energy? There are many different forms of energy, such as kinetic, sound, thermal and light energy. Each form of energy can be transferred or converted into an another form. All energy transfers follow the law of conservation of energy: ...
... What is conservation of energy? There are many different forms of energy, such as kinetic, sound, thermal and light energy. Each form of energy can be transferred or converted into an another form. All energy transfers follow the law of conservation of energy: ...
Thermodynamic system
... • In isochoric process, no mechanical work performed • In adiabatic process, no heat is exchanged with environment • Reversible process: by reversing the process, one can bring both the system and its environment back into the intial state • Whenever energy is dissipated (mechanical into heat, e.g. ...
... • In isochoric process, no mechanical work performed • In adiabatic process, no heat is exchanged with environment • Reversible process: by reversing the process, one can bring both the system and its environment back into the intial state • Whenever energy is dissipated (mechanical into heat, e.g. ...
Answer Key Physics Study Guide A
... As things get further away from each other, gravitational forces __decrease by the square of the distance______ As things get closer, gravitational forces __increase______________ As things get more mass, gravitational forces ____increase___________ As things get less mass, gravitational forces __de ...
... As things get further away from each other, gravitational forces __decrease by the square of the distance______ As things get closer, gravitational forces __increase______________ As things get more mass, gravitational forces ____increase___________ As things get less mass, gravitational forces __de ...
gravitational potential energy
... In this case, the work depends only on the initial and final positions of the object with the path between the positions of no consequence. Typical conservative forces encountered in dynamics are gravitational forces (i.e., weight) and elastic forces (i.e., springs). What is a common force that is n ...
... In this case, the work depends only on the initial and final positions of the object with the path between the positions of no consequence. Typical conservative forces encountered in dynamics are gravitational forces (i.e., weight) and elastic forces (i.e., springs). What is a common force that is n ...
Lecture Notes for Section 18-5 - Course ON-LINE
... In this case, the work depends only on the initial and final positions of the object with the path between the positions of no consequence. Typical conservative forces encountered in dynamics are gravitational forces (i.e., weight) and elastic forces (i.e., springs). What is a common force that is n ...
... In this case, the work depends only on the initial and final positions of the object with the path between the positions of no consequence. Typical conservative forces encountered in dynamics are gravitational forces (i.e., weight) and elastic forces (i.e., springs). What is a common force that is n ...
Name: Core: ______ Date: ENERGY REVIEW – INNOVATION LAB
... 22. Give one example of the transformation of electrical energy. Ceiling fans transform electric energy into kinetic energy. Toasters, electric heaters, and electric stoves transform electric energy into thermal energy. Televisions transform electric energy into sound energy and light (radiant) ener ...
... 22. Give one example of the transformation of electrical energy. Ceiling fans transform electric energy into kinetic energy. Toasters, electric heaters, and electric stoves transform electric energy into thermal energy. Televisions transform electric energy into sound energy and light (radiant) ener ...
Chapter 9 Study Guide – Energy and Energy Resources
... Closed system – a group of objects that transfer energy only to each other Law of conservation of energy – states that energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed from one form to another Any time one form of energy is converted into another form, some of the original energy always gets ...
... Closed system – a group of objects that transfer energy only to each other Law of conservation of energy – states that energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be changed from one form to another Any time one form of energy is converted into another form, some of the original energy always gets ...
WRL0638.tmp - Symposium on Chemical Physics
... This postulate has its most profound basis in the microscopic laws of physics. One can use either classical or quantum mechanics. In either case the system as a whole evolves in time and it satisfies the law of conservation of energy. This is true only for conservative systems, but this suffices as ...
... This postulate has its most profound basis in the microscopic laws of physics. One can use either classical or quantum mechanics. In either case the system as a whole evolves in time and it satisfies the law of conservation of energy. This is true only for conservative systems, but this suffices as ...