Chapter 2: Laws of Motion
... due to gravity velocity weight air resistance terminal speed ...
... due to gravity velocity weight air resistance terminal speed ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Acceleration= Net Force/ Mass Acceleration is measured in meter per second per second (m/s²) ...
... Acceleration= Net Force/ Mass Acceleration is measured in meter per second per second (m/s²) ...
Blank Jeopardy
... Two ways to describe the motion of an object already in motion, according to Newton’s First Law ...
... Two ways to describe the motion of an object already in motion, according to Newton’s First Law ...
ppt
... • Protons and electrons have mass, charge • Also have angular momentum (spin) which creates tiny magnetic field • So energy of H atom is different depending on orientation of spins (if same ↓, if opposite directions ↑, but energy difference = 10-6 x electron orbits) • photon emitted in a spin-flip t ...
... • Protons and electrons have mass, charge • Also have angular momentum (spin) which creates tiny magnetic field • So energy of H atom is different depending on orientation of spins (if same ↓, if opposite directions ↑, but energy difference = 10-6 x electron orbits) • photon emitted in a spin-flip t ...
Gravitation
... Understand how the acceleration due to gravity acting upon a mass is affected by the location and mass of the other object in question. Quantitatively apply Newton’s law of universal gravitation to solve problems. ...
... Understand how the acceleration due to gravity acting upon a mass is affected by the location and mass of the other object in question. Quantitatively apply Newton’s law of universal gravitation to solve problems. ...
Newton`s 2nd and 3rd Laws
... In water less body support required because the water helps lift the mass *Animals can be larger if they live in the water ...
... In water less body support required because the water helps lift the mass *Animals can be larger if they live in the water ...
ENGINEERING MECHANICS STATIC
... ENGINEERING MECHANICS STATIC Third Law: - Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first or: For every action, there is an equal an opposite reaction ...
... ENGINEERING MECHANICS STATIC Third Law: - Whenever one object exerts a force on a second object, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first or: For every action, there is an equal an opposite reaction ...
Name ______ Period ______ Newton`s Laws Study Guide ______
... 10. The motion of a body when only gravity is acting on it is called ________________. 11. Acceleration due to gravity has a value of _________________. 12. What is the difference between weight and mass? 13. The constant velocity of a falling object when the forces of air resistance and gravity bal ...
... 10. The motion of a body when only gravity is acting on it is called ________________. 11. Acceleration due to gravity has a value of _________________. 12. What is the difference between weight and mass? 13. The constant velocity of a falling object when the forces of air resistance and gravity bal ...
2. Velocity dispersions of galaxies
... launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 36A on March 3, 1972 at 01:49:00 UTC. Pioneer 10 is heading in the direction of Aldebaran, located in Taurus. By some definitions, Pioneer 10 has become the first artificial object to leave the solar system. It is the first human-built ...
... launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Complex 36A on March 3, 1972 at 01:49:00 UTC. Pioneer 10 is heading in the direction of Aldebaran, located in Taurus. By some definitions, Pioneer 10 has become the first artificial object to leave the solar system. It is the first human-built ...
Newton`sLawsofMotionppt
... • According to Newton, whenever objects A and B interact with each other, they exert forces upon each other. When you sit in your chair, your body exerts a downward force on the chair and the chair exerts an upward force on your body. ...
... • According to Newton, whenever objects A and B interact with each other, they exert forces upon each other. When you sit in your chair, your body exerts a downward force on the chair and the chair exerts an upward force on your body. ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
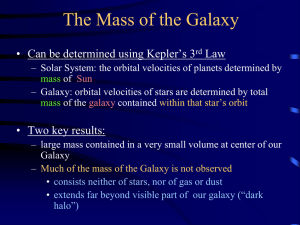
... The Mass of the Galaxy • Can be determined using Kepler’s 3rd Law – Solar System: the orbital velocities of planets determined by mass of Sun – Galaxy: orbital velocities of stars are determined by total mass of the galaxy contained within that star’s orbit ...
... The Mass of the Galaxy • Can be determined using Kepler’s 3rd Law – Solar System: the orbital velocities of planets determined by mass of Sun – Galaxy: orbital velocities of stars are determined by total mass of the galaxy contained within that star’s orbit ...
6.2 Newton`s Second Law
... Acceleration is the result of unbalanced forces. A larger force makes a proportionally larger acceleration. Acceleration is inversely proportional to mass. ...
... Acceleration is the result of unbalanced forces. A larger force makes a proportionally larger acceleration. Acceleration is inversely proportional to mass. ...
Kinematics, Momentum and Energy
... Newton’s First Law Inertia An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted on by an external force. ...
... Newton’s First Law Inertia An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion will stay in motion unless acted on by an external force. ...
HOMEWORK – DUE FRIDAY, NOVEMBER 22ND NEWTON`S
... 1. How does Newton’s first law of motion apply to a ball rolling across the gym floor after an unbalanced force is applied? A. The ball will stop at the line halfway across the gym. B. The ball will continue to roll until an unbalanced force is applied. C. The ball will start bouncing until it hits ...
... 1. How does Newton’s first law of motion apply to a ball rolling across the gym floor after an unbalanced force is applied? A. The ball will stop at the line halfway across the gym. B. The ball will continue to roll until an unbalanced force is applied. C. The ball will start bouncing until it hits ...
Newton Review
... Newton Review Use Chapters 1 & 2 in your book to help you find the answers to the questions below. 1. Write Newton’s first law. Law of Inertia: objects remain in motion, or at rest, until a force acts upon them. 2. Give an example of Newton’s first law using a rocket in your example. A rocket lifts ...
... Newton Review Use Chapters 1 & 2 in your book to help you find the answers to the questions below. 1. Write Newton’s first law. Law of Inertia: objects remain in motion, or at rest, until a force acts upon them. 2. Give an example of Newton’s first law using a rocket in your example. A rocket lifts ...
Newton`s Laws
... 11 The frog leaps from its resting position at the lake’s bank onto a lily pad. If the frog has a mass of 0.5 kg and the acceleration of the leap is 3 m/s2, what is the force the frog exerts on the lake’s bank when leaping? ...
... 11 The frog leaps from its resting position at the lake’s bank onto a lily pad. If the frog has a mass of 0.5 kg and the acceleration of the leap is 3 m/s2, what is the force the frog exerts on the lake’s bank when leaping? ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.