Milky Way
... clusters in our galaxy? • Trigonometric parallax good out to 100 pc. • We believe galaxy is ~30 kpc wide. • How do we know? ...
... clusters in our galaxy? • Trigonometric parallax good out to 100 pc. • We believe galaxy is ~30 kpc wide. • How do we know? ...
Forces (Dynamics) – Notes Day 1
... b. Gravity between an object and Earth (or any planet for that matter is called _______________ i. So, does gravity “push down” or “pull toward”???? c. If gravity exists everywhere, why don’t two masses attract each other like ...
... b. Gravity between an object and Earth (or any planet for that matter is called _______________ i. So, does gravity “push down” or “pull toward”???? c. If gravity exists everywhere, why don’t two masses attract each other like ...
Did you read the chapter?!
... stronger forces cause more acceleration larger mass results in less acceleration acceleration is in the direction of the net force ...
... stronger forces cause more acceleration larger mass results in less acceleration acceleration is in the direction of the net force ...
Study Guide Physics Chapter 7, 8
... 9. Which has more momentum a small bus or a large bus when both are moving at the same speed? 10. Which has more momentum a bus moving slowly or the same bus moving fast? 11. What is an Impulse? 12. Why do cars have padded dash boards, seatbelts, and air bags? 13. How does the force, acceleration, i ...
... 9. Which has more momentum a small bus or a large bus when both are moving at the same speed? 10. Which has more momentum a bus moving slowly or the same bus moving fast? 11. What is an Impulse? 12. Why do cars have padded dash boards, seatbelts, and air bags? 13. How does the force, acceleration, i ...
Gravity Simulation Introduction: Every object around you is attracted
... Gravity Simulation Introduction: Every object around you is attracted to you. In fact, every object in the galaxy is attracted to every other object in the galaxy. Newton postulated and Cavendish confirmed that all objects with mass are attracted to all other objects with mass by a force that is pro ...
... Gravity Simulation Introduction: Every object around you is attracted to you. In fact, every object in the galaxy is attracted to every other object in the galaxy. Newton postulated and Cavendish confirmed that all objects with mass are attracted to all other objects with mass by a force that is pro ...
Section 6.2
... The greater the mass, the smaller the acceleration for a given force. Mass is inversely related to force. An object with twice the mass will have half the acceleration if the same force is applied. ...
... The greater the mass, the smaller the acceleration for a given force. Mass is inversely related to force. An object with twice the mass will have half the acceleration if the same force is applied. ...
Biomechanics
... Equilibrium: a 'perfect' situation where more than one force acts on a body but, because the sum of forces is zero, no change in velocity (speed) results; balance Conservation of Energy: the principle that states that energy can neither be created or destroyed, it can only be converted from one form ...
... Equilibrium: a 'perfect' situation where more than one force acts on a body but, because the sum of forces is zero, no change in velocity (speed) results; balance Conservation of Energy: the principle that states that energy can neither be created or destroyed, it can only be converted from one form ...
Newton`s Laws Review
... A 1.167 kg block of wood is initially at rest at the top of a ramp that makes an angle of 43.1 o from the horizontal. If the coefficient of sliding friction is 0.282, what will be the acceleration of the block as it slides down the ramp? ...
... A 1.167 kg block of wood is initially at rest at the top of a ramp that makes an angle of 43.1 o from the horizontal. If the coefficient of sliding friction is 0.282, what will be the acceleration of the block as it slides down the ramp? ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... m/sec/sec? 132 N = 66 kg x 2 m/s/s 4. What is the force on a 1000 kg elevator that is falling freely at 9.8 m/sec/sec? 9800 N = 1000 kg x 9.8 m/s/s ...
... m/sec/sec? 132 N = 66 kg x 2 m/s/s 4. What is the force on a 1000 kg elevator that is falling freely at 9.8 m/sec/sec? 9800 N = 1000 kg x 9.8 m/s/s ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Without the upward force of the hand there is not equilibrium of forces and motion occurs. ...
... Without the upward force of the hand there is not equilibrium of forces and motion occurs. ...
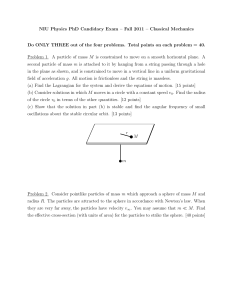
NIU Physics PhD Candidacy Exam – Fall 2011 – Classical
... Problem 3. Consider an infinite number of identical pendulums of mass M in a uniform gravitational field with acceleration g, each hanging by a massless string of length `, and coupled to each other with massless springs of spring constant K as shown. In the equilibrium position, the springs are at ...
... Problem 3. Consider an infinite number of identical pendulums of mass M in a uniform gravitational field with acceleration g, each hanging by a massless string of length `, and coupled to each other with massless springs of spring constant K as shown. In the equilibrium position, the springs are at ...
Motion - RowesPhysicalScience
... You can change an objects motion by pushing it, pulling it, nudging it, or by any number of other things; all of which are referred to as air forces. Friction is a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact. Static Friction – A force is applied to an object but does not move. ...
... You can change an objects motion by pushing it, pulling it, nudging it, or by any number of other things; all of which are referred to as air forces. Friction is a force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact. Static Friction – A force is applied to an object but does not move. ...
Forces Review
... The questions below are intended to assist you with reviewing the information previously covered on forces. This is not everything we have covered on forces but it does represent an overview of many of the topics we have studies so far. 1. Three spring scales are attached along a straight line as sh ...
... The questions below are intended to assist you with reviewing the information previously covered on forces. This is not everything we have covered on forces but it does represent an overview of many of the topics we have studies so far. 1. Three spring scales are attached along a straight line as sh ...
Freefall and Newton`s 2nd Law ppt
... If the same force acts on two different objects with different masses, how does the object’s acceleration (movement away) compare? ...
... If the same force acts on two different objects with different masses, how does the object’s acceleration (movement away) compare? ...
Topic 6 Fields and Forces Name: The directives after the numbered
... Know the relationship between the various variables in the equation. ...
... Know the relationship between the various variables in the equation. ...
Relative Motion
... to discuss them. Group 2 Devise an experiment to test what is important in horizontal acceleration. You have a bowling ball, and tennis ball as equipment. (don't drop the bowling ball) List the things that effect the acceleration as you push a ball. Group 3 Discuss moving the contents of your ho ...
... to discuss them. Group 2 Devise an experiment to test what is important in horizontal acceleration. You have a bowling ball, and tennis ball as equipment. (don't drop the bowling ball) List the things that effect the acceleration as you push a ball. Group 3 Discuss moving the contents of your ho ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... People have been very curious about stars in the sky, making observations for a long time. But the data people collected have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional ...
... People have been very curious about stars in the sky, making observations for a long time. But the data people collected have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.