Honors Physics – Ch 7 Practice Problems
... 4. The passenger liners Carnival Destiny and Grand Princess, built recently, have a mass of about 1.0 × 108 kg each. How far apart must these two ships be to exert a gravitational attraction of 1.0 × 10-3 N on each other? 5. Jupiter, the largest planet in the solar system, has a mass 318 times that ...
... 4. The passenger liners Carnival Destiny and Grand Princess, built recently, have a mass of about 1.0 × 108 kg each. How far apart must these two ships be to exert a gravitational attraction of 1.0 × 10-3 N on each other? 5. Jupiter, the largest planet in the solar system, has a mass 318 times that ...
forces and motion study guide
... The force of attraction between Earth and other objects A measure of the gravitational force acting on an object A force that resists motion between objects that are touching A force that acts between any two objects and pulls them together ...
... The force of attraction between Earth and other objects A measure of the gravitational force acting on an object A force that resists motion between objects that are touching A force that acts between any two objects and pulls them together ...
Chapter 2 question 2 - leo physics website
... In order to apply the law of conservation of momentum, the system of reference should consists both the car and the Earth. During the collision, the car exerts a force on the Earth and the Earth exerts the same force on the car in opposite direction. These forces of impact are internal forces. Ther ...
... In order to apply the law of conservation of momentum, the system of reference should consists both the car and the Earth. During the collision, the car exerts a force on the Earth and the Earth exerts the same force on the car in opposite direction. These forces of impact are internal forces. Ther ...
Newton`s second law of motion
... Looking at the results Discuss your students’ results: Do they find that acceleration is proportional to force, and inversely proportional to mass? Numerically, are their results consistent with the equation F = ma? You may wish to point out that the experiment can only show proportionality. In othe ...
... Looking at the results Discuss your students’ results: Do they find that acceleration is proportional to force, and inversely proportional to mass? Numerically, are their results consistent with the equation F = ma? You may wish to point out that the experiment can only show proportionality. In othe ...
CH 3—Forces
... • The force of air resistance increases until it becomes large enough to cancel the force of gravity. • The forces on the falling objects are balanced, so the object no longer accelerates. • It then falls at a constant speed called the terminal velocity (highest velocity a falling object will reach) ...
... • The force of air resistance increases until it becomes large enough to cancel the force of gravity. • The forces on the falling objects are balanced, so the object no longer accelerates. • It then falls at a constant speed called the terminal velocity (highest velocity a falling object will reach) ...
PPT
... Ch. 28: Magnetic fields, forces on moving charges, crossed fields, Hall effect, cyclotrons, force and torque on current carrying wires and loops, magnetic dipoles and dipole moment Ch. 29: Sources of magnetic field, Biot-Savart Law, calculating the magnetic field for various current geometries, Ampe ...
... Ch. 28: Magnetic fields, forces on moving charges, crossed fields, Hall effect, cyclotrons, force and torque on current carrying wires and loops, magnetic dipoles and dipole moment Ch. 29: Sources of magnetic field, Biot-Savart Law, calculating the magnetic field for various current geometries, Ampe ...
9.4 - Hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Keplar´s Third Law The square of the times of revolution of the planets (i.e. Their periodic time T ) about the sun are proportional to the cubes of their mean distance (r) from it. We have considered a circular orbit but more advanced mathematics gives the same result for an elliptical one. ...
... Keplar´s Third Law The square of the times of revolution of the planets (i.e. Their periodic time T ) about the sun are proportional to the cubes of their mean distance (r) from it. We have considered a circular orbit but more advanced mathematics gives the same result for an elliptical one. ...
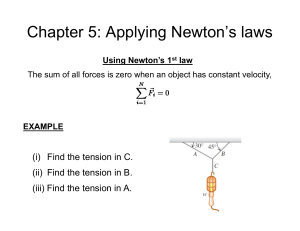
Newton`s First Law
... Newton’s First Law An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion at constant velocity (that is, constant speed in a straight line) unless the object experiences a net external force ...
... Newton’s First Law An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion at constant velocity (that is, constant speed in a straight line) unless the object experiences a net external force ...
Newton`s Second Law
... Capstone to record the motion. Determine what happens to the acceleration of the cart when the net force is kept constant and the mass changes, and then what happens when the mass is kept constant but the net force changes. The purpose of Experiment 2 is to find the mass of a system by applying a kn ...
... Capstone to record the motion. Determine what happens to the acceleration of the cart when the net force is kept constant and the mass changes, and then what happens when the mass is kept constant but the net force changes. The purpose of Experiment 2 is to find the mass of a system by applying a kn ...
IPC – Unit 2 - Cloudfront.net
... 80 km/hr to 40 km/hr as it travels up a hill in 10 seconds. What is the car’s acceleration? ...
... 80 km/hr to 40 km/hr as it travels up a hill in 10 seconds. What is the car’s acceleration? ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.