Newtons Laws and Its Application
... Broken Atwood’s machine Example4: Two masses connected by a rope and a pulley (Atwood’s machine). The connection part of m2 is broken and m2 is moving with constant acceleration a0 relative to the rope. What are the accelerations of m1 and m2 relative to the ground? (Ignoring the mass of rope and p ...
... Broken Atwood’s machine Example4: Two masses connected by a rope and a pulley (Atwood’s machine). The connection part of m2 is broken and m2 is moving with constant acceleration a0 relative to the rope. What are the accelerations of m1 and m2 relative to the ground? (Ignoring the mass of rope and p ...
Study Guide For Unit 3 Test
... If an object's velocity is not changing, the sum of the forces on the object is zero. If an object's velocity is changing, the sum of the forces on the object is not zero. This non-zero sum of forces is referred to as the “net force.” RECALL: Dry ice demo Newton’s 3rd law of motion Pairs o ...
... If an object's velocity is not changing, the sum of the forces on the object is zero. If an object's velocity is changing, the sum of the forces on the object is not zero. This non-zero sum of forces is referred to as the “net force.” RECALL: Dry ice demo Newton’s 3rd law of motion Pairs o ...
Lect7
... force. An object in motion continues to travel with constant speed in a straight line unless acted on by an external force. Another way to say the same thing: Law of Inertia • When no net force, • velocity is constant • acceleration is zero --- All in vector form ! ...
... force. An object in motion continues to travel with constant speed in a straight line unless acted on by an external force. Another way to say the same thing: Law of Inertia • When no net force, • velocity is constant • acceleration is zero --- All in vector form ! ...
Document
... "Every action has an equal and opposite re-action." This is Newton's third law and it also has plays a role in exactly how both airbags and crumple zones work. Newton's third law would probably be the most important of all of them. When you have an impact with your car, not only does your car hit a ...
... "Every action has an equal and opposite re-action." This is Newton's third law and it also has plays a role in exactly how both airbags and crumple zones work. Newton's third law would probably be the most important of all of them. When you have an impact with your car, not only does your car hit a ...
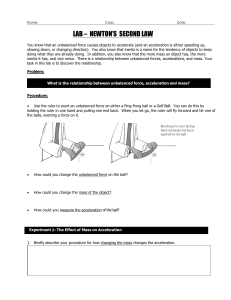
LAB – NEWTON`S SECOND LAW
... 2. When you keep the unbalanced force the same and increase the mass, how does the acceleration change? ...
... 2. When you keep the unbalanced force the same and increase the mass, how does the acceleration change? ...
Chapter 10 - Section 3
... (c) Inferring Use what you know about inertia to explain why you feel pressed back into the seat of a car when it accelerates. (a) Defining State Newton’s second law of motion in your own words. (b) Problem Solving How could you keep an object’s acceleration the same if the force acting on the objec ...
... (c) Inferring Use what you know about inertia to explain why you feel pressed back into the seat of a car when it accelerates. (a) Defining State Newton’s second law of motion in your own words. (b) Problem Solving How could you keep an object’s acceleration the same if the force acting on the objec ...
Document
... attractive force between all massive objects. F = G m1 m2 / R 2 where R is the separation, and G is Newton’s gravitational constant: G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2 Gravity is very weak between objects on a human scale. In fact, it is the weakest of all known forces, by far. It is important only because it ...
... attractive force between all massive objects. F = G m1 m2 / R 2 where R is the separation, and G is Newton’s gravitational constant: G = 6.67 x 10-11 Nm2/kg2 Gravity is very weak between objects on a human scale. In fact, it is the weakest of all known forces, by far. It is important only because it ...
Newtons Laws - Cardinal Newman High School
... For example: When you kick a soccer ball, do you feel anything in your foot? ...
... For example: When you kick a soccer ball, do you feel anything in your foot? ...
Free fall
... two objects would fall at the same rate regardless of their mass. Legend has it that in 1590, Galileo planned out an experiment. He climbed to the top of the Leaning Tower of Pisa and dropped several large objects to test his theory. He wanted to show that two different objects fall at the same rate ...
... two objects would fall at the same rate regardless of their mass. Legend has it that in 1590, Galileo planned out an experiment. He climbed to the top of the Leaning Tower of Pisa and dropped several large objects to test his theory. He wanted to show that two different objects fall at the same rate ...
forces and newton`s laws of motion
... FAy = FA sin45o = (40.0N)(0.707) = 28.3N FBx = FB cos37o = (30.0N)(0.799) =24.0N FBy = FB sin37o = -(30.0N)(0.602) = -18.1N FRx = FAx + FBx = 28.3N + 24.0N = 52.3N FRy = FAy + FBy = 28.3N -18.1N = 10.2N Then use Pythagorean theorem and tan-1 ...
... FAy = FA sin45o = (40.0N)(0.707) = 28.3N FBx = FB cos37o = (30.0N)(0.799) =24.0N FBy = FB sin37o = -(30.0N)(0.602) = -18.1N FRx = FAx + FBx = 28.3N + 24.0N = 52.3N FRy = FAy + FBy = 28.3N -18.1N = 10.2N Then use Pythagorean theorem and tan-1 ...
Newton`s Laws
... 3. A 2.5 kg basketball is dropped from the top of a building. Its acceleration is found to be 9.4 m/s 2 as it drops to the ground. What is the force of air friction on the ball as it falls? ...
... 3. A 2.5 kg basketball is dropped from the top of a building. Its acceleration is found to be 9.4 m/s 2 as it drops to the ground. What is the force of air friction on the ball as it falls? ...
File - Mr. Romero
... Fill in given numbers and units F = 1400 kg x 2 meters per second/second Solve for the unknown ...
... Fill in given numbers and units F = 1400 kg x 2 meters per second/second Solve for the unknown ...
Types of Forces with Newton`s Laws
... Newton’s Second Law • The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object and inversely proportional to the object’s mass. ...
... Newton’s Second Law • The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object and inversely proportional to the object’s mass. ...
Forces
... Newton’s Second Law • The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object and inversely proportional to the object’s mass. ...
... Newton’s Second Law • The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object and inversely proportional to the object’s mass. ...
IB Mechanics objectives
... Teacher’s notes Quantities should be identified as scalar or vector quantities. See sub-topic 1.3. ...
... Teacher’s notes Quantities should be identified as scalar or vector quantities. See sub-topic 1.3. ...
HW #5
... ȈF and the acceleration a that it causes for an object of mass m. The net force is the vector sum of all the external forces that act on the object. Here the external forces are the drive force, the force due to the wind, and the resistive force of the water. SOLUTION We choose the direction of the ...
... ȈF and the acceleration a that it causes for an object of mass m. The net force is the vector sum of all the external forces that act on the object. Here the external forces are the drive force, the force due to the wind, and the resistive force of the water. SOLUTION We choose the direction of the ...
PEKA 5
... 1. From the plotted graph of acceleration against mass, state the relationship between acceleration and the mass of the trolley when pulled by a constant force. Does the result support your hypothesis? The graph shows that the bigger the mass of the object, the smaller is the acceleration when the f ...
... 1. From the plotted graph of acceleration against mass, state the relationship between acceleration and the mass of the trolley when pulled by a constant force. Does the result support your hypothesis? The graph shows that the bigger the mass of the object, the smaller is the acceleration when the f ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.