The Big Plot
... 1) The quantity, its symbol, its standard international unit, and its unit’s symbol are represented in the following table. Fill the blanks by following the example. On the last column write a V if the quantity is vector and S if the quantity is a scalar. Note some units could correspond to more tha ...
... 1) The quantity, its symbol, its standard international unit, and its unit’s symbol are represented in the following table. Fill the blanks by following the example. On the last column write a V if the quantity is vector and S if the quantity is a scalar. Note some units could correspond to more tha ...
Photo Album - Texas A&M University
... As gravitational waves pass through spacetime, they cause small ripples. The stretching and shrinking is on the order of 1 part in 1021 even due to a strong gravitational wave source. Due to their small magnitude, gravitational waves would be difficult to detect. Large astronomical events could crea ...
... As gravitational waves pass through spacetime, they cause small ripples. The stretching and shrinking is on the order of 1 part in 1021 even due to a strong gravitational wave source. Due to their small magnitude, gravitational waves would be difficult to detect. Large astronomical events could crea ...
PPT - CEProfs
... law of conservation of energy--deals with quantities of energy •Energy can change forms: from potential energy to kinetic energy, for example--but the total amount never changes. ...
... law of conservation of energy--deals with quantities of energy •Energy can change forms: from potential energy to kinetic energy, for example--but the total amount never changes. ...
!
... plans to hold the Earth to ransom, saying that the stronger gravity at the surface of the squeezed Sun will cause the Sun to collapse. Is the villain’s threat credible? Explain why or why not. (3 points)! ...
... plans to hold the Earth to ransom, saying that the stronger gravity at the surface of the squeezed Sun will cause the Sun to collapse. Is the villain’s threat credible? Explain why or why not. (3 points)! ...
survivor_1_
... If Fnet , the vector sum of all forces acting on an object, is not equal to zero then the object _____ . • A) has no inertia • B) has uniform velocity • C) is in equilibrium • D) will accelerate 20 seconds ...
... If Fnet , the vector sum of all forces acting on an object, is not equal to zero then the object _____ . • A) has no inertia • B) has uniform velocity • C) is in equilibrium • D) will accelerate 20 seconds ...
Motion Study Guide
... Briefly Explain Newton’s 1st, 2nd, & 3rd Laws of Motion. 1ST: OBJECTS WILL CONTINUE TO DO WHATEVER THEY ARE DOING UNTIL AN UNBALANCED FORCE CHANGES IT 2ND: THE AMOUNT OF ACCELERATION IS AFFECTED BY THE MASS AND FORCE THAT IS APPLIED; IF YOU INCREASE THE MASS THE ACCELERATION WILL DECREASE; IF YOU IN ...
... Briefly Explain Newton’s 1st, 2nd, & 3rd Laws of Motion. 1ST: OBJECTS WILL CONTINUE TO DO WHATEVER THEY ARE DOING UNTIL AN UNBALANCED FORCE CHANGES IT 2ND: THE AMOUNT OF ACCELERATION IS AFFECTED BY THE MASS AND FORCE THAT IS APPLIED; IF YOU INCREASE THE MASS THE ACCELERATION WILL DECREASE; IF YOU IN ...
Chapter 3
... • Can you scientifically explain why you would rather kick the lighter object? – More massive objects have more inertia – What does that mean? – They want to move less so kicking them will hurt more! ...
... • Can you scientifically explain why you would rather kick the lighter object? – More massive objects have more inertia – What does that mean? – They want to move less so kicking them will hurt more! ...
Galaxy Characteristics
... faint core large core radius Shape Large Ellipticals – more spherical (E0) Motion of stars – very random Virial Theorem – relation of kinetic energy to potential (gravitational) energy of a system ...
... faint core large core radius Shape Large Ellipticals – more spherical (E0) Motion of stars – very random Virial Theorem – relation of kinetic energy to potential (gravitational) energy of a system ...
8A Quick Quiz - Grade10ScienceISZL
... Gravity is the force of ____________ between _____________. Between objects on Earth, it is a______________ force, but if the mass is very, very ____________ as with a planet or a star, the gravity can be very ____________. The region where a gravitational force can be felt is often referred to as a ...
... Gravity is the force of ____________ between _____________. Between objects on Earth, it is a______________ force, but if the mass is very, very ____________ as with a planet or a star, the gravity can be very ____________. The region where a gravitational force can be felt is often referred to as a ...
File
... ____ 10. Two perpendicular forces, one of 45.0 N directed upward and the second of 60.0 N directed to the right, act simultaneously on an object with a mass of 35.0 kg. What is the magnitude of the resultant acceleration of the object? a. 2.14 m/s2 b. 3.00 m/s2 c. 5.25 m/s2 d. 1.41 m/s2 ____ 11. An ...
... ____ 10. Two perpendicular forces, one of 45.0 N directed upward and the second of 60.0 N directed to the right, act simultaneously on an object with a mass of 35.0 kg. What is the magnitude of the resultant acceleration of the object? a. 2.14 m/s2 b. 3.00 m/s2 c. 5.25 m/s2 d. 1.41 m/s2 ____ 11. An ...
5.7 Newtons Laws of motion
... When a cannon is fired, there is an interaction between the cannon and the cannonball. The sudden force that the cannon exerts on the cannonball is exactly equal and opposite to the force the cannonball exerts on the cannon. This is why the cannon recoils (kicks). But the effects of these equal forc ...
... When a cannon is fired, there is an interaction between the cannon and the cannonball. The sudden force that the cannon exerts on the cannonball is exactly equal and opposite to the force the cannonball exerts on the cannon. This is why the cannon recoils (kicks). But the effects of these equal forc ...
Review - Hingham Schools
... Be able to identify and diagram the forces on an object. Know what net force means and understand the direction it points relative to a and v for different types of motion. Know the differences between mass and weight. Be able to calculate weight given the mass and vice versa. Be able to apply Newto ...
... Be able to identify and diagram the forces on an object. Know what net force means and understand the direction it points relative to a and v for different types of motion. Know the differences between mass and weight. Be able to calculate weight given the mass and vice versa. Be able to apply Newto ...
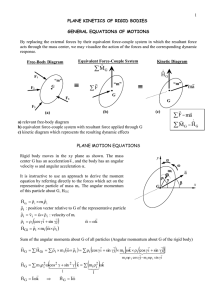
Plane Kinetics of Rigid Bodies
... GENERAL EQUATIONS OF MOTIONS By replacing the external forces by their equivalent force-couple system in which the resultant force acts through the mass center, we may visualize the action of the forces and the corresponding dynamic ...
... GENERAL EQUATIONS OF MOTIONS By replacing the external forces by their equivalent force-couple system in which the resultant force acts through the mass center, we may visualize the action of the forces and the corresponding dynamic ...
part 1
... move with the same velocity along that line unless an external force causes it to do otherwise. If you have two objects with different masses, the one with more mass is said to have more inertia (a greater tendency to not change its current speed or direction). This then leads us to intepret the mea ...
... move with the same velocity along that line unless an external force causes it to do otherwise. If you have two objects with different masses, the one with more mass is said to have more inertia (a greater tendency to not change its current speed or direction). This then leads us to intepret the mea ...
Physical Science Motion and Forces Worksheet
... 29. Why is your weight less on the Moon than on Earth, but your mass is the same? 30. The size of the gravitational force between two objects depends on their ___ and _____ 31. The law that states that every object maintains constant velocity unless acted on by an unbalanced force is _____ 32. A tug ...
... 29. Why is your weight less on the Moon than on Earth, but your mass is the same? 30. The size of the gravitational force between two objects depends on their ___ and _____ 31. The law that states that every object maintains constant velocity unless acted on by an unbalanced force is _____ 32. A tug ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.