Vectors Review for Test 2014 Answers 1
... 4. Bob is a soccer player who has just scored the winning goal in the game. Bob, who is also an observant physics student, noticed that when he received the pass, the soccer ball was moving 4.8 m/s 8° N of E and that after he kicked the ball it was moving at 25 m/s 41° E of S. What is the ball's ch ...
... 4. Bob is a soccer player who has just scored the winning goal in the game. Bob, who is also an observant physics student, noticed that when he received the pass, the soccer ball was moving 4.8 m/s 8° N of E and that after he kicked the ball it was moving at 25 m/s 41° E of S. What is the ball's ch ...
Lecture 7: Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity
... uniform sphere on a particle outside the sphere is the same as the force exerted if the entire mass of the sphere were concentrated at its center. This is a result from Gauss’s law and stems from the fact that the gravitational force is inversely proportional to square of the distance between two pa ...
... uniform sphere on a particle outside the sphere is the same as the force exerted if the entire mass of the sphere were concentrated at its center. This is a result from Gauss’s law and stems from the fact that the gravitational force is inversely proportional to square of the distance between two pa ...
Document
... Calculate the Acceleration of the Cart Note: This formula will work because the Cart started with a velocity of zero and accelerated at an (approximately) constant rate. In this particular case, the final velocity is the average velocity x 2. ...
... Calculate the Acceleration of the Cart Note: This formula will work because the Cart started with a velocity of zero and accelerated at an (approximately) constant rate. In this particular case, the final velocity is the average velocity x 2. ...
Chapter 5 Worksheets - School District of La Crosse
... 16. To understand forces acting in 2 directions, what must we do? ...
... 16. To understand forces acting in 2 directions, what must we do? ...
mj force and motion - Doral Academy Preparatory
... What you should know: • Changes in motion and position can be measured. • The types of forces that act upon an object can be predicted and measured. • Gravity is a universal force that every mass exerts on every other mass. • Many forces act at a distance. • Common contact forces include friction a ...
... What you should know: • Changes in motion and position can be measured. • The types of forces that act upon an object can be predicted and measured. • Gravity is a universal force that every mass exerts on every other mass. • Many forces act at a distance. • Common contact forces include friction a ...
Part IV
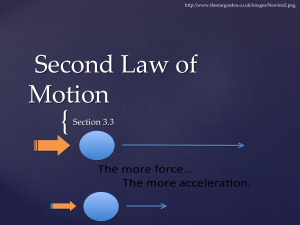
... • Newton’s 2nd Law is the relation between acceleration & force. • Acceleration is proportional to force and inversely proportional to mass. It takes a force to change either the direction of motion or the speed of an object. • More force means more acceleration; the same force exerted on a more mas ...
... • Newton’s 2nd Law is the relation between acceleration & force. • Acceleration is proportional to force and inversely proportional to mass. It takes a force to change either the direction of motion or the speed of an object. • More force means more acceleration; the same force exerted on a more mas ...
Chapter 4 Introducing Forces
... Galileo’s thought experiments led to our understanding of inertia-objects rolling down inclines will speed up, those rolling up inclines will slow down and those rolling along a horizontal surface will continue to roll. His work built on Aristotle’s and Buridan who believed respectively that constan ...
... Galileo’s thought experiments led to our understanding of inertia-objects rolling down inclines will speed up, those rolling up inclines will slow down and those rolling along a horizontal surface will continue to roll. His work built on Aristotle’s and Buridan who believed respectively that constan ...
1 - Hingham Schools
... A. The force on the apple is greater than the force on the Earth because the Earth is more massive. B. The force on the Earth is greater than the force on the apple because the Earth is more massive. C. The force on the apple is less than the force on the Earth because the tree is supporting the app ...
... A. The force on the apple is greater than the force on the Earth because the Earth is more massive. B. The force on the Earth is greater than the force on the apple because the Earth is more massive. C. The force on the apple is less than the force on the Earth because the tree is supporting the app ...
Newton`s 1st Law Newton`s 1st Law Conservation of Momentum
... • Linear kinetics is the study of forces related to linear motion and can be explained by Newton’s Laws. ...
... • Linear kinetics is the study of forces related to linear motion and can be explained by Newton’s Laws. ...
Second
... the weight Fg of an object, the magnitude of the force of gravity acting on it, if the acceleration a is the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s2. ...
... the weight Fg of an object, the magnitude of the force of gravity acting on it, if the acceleration a is the acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s2. ...
Acceleration due to Gravity
... Put a string over the pulley and attach the pulley firmly to a support apparatus. Attach known masses to both ends of the string and record the time necessary for the heavier mass to fall a known distance. No masses should come in contact with the pulley, or the floor. Information recorded should be ...
... Put a string over the pulley and attach the pulley firmly to a support apparatus. Attach known masses to both ends of the string and record the time necessary for the heavier mass to fall a known distance. No masses should come in contact with the pulley, or the floor. Information recorded should be ...
Solutions - faculty.ucmerced.edu
... position is at x(t = 0) = −A, and so δ = π. The amplitude is A = 2.5 cm, and ω = 2πf = 11π. So, we can immediately write x(t) = 2.5 cos(11πt + π) = −2.5 cos(11πt). We’ll take the last expression for x(t) = −2.5 cos(11πt) for convenience. Now, the velocity is v = ẋ = 27.5π sin(11πt) ≈ 86.4 sin(11πt) ...
... position is at x(t = 0) = −A, and so δ = π. The amplitude is A = 2.5 cm, and ω = 2πf = 11π. So, we can immediately write x(t) = 2.5 cos(11πt + π) = −2.5 cos(11πt). We’ll take the last expression for x(t) = −2.5 cos(11πt) for convenience. Now, the velocity is v = ẋ = 27.5π sin(11πt) ≈ 86.4 sin(11πt) ...
Chapters One and Two - elementaryscienceteachers
... – Gravitational pull on an object can be measured in newtons. Since F=M x A, one calculates weight (N) by multiplying mass (Kg) times the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s2). ...
... – Gravitational pull on an object can be measured in newtons. Since F=M x A, one calculates weight (N) by multiplying mass (Kg) times the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s2). ...
Name
... b. A soccer ball accelerates more than a bowling ball when thrown with the same force. c. A magician pulls a tablecloth out from under dishes and glasses on a table without disturbing them. d. A student leaves a pencil on a desk and the pencil stays in the same spot until another student picks it up ...
... b. A soccer ball accelerates more than a bowling ball when thrown with the same force. c. A magician pulls a tablecloth out from under dishes and glasses on a table without disturbing them. d. A student leaves a pencil on a desk and the pencil stays in the same spot until another student picks it up ...
Balanced Forces
... – Weight = mass × gravitational ____________________ g on Earth is 9.8m/s2 – SI Unit = ____________________ – Weight can ____________________with a change in ____________________. – Mass: A measure of how much ____________________ an object has – You know an object has mass because it has ________ ...
... – Weight = mass × gravitational ____________________ g on Earth is 9.8m/s2 – SI Unit = ____________________ – Weight can ____________________with a change in ____________________. – Mass: A measure of how much ____________________ an object has – You know an object has mass because it has ________ ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.