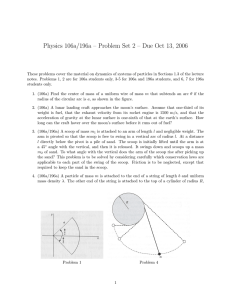
Higher Physics – Unit 2
... large body, the mass must be given enough kinetic energy so that when it reaches “infinity” its kinetic energy is 0. ...
... large body, the mass must be given enough kinetic energy so that when it reaches “infinity” its kinetic energy is 0. ...
Calculating Energy Notes - Edmonds School District
... Kinetic Energy • The kinetic (motion) energy of any moving object depends on both its mass and velocity. • Velocity = distance(in meters) ÷ time(in seconds) ...
... Kinetic Energy • The kinetic (motion) energy of any moving object depends on both its mass and velocity. • Velocity = distance(in meters) ÷ time(in seconds) ...
ysics P2 Graded Task Bungee Jumping with equations
... Draw a velocity time graph of the jumpers fall using the information in the box above. Calculate the momentum of the jumper when they are at 20m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the jumper at this velocity. The bungee cord stretches as he falls. Name the energy stored in the cord. ...
... Draw a velocity time graph of the jumpers fall using the information in the box above. Calculate the momentum of the jumper when they are at 20m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy of the jumper at this velocity. The bungee cord stretches as he falls. Name the energy stored in the cord. ...
Spring-Mass Problems An object has weight w (in pounds
... If there is to be just the one repeated root, then the discriminant (the portion under the radical) must be ...
... If there is to be just the one repeated root, then the discriminant (the portion under the radical) must be ...