Slide 1
... it rebounds to its original height. Is this SHM? Look for equilibrium position in the middle and a force that is directed toward it from both sides of the equilibrium. If that force changes as the distance changes you found restoring force!!! ...
... it rebounds to its original height. Is this SHM? Look for equilibrium position in the middle and a force that is directed toward it from both sides of the equilibrium. If that force changes as the distance changes you found restoring force!!! ...
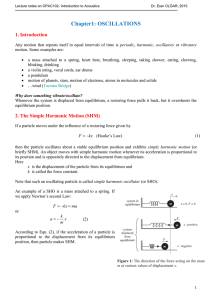
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION: SHIFTED ORIGIN AND PHASE
... 3. A particle with mass 200.0 gm experiences a force whose associated potential energy function is Ep = (4.0 J/m2 ) · (x − 0.20 m)2 . Find the angular frequency of the motion. 4. A 50.0 kg woman standing on the end of a diving board caused it to be lowered by 30.0 cm and it then oscillated up and do ...
... 3. A particle with mass 200.0 gm experiences a force whose associated potential energy function is Ep = (4.0 J/m2 ) · (x − 0.20 m)2 . Find the angular frequency of the motion. 4. A 50.0 kg woman standing on the end of a diving board caused it to be lowered by 30.0 cm and it then oscillated up and do ...
Click
... the applications and implications of energy based on: –evaluation of risks and benefits ...
... the applications and implications of energy based on: –evaluation of risks and benefits ...
pompton lakes high school - Pompton Lakes School District
... versus time. Describe motion in terms of changing velocity Compare graphical representations of accelerated and non-accelerated motions. Apply kinematic equations to calculate distance, time or velocity under conditions of constant ...
... versus time. Describe motion in terms of changing velocity Compare graphical representations of accelerated and non-accelerated motions. Apply kinematic equations to calculate distance, time or velocity under conditions of constant ...
Physics Christmas Assignment In order to retake the 9 week test
... A space probe has just performed a flyby close to the planet Jupiter. It is now heading toward the outer reaches of the solar system where it will arrive in orbit around Neptune. Which of the following graphs best represents the relationship between the gravitational force exerted by Jupiter upon th ...
... A space probe has just performed a flyby close to the planet Jupiter. It is now heading toward the outer reaches of the solar system where it will arrive in orbit around Neptune. Which of the following graphs best represents the relationship between the gravitational force exerted by Jupiter upon th ...
work, energy and power
... bow-string possesses potential energy. When it is released, the arrow flies off at a great speed. The earth’s crust is not uniform, but has discontinuities and dislocations that are called fault lines. These fault lines in the earth’s crust ...
... bow-string possesses potential energy. When it is released, the arrow flies off at a great speed. The earth’s crust is not uniform, but has discontinuities and dislocations that are called fault lines. These fault lines in the earth’s crust ...
A x
... “At x=0 all spring potential energy is converted into kinetic energy and so the velocity will be greatest at this point.” ...
... “At x=0 all spring potential energy is converted into kinetic energy and so the velocity will be greatest at this point.” ...
ENERGY Types of Energy and Energy Transfers
... Using the diagram above calculate the kinetic energy of the car and the lorry. How fast would the car have to go to have the same kinetic energy as the lorry? The mass of the lift and the passengers in the diagram is 200 kg. Each floor of the building is 5 m high. a. Show that the gravitational pote ...
... Using the diagram above calculate the kinetic energy of the car and the lorry. How fast would the car have to go to have the same kinetic energy as the lorry? The mass of the lift and the passengers in the diagram is 200 kg. Each floor of the building is 5 m high. a. Show that the gravitational pote ...
work, energy and power
... potential energy is the ‘stored energy’ by virtue of the position or configuration of a body. The body left to itself releases this stored energy in the form of kinetic energy. Let us make our notion of potential energy more concrete. The gravitational force on a ball of mass m is mg . g may be trea ...
... potential energy is the ‘stored energy’ by virtue of the position or configuration of a body. The body left to itself releases this stored energy in the form of kinetic energy. Let us make our notion of potential energy more concrete. The gravitational force on a ball of mass m is mg . g may be trea ...
Summary of lesson
... Q20. Compare the speed of the car at the bottom of the first hill in this simulation to the speed of the car at the bottom of the first hill when there was no friction. What difference do you observe? Is this consistent with your observations above? Sample Answer: The speed is 30.4 m/s with friction ...
... Q20. Compare the speed of the car at the bottom of the first hill in this simulation to the speed of the car at the bottom of the first hill when there was no friction. What difference do you observe? Is this consistent with your observations above? Sample Answer: The speed is 30.4 m/s with friction ...
The Equilibrium Constant
... Increase in temperature shifts equilibrium to the _________________: More __________. Kc ____________________. Decrease in temperature shifts equilibrium to the ________________: More ___________. Kc ______________________. If ∆H < 0 (Exothermic): Increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to th ...
... Increase in temperature shifts equilibrium to the _________________: More __________. Kc ____________________. Decrease in temperature shifts equilibrium to the ________________: More ___________. Kc ______________________. If ∆H < 0 (Exothermic): Increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to th ...
Lecture19
... kinetic energy and so the velocity will be greatest at this point.” Its 5:34 in the morning. Answer JUSTIFIED. ...
... kinetic energy and so the velocity will be greatest at this point.” Its 5:34 in the morning. Answer JUSTIFIED. ...
Energy - Georgia Standards
... Other chemical reactions can produce energy but not be explosive. They may occur more slowly, and the resulting molecules may take up the same amount of room as the original molecules. Food energy is a form of chemical energy. Plants absorb energy from sunlight and store it in energy-rich chemicals, ...
... Other chemical reactions can produce energy but not be explosive. They may occur more slowly, and the resulting molecules may take up the same amount of room as the original molecules. Food energy is a form of chemical energy. Plants absorb energy from sunlight and store it in energy-rich chemicals, ...
sy30_may10_s12
... Circular orbits: Dynamical quantities (v,E,K,U,F) involve radius K(r) = - ½ U(r) Employ conservation of angular momentum in elliptical orbits No need to derive Kepler’s Laws (know the reasons for them) Energy transfer when orbit radius changes(e.g. escape velocity) Physics 201: Lecture 30, Pg 18 ...
... Circular orbits: Dynamical quantities (v,E,K,U,F) involve radius K(r) = - ½ U(r) Employ conservation of angular momentum in elliptical orbits No need to derive Kepler’s Laws (know the reasons for them) Energy transfer when orbit radius changes(e.g. escape velocity) Physics 201: Lecture 30, Pg 18 ...
x - Physics@Brock
... (e) Determine the positions at which the kinetic energy and the potential energy of the oscillator are equal. ...
... (e) Determine the positions at which the kinetic energy and the potential energy of the oscillator are equal. ...