Midterm solutions - Bryn Mawr College
... (A) Have the elephant stand on one scale. (B) Have the elephant stand on two scales at the same time with different parts of his body (say one under each foot) and subtract the readings from each other. (C) Have the elephant stand on four scales at the same time with different parts of his body (say ...
... (A) Have the elephant stand on one scale. (B) Have the elephant stand on two scales at the same time with different parts of his body (say one under each foot) and subtract the readings from each other. (C) Have the elephant stand on four scales at the same time with different parts of his body (say ...
Problem: Average Velocity (1988)
... 1. In which of the following situations would an object be accelerated? I. It moves in a straight line at constant speed. II. It moves with uniform circular motion. III. It travels as a projectile in a gravitational field with negligible air resistance. (A) I only (B) III only (C) I and II only (D) ...
... 1. In which of the following situations would an object be accelerated? I. It moves in a straight line at constant speed. II. It moves with uniform circular motion. III. It travels as a projectile in a gravitational field with negligible air resistance. (A) I only (B) III only (C) I and II only (D) ...
Force - wilson physics
... 1. In which of the following situations would an object be accelerated? I. It moves in a straight line at constant speed. II. It moves with uniform circular motion. III. It travels as a projectile in a gravitational field with negligible air resistance. (A) I only (B) III only (C) I and II only (D) ...
... 1. In which of the following situations would an object be accelerated? I. It moves in a straight line at constant speed. II. It moves with uniform circular motion. III. It travels as a projectile in a gravitational field with negligible air resistance. (A) I only (B) III only (C) I and II only (D) ...
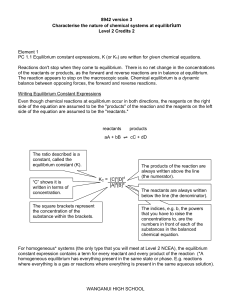
Wanganui High School
... (the numerator). The reactants are always written below the line (the denominator). ...
... (the numerator). The reactants are always written below the line (the denominator). ...
Forces - Faculty Perry, Oklahoma
... Friction is caused when 2 surfaces rub together. Friction is a force that acts in the opposite direction of a moving object. ...
... Friction is caused when 2 surfaces rub together. Friction is a force that acts in the opposite direction of a moving object. ...
TRUE/FALSE. Write `T` if the statement is true and
... 43) Consider a plot of the displacement (x) vs. applied force (F) for an ideal elastic spring. The slope of the curve would be A) the reciprocal of the acceleration of gravity. B) the reciprocal of the spring constant.XXX C) the reciprocal of the displacement. D) the spring constant. E) the accelera ...
... 43) Consider a plot of the displacement (x) vs. applied force (F) for an ideal elastic spring. The slope of the curve would be A) the reciprocal of the acceleration of gravity. B) the reciprocal of the spring constant.XXX C) the reciprocal of the displacement. D) the spring constant. E) the accelera ...
Conservation of Linear Momentum
... between system components. (Black vectors are total momentum vectors.) There are two equations in the two unknowns, v 1f and v 2f . These are the conservation of kinetic energy (a scaler equation, no direction) and the conservation of linear momentum (signs matter) For a tilted track there would be ...
... between system components. (Black vectors are total momentum vectors.) There are two equations in the two unknowns, v 1f and v 2f . These are the conservation of kinetic energy (a scaler equation, no direction) and the conservation of linear momentum (signs matter) For a tilted track there would be ...
CHM – 124 Principles of Chemistry
... Section III. - At the end of this section, the student should be able to: ...
... Section III. - At the end of this section, the student should be able to: ...
8 Forces, energy and motion
... energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can only be transformed into another form of energy or transferred to another object. What happens to the lost gravitational potential energy of each of the three people referred to in question 7? ...
... energy cannot be created or destroyed. It can only be transformed into another form of energy or transferred to another object. What happens to the lost gravitational potential energy of each of the three people referred to in question 7? ...
6.1 Energy - learnphysics
... 2. Energy can be converted from one form to another. 3. The Principle of Conservation of Energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed in any process. It can be converted from one form to another or transferred from one body to another but the total amount remains constant. ...
... 2. Energy can be converted from one form to another. 3. The Principle of Conservation of Energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed in any process. It can be converted from one form to another or transferred from one body to another but the total amount remains constant. ...
Glossary
... Flow stress: The stress required to produce plastic deformation in a solid metal. Free energy: Free energy is a measure of the ability of a system to do work, such that a reduction in free energy could in principle yield an equivalent quantity of work. The Helmholtz free energy describes the free en ...
... Flow stress: The stress required to produce plastic deformation in a solid metal. Free energy: Free energy is a measure of the ability of a system to do work, such that a reduction in free energy could in principle yield an equivalent quantity of work. The Helmholtz free energy describes the free en ...
SM_chapter7
... mattresses behave as a linear spring with force constant 19.4 kN/m. Find the maximum amount by which they are compressed when the child lands on them. Physical meaning: The positive value of x represents the maximum spring compression. The negative value represents the maximum extension of the equiv ...
... mattresses behave as a linear spring with force constant 19.4 kN/m. Find the maximum amount by which they are compressed when the child lands on them. Physical meaning: The positive value of x represents the maximum spring compression. The negative value represents the maximum extension of the equiv ...
Lecture 18. Chemical Equilibrium (Ch. 5)
... Thus, the equilibrium is strongly shifted to the right, favoring the production of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen. The calculation of the equilibrium constant K is only the first step in evaluating the reaction (e.g., its usefulness for applications). However, the value of K tells us nothing abo ...
... Thus, the equilibrium is strongly shifted to the right, favoring the production of ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen. The calculation of the equilibrium constant K is only the first step in evaluating the reaction (e.g., its usefulness for applications). However, the value of K tells us nothing abo ...
SFU Phys101 Summer 2013 ( MPCHEN69716 )
... The minus sign indicates that the force is in the opposite direction to that of the spring's displacement from its equilibrium length and is "trying" to restore the spring to its equilibrium position. The magnitude of the force is given by , where is the magnitude of the displacement. In Haiti, publ ...
... The minus sign indicates that the force is in the opposite direction to that of the spring's displacement from its equilibrium length and is "trying" to restore the spring to its equilibrium position. The magnitude of the force is given by , where is the magnitude of the displacement. In Haiti, publ ...
SEC - Warrenphysics
... in 23 s at constant speed. At what average rate does the force from the cable do work on the cab? 31E. A 100 kg block is pulled at a constant speed of 5.0 m/s across a horizontal floor by an applied force of 122 N directed 37° above the horizontal. What is the rate at which the force does work on th ...
... in 23 s at constant speed. At what average rate does the force from the cable do work on the cab? 31E. A 100 kg block is pulled at a constant speed of 5.0 m/s across a horizontal floor by an applied force of 122 N directed 37° above the horizontal. What is the rate at which the force does work on th ...
Chapter ( 1 ) 1- Write the scientific term : 1. Simple symbolic formula
... 2. The half life period of a radioactive phosphorous equals 14 hour , the time needed for the decay of ...
... 2. The half life period of a radioactive phosphorous equals 14 hour , the time needed for the decay of ...
phys1441-120610
... Identify all the forces and draw a free-body diagram with them indicated on it with their directions and locations properly indicated Choose a convenient set of x and y axes and write down force equation for each x and y component with correct signs. Apply the equations that specify the balance of f ...
... Identify all the forces and draw a free-body diagram with them indicated on it with their directions and locations properly indicated Choose a convenient set of x and y axes and write down force equation for each x and y component with correct signs. Apply the equations that specify the balance of f ...
gravitational potential energy
... Question: What is the change in gravitational potential energy of a 50-kg person who climbs a flight of stairs with a height of 3 meters and a horizontal extent of 5 meters? Answer: The change in gravitational potential energy is GPE = mgh = (50 kg)(10 m/s2)(3 m) = 1500 J ...
... Question: What is the change in gravitational potential energy of a 50-kg person who climbs a flight of stairs with a height of 3 meters and a horizontal extent of 5 meters? Answer: The change in gravitational potential energy is GPE = mgh = (50 kg)(10 m/s2)(3 m) = 1500 J ...
Unit 6 - Marie Isokpunwu
... The two examples above illustrate the two forms of potential energy to be discussed in this course gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy. Gravitational potential energy is the energy stored in an object as the result of its vertical position or height. The energy is stored as t ...
... The two examples above illustrate the two forms of potential energy to be discussed in this course gravitational potential energy and elastic potential energy. Gravitational potential energy is the energy stored in an object as the result of its vertical position or height. The energy is stored as t ...
Chapter 6: Forces and Equilibrium
... has two important characteristics: — The force always acts in a direction that tries to return the spring to its unstretched shape. — The strength of the force is proportional to the amount of extension or compression in the spring. ...
... has two important characteristics: — The force always acts in a direction that tries to return the spring to its unstretched shape. — The strength of the force is proportional to the amount of extension or compression in the spring. ...