Episode 214 - Teaching Advanced Physics
... What is the force acting against the movement? (mg) We say that the lifting force is doing work against gravity. Some students may feel that it takes a larger force than mg to raise the object; however, if the object is raised at a steady speed, it is in equilibrium and the lifting force will just b ...
... What is the force acting against the movement? (mg) We say that the lifting force is doing work against gravity. Some students may feel that it takes a larger force than mg to raise the object; however, if the object is raised at a steady speed, it is in equilibrium and the lifting force will just b ...
Lesson 1.1 Mechanisms - Key Terms Term Definition
... A part of the physical world as described by its thermodynamic properties s ...
... A part of the physical world as described by its thermodynamic properties s ...
recitation ch7-2
... Reflect: Fon spring is always the force applied to one end of the spring, thus we did not need to double the 15.0 N force. Consider a free-body diagram of a spring at rest; forces of equal magnitude and opposite direction are always applied to both ends of every section of the spring examined. 7.31. ...
... Reflect: Fon spring is always the force applied to one end of the spring, thus we did not need to double the 15.0 N force. Consider a free-body diagram of a spring at rest; forces of equal magnitude and opposite direction are always applied to both ends of every section of the spring examined. 7.31. ...
Work Power Energy Notes
... A 60-kg skier is at the top of a ski slope. At this highest point the skier is 10 m vertically above the chalet. What is the skier’s gravitational potential energy at the peak? What is the skier’s gravitational potential energy at the chalet? What is the skier’s gravitational potential energy at a p ...
... A 60-kg skier is at the top of a ski slope. At this highest point the skier is 10 m vertically above the chalet. What is the skier’s gravitational potential energy at the peak? What is the skier’s gravitational potential energy at the chalet? What is the skier’s gravitational potential energy at a p ...
Slide 1
... The force acting upon an object to cause a displacement There must be a displacement Force and displacement must be in the same direction Scalar quantity ...
... The force acting upon an object to cause a displacement There must be a displacement Force and displacement must be in the same direction Scalar quantity ...
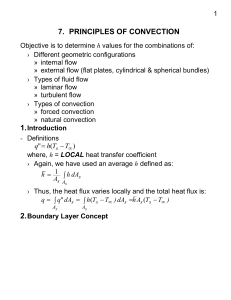
Convection Principles
... some point where velocity is almost that of free stream (u) du dy At the plate surface, us = 0 (i.e., nonslip surface) › Velocity BL thickness, The distance from the wall to a point where u( y) 0.99u - Thermal Boundary Layer › The thermal BL develops because of the temperature difference ...
... some point where velocity is almost that of free stream (u) du dy At the plate surface, us = 0 (i.e., nonslip surface) › Velocity BL thickness, The distance from the wall to a point where u( y) 0.99u - Thermal Boundary Layer › The thermal BL develops because of the temperature difference ...
PHYS 101 Lecture 10 - Simon Fraser University
... The total work is zero, since the forces cancel out in the direction of motion. Similarly, ΔK = 0 since the object is at rest at the top and bottom. The work we have done on the block has not resulted in a change in kinetic energy! Even though this is a nice consistent picture, we find it unsatisfac ...
... The total work is zero, since the forces cancel out in the direction of motion. Similarly, ΔK = 0 since the object is at rest at the top and bottom. The work we have done on the block has not resulted in a change in kinetic energy! Even though this is a nice consistent picture, we find it unsatisfac ...
Work Energy Theory - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... Then the Work-Energy Theorem says: The total work done by all external forces acting on a particle is equal to the increase in its kinetic energy. Proof: from Newton’s Second Law, and the definition of Work. ...
... Then the Work-Energy Theorem says: The total work done by all external forces acting on a particle is equal to the increase in its kinetic energy. Proof: from Newton’s Second Law, and the definition of Work. ...
8.8.b Conservation of Energy 2
... • A simple pendulum consists of a mass (called a bob) hung by a string from a fixed support. • It hangs vertically in its equilibrium position. • When the bob is displaced from equilibrium and then released, it begins a back and forth motion about its fixed equilibrium position. ...
... • A simple pendulum consists of a mass (called a bob) hung by a string from a fixed support. • It hangs vertically in its equilibrium position. • When the bob is displaced from equilibrium and then released, it begins a back and forth motion about its fixed equilibrium position. ...
Motion Forces and Work rvw pak 13.14
... 7.P.2.3 Recognize that energy can be transferred from one system to another when two objects push or pull on each other over a distance (work) and electrical circuits require a complete loop through which an electrical current can pass. 7.P.2.4 Explain how simple machines such as inclined planes, pu ...
... 7.P.2.3 Recognize that energy can be transferred from one system to another when two objects push or pull on each other over a distance (work) and electrical circuits require a complete loop through which an electrical current can pass. 7.P.2.4 Explain how simple machines such as inclined planes, pu ...
updated midterm study guide
... What is the transfer of thermal energy with no overall transfer of matter? ______________________________ In order for conduction to occur, materials must be______________________________ An example of a good conductor is______________________________ If a material does not conduct thermal energy we ...
... What is the transfer of thermal energy with no overall transfer of matter? ______________________________ In order for conduction to occur, materials must be______________________________ An example of a good conductor is______________________________ If a material does not conduct thermal energy we ...
Practice Packet for Chapter 5: Work and Energy Name Read pages
... No, Work is something that an object does to other objects. An object can do work if it has energy. 3) A force sets an object in motion. What do we call the quantity force x distance, and what quantity does this change? ...
... No, Work is something that an object does to other objects. An object can do work if it has energy. 3) A force sets an object in motion. What do we call the quantity force x distance, and what quantity does this change? ...
forces_and_energy_review
... 17. What is the difference between average speed and instantaneous speed? How do you measure average speed? Average speed is the general speed over a distance and instantaneous speed is at one specific moment. Average speed is calculated by take the total distance traveled and dividing it by the tim ...
... 17. What is the difference between average speed and instantaneous speed? How do you measure average speed? Average speed is the general speed over a distance and instantaneous speed is at one specific moment. Average speed is calculated by take the total distance traveled and dividing it by the tim ...
presentation source
... PEf = m |g| yf = (5 kg)(10 m/s2)(0.5 m) = 25 J PEi = m |g| yi = (5 kg)(10 m/s2)(0.0 m) = 0 J Wg = 0 - 25 J = - 25 J Thus, we get the same answer from Potential Energy as we got with Force Balance. ...
... PEf = m |g| yf = (5 kg)(10 m/s2)(0.5 m) = 25 J PEi = m |g| yi = (5 kg)(10 m/s2)(0.0 m) = 0 J Wg = 0 - 25 J = - 25 J Thus, we get the same answer from Potential Energy as we got with Force Balance. ...
Power Point
... The work done by the net force is equal to the change of kinetic energy. The net force is the sum of conservative forces (gravitational force, elastic force, …) and nonconservative force (friction force ..). The work done by conservative forces can be written as the change of potential energy. Then ...
... The work done by the net force is equal to the change of kinetic energy. The net force is the sum of conservative forces (gravitational force, elastic force, …) and nonconservative force (friction force ..). The work done by conservative forces can be written as the change of potential energy. Then ...
Conservation of Mechanical Energy
... Conservation of Mechanical Energy I. Introduction A. In the absence of dissipative forces (i.e. non-conservative forces that do work, such as kinetic friction), the mechanical energy of an isolated system is conserved. This can be written in the form: Kf + Uf = Ki + Ui. Thus the sum of the kineti ...
... Conservation of Mechanical Energy I. Introduction A. In the absence of dissipative forces (i.e. non-conservative forces that do work, such as kinetic friction), the mechanical energy of an isolated system is conserved. This can be written in the form: Kf + Uf = Ki + Ui. Thus the sum of the kineti ...