Review2
... When two bodies interact, the forces on the bodies from each other are always equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. For every "action" force, there is always an equal and opposite "reaction" force; we call these a "third-law force pair." •When a table supports an object against the force of ...
... When two bodies interact, the forces on the bodies from each other are always equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. For every "action" force, there is always an equal and opposite "reaction" force; we call these a "third-law force pair." •When a table supports an object against the force of ...
background
... disturbances of the same kind overlap, the resultant amplitude at any point in the region is the algebraic sum of the amplitudes of each contributing wave. The Principle of Superposition leads to the phenomena known as interference. For example, assume that there are two monochromatic and coherent l ...
... disturbances of the same kind overlap, the resultant amplitude at any point in the region is the algebraic sum of the amplitudes of each contributing wave. The Principle of Superposition leads to the phenomena known as interference. For example, assume that there are two monochromatic and coherent l ...
AP Physics Chapter 5-8 Key Equations and Ideas Forces (pulleys
... A force does positive work when it has a vector component in the same direction as the displacement, and it does negative work when it has a vector component in the opposite direction. The force does zero work when it is perpendicular to the displacement. ...
... A force does positive work when it has a vector component in the same direction as the displacement, and it does negative work when it has a vector component in the opposite direction. The force does zero work when it is perpendicular to the displacement. ...
HW1
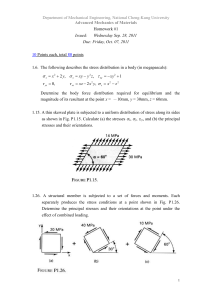
... Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Cheng-Kung University Advanced Mechanics of Materials 1.35. For a given state of stress at a point in a frame, certain stress components are known for each of the two orientations shown in Fig. P1.35. Using Mohr’s circle, determine the following stress ...
... Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Cheng-Kung University Advanced Mechanics of Materials 1.35. For a given state of stress at a point in a frame, certain stress components are known for each of the two orientations shown in Fig. P1.35. Using Mohr’s circle, determine the following stress ...
The Aristotelian approach
... - we don’t actually see forces, we see objects behave in a certain way, and infer that a force is present - the force is phenomenological concept, it make easy to discuss observed behavior of objects - we can measure it by a spring: measuring the amount of stretch using some arbitrary scale. - besid ...
... - we don’t actually see forces, we see objects behave in a certain way, and infer that a force is present - the force is phenomenological concept, it make easy to discuss observed behavior of objects - we can measure it by a spring: measuring the amount of stretch using some arbitrary scale. - besid ...
1 HOOKE`S LAW AND SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Objectives
... watch, the motion of the piston in a car engine, a beating heart, the alternating current of electricity, the vibration of atoms and molecules about their equilibrium position as well as sound, radio, and light waves - all undergo a periodic or oscillatory motion, which repeats itself regularly in t ...
... watch, the motion of the piston in a car engine, a beating heart, the alternating current of electricity, the vibration of atoms and molecules about their equilibrium position as well as sound, radio, and light waves - all undergo a periodic or oscillatory motion, which repeats itself regularly in t ...