Newton`s Laws
... matter in something or a measure of its inertia What is weight? Answer: Force on a body due to gravity ...
... matter in something or a measure of its inertia What is weight? Answer: Force on a body due to gravity ...
survey of physics - Stevenson High School
... You drive 30 km/hr North for1.5 hours and then turn West and drive 40 km/hr for 0.75 hour. How far away are you from your starting point (as the crow flies) and what direction? ...
... You drive 30 km/hr North for1.5 hours and then turn West and drive 40 km/hr for 0.75 hour. How far away are you from your starting point (as the crow flies) and what direction? ...
Part I: Centripetal force from the rotational motion
... OBJECTIVE The purpose of this experiment is to calculate the centripetal force needed to keep an object in uniform circular path. We accomplish that in two ways; by finding the weight needed to stretch a rotating mass until it reaches a sensitive probe and also by allowing this mass to rotate at a s ...
... OBJECTIVE The purpose of this experiment is to calculate the centripetal force needed to keep an object in uniform circular path. We accomplish that in two ways; by finding the weight needed to stretch a rotating mass until it reaches a sensitive probe and also by allowing this mass to rotate at a s ...
Student AP Physics 1 Date Oscillations – MC 1. A mass m, attached
... A sphere of mass m1, which is attached to a spring, is displaced downward from its equilibrium position as shown above left and released from rest. A sphere of mass m2, which is suspended from a string of length L, is displaced to the right as shown above right and released from rest so that it swin ...
... A sphere of mass m1, which is attached to a spring, is displaced downward from its equilibrium position as shown above left and released from rest. A sphere of mass m2, which is suspended from a string of length L, is displaced to the right as shown above right and released from rest so that it swin ...
DOC - People Server at UNCW
... and calculate the effective radius as one half of the average between this diameter and the bare shaft diameter. 5. Use the two-meter stick to measure the distance between the bottom of the weight hanger and the floor at the hanger’s highest height. 6. Carefully hold one finger in front of one arm o ...
... and calculate the effective radius as one half of the average between this diameter and the bare shaft diameter. 5. Use the two-meter stick to measure the distance between the bottom of the weight hanger and the floor at the hanger’s highest height. 6. Carefully hold one finger in front of one arm o ...
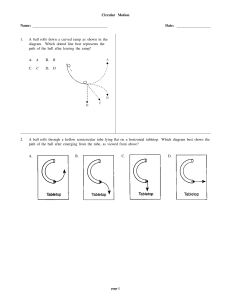
Circular Motion Name: Date: 1. A ball rolls down a curved ramp as
... If object O is moving in a uniform circular motion around point P at constant speed, which vector shown represents a centripetal force? A. ...
... If object O is moving in a uniform circular motion around point P at constant speed, which vector shown represents a centripetal force? A. ...
Newton`s 2nd Law
... What does F =MA mean? Force is directly proportional to mass and acceleration. Imagine a ball of a certain mass moving at a certain acceleration. This ball has a certain force. Now imagine we make the ball twice as big (double the mass) but keep the acceleration constant. F = ma says that this new ...
... What does F =MA mean? Force is directly proportional to mass and acceleration. Imagine a ball of a certain mass moving at a certain acceleration. This ball has a certain force. Now imagine we make the ball twice as big (double the mass) but keep the acceleration constant. F = ma says that this new ...
Document
... and the train would be moving with the same horizontal velocity, and when the ball is tossed, it is given an additional velocity component in the vertical direction, but the original horizontal velocity component remains unchanged, and lands in the center of the train. ...
... and the train would be moving with the same horizontal velocity, and when the ball is tossed, it is given an additional velocity component in the vertical direction, but the original horizontal velocity component remains unchanged, and lands in the center of the train. ...
Seismic Waves
... Seismic Waves Slinky – P, S, Rayleigh, Love waves; Reflection and transmission; energy carried by waves; elastic rebound/plate motions and the slinky; 5-slinky model – waves in all directions, travel times to different distances. Human wave demo – P and S waves in solids and ...
... Seismic Waves Slinky – P, S, Rayleigh, Love waves; Reflection and transmission; energy carried by waves; elastic rebound/plate motions and the slinky; 5-slinky model – waves in all directions, travel times to different distances. Human wave demo – P and S waves in solids and ...
presentation source
... Think of the average height of 6 monsters that are 5m high and 7 that are 10 m high ...
... Think of the average height of 6 monsters that are 5m high and 7 that are 10 m high ...
Non-Linear Static Analysis of Multi-Storied Building
... IS 1893(Part1):2002, Criteria for earthquake resistant design of structures, Part 1 General provisions and buildings, Bureau of Indian Standard, 2002. ...
... IS 1893(Part1):2002, Criteria for earthquake resistant design of structures, Part 1 General provisions and buildings, Bureau of Indian Standard, 2002. ...
Newton to Einstein Exercise 2 – Kinetics
... include in coursework and exam answers, plus examples of the kind of checking you should routinely do. There should be diagrams too, but these are very tedious to produce in Word, so I have omitted them. ...
... include in coursework and exam answers, plus examples of the kind of checking you should routinely do. There should be diagrams too, but these are very tedious to produce in Word, so I have omitted them. ...