What is this unbalanced force that acts on an
... becoming motionless seemingly without an outside force? It’s a force we sometimes cannot see – friction. ...
... becoming motionless seemingly without an outside force? It’s a force we sometimes cannot see – friction. ...
Earthquakes
... A tsunami spreads out from an earthquake's epicenter and speeds across the ocean. ...
... A tsunami spreads out from an earthquake's epicenter and speeds across the ocean. ...
Gravity and Orbits Talk
... – Gravity is a MUTUAL, ATTRACTIVE force – Force of gravity is proportional to mass – Force of gravity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance (Inverse Square Law) – Force = mass x acceleration; Fgrav = GM1M2/d2 • Orbits: – The speed of the object dictates the shape of its orbit – Orb ...
... – Gravity is a MUTUAL, ATTRACTIVE force – Force of gravity is proportional to mass – Force of gravity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance (Inverse Square Law) – Force = mass x acceleration; Fgrav = GM1M2/d2 • Orbits: – The speed of the object dictates the shape of its orbit – Orb ...
Forces and Motion - Cortez High School
... Does not require contact to act Upward force usually balances the ...
... Does not require contact to act Upward force usually balances the ...
Balanced Forces
... Notice that all the forces are unequal and pointed in the opposite direction. Hence they are unbalanced and in opposition to each other – or one partially cancels the other. ...
... Notice that all the forces are unequal and pointed in the opposite direction. Hence they are unbalanced and in opposition to each other – or one partially cancels the other. ...
A moving company uses the pulley system in figure 1 to lift heavy
... 9. Would it take more, less or the same force to move the crate, if the ground was made of a substance which would make the coefficient of friction .3? 10. Will it take more, less or the same force to pull the crate on the ramp at a constant speed as it does the crate on the ground at a constant spe ...
... 9. Would it take more, less or the same force to move the crate, if the ground was made of a substance which would make the coefficient of friction .3? 10. Will it take more, less or the same force to pull the crate on the ramp at a constant speed as it does the crate on the ground at a constant spe ...
Seismicity, crustal structure, and morphology of the Louisville Ridge
... overthrusting Indo-Australian and subducting Pacific plates. We have found in previous studies, for example, that seamounts of the type that make up the Louisville Ridge may act as either a barrier or asperity during large subduction zone earthquakes. Shallow earthquakes for the period 1964-present ...
... overthrusting Indo-Australian and subducting Pacific plates. We have found in previous studies, for example, that seamounts of the type that make up the Louisville Ridge may act as either a barrier or asperity during large subduction zone earthquakes. Shallow earthquakes for the period 1964-present ...
Introduction to Gravity and Orbits Isaac Newton Newton`s Laws of
... – Gravity is a MUTUAL, ATTRACTIVE force – Force of gravity is proportional to mass – Force of gravity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance (Inverse Square Law) – Force = mass x acceleration; Fgrav = GM1M2/d2 • Orbits: – The speed of the object dictates the shape of its orbit – Orb ...
... – Gravity is a MUTUAL, ATTRACTIVE force – Force of gravity is proportional to mass – Force of gravity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance (Inverse Square Law) – Force = mass x acceleration; Fgrav = GM1M2/d2 • Orbits: – The speed of the object dictates the shape of its orbit – Orb ...
ch15
... and whose mass m is 135 g, suspended at its midpoint from a long wire. Its period Ta of angular SHM is measured to be 2.53 s. An irregularly shaped object, which we call object X, is then hung from the same wire, as in Fig. b, and its period Tb is found to be 4.76 s. What is the rotational inertia o ...
... and whose mass m is 135 g, suspended at its midpoint from a long wire. Its period Ta of angular SHM is measured to be 2.53 s. An irregularly shaped object, which we call object X, is then hung from the same wire, as in Fig. b, and its period Tb is found to be 4.76 s. What is the rotational inertia o ...
laws of motion
... (a) At what angle of inclination θ of the plane to the horizontal will the box just start to slide down the plane? (b) What is the force acting on the box down the plane, if the angle of inclination of the plane is increased to α > θ ? (c) What is the force needed to be applied upwards along the pla ...
... (a) At what angle of inclination θ of the plane to the horizontal will the box just start to slide down the plane? (b) What is the force acting on the box down the plane, if the angle of inclination of the plane is increased to α > θ ? (c) What is the force needed to be applied upwards along the pla ...
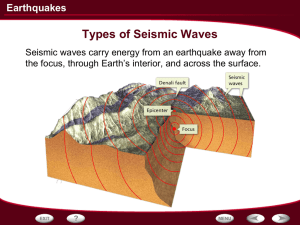
Earthquakes and Earth`s Interior Summary
... Energy released at an earthquake’s focus radiates outward as body waves, which are of two kinds: P waves (Primary waves, which are compressional) and S waves (Secondary waves, which are shear waves). Earthquake energy also causes Earth’s surface to vibrate. These vibrations travel laterally as surfa ...
... Energy released at an earthquake’s focus radiates outward as body waves, which are of two kinds: P waves (Primary waves, which are compressional) and S waves (Secondary waves, which are shear waves). Earthquake energy also causes Earth’s surface to vibrate. These vibrations travel laterally as surfa ...
Document
... - Values of s and k depend on nature of surface. - s and k don’t depend on the area of contact. - s and k don’t depend on speed. - s, max is usually a bit larger than k. - Range from about 0.003 (k for synovial joints in humans) to 1 (s for rubber on concrete). See table 5.2 in book. ...
... - Values of s and k depend on nature of surface. - s and k don’t depend on the area of contact. - s and k don’t depend on speed. - s, max is usually a bit larger than k. - Range from about 0.003 (k for synovial joints in humans) to 1 (s for rubber on concrete). See table 5.2 in book. ...
Lab 2: The Interior of the Earth
... In our lab activity you learned that waves travel at a constant speed. Scientists cannot observe earthquake waves moving through the Earth in the same way you can observe waves moving through water. They can, however, record and study the energy from the earthquake waves as the waves arrive at a rec ...
... In our lab activity you learned that waves travel at a constant speed. Scientists cannot observe earthquake waves moving through the Earth in the same way you can observe waves moving through water. They can, however, record and study the energy from the earthquake waves as the waves arrive at a rec ...
Document
... 9.1: Linear Momentum and Its Conservation Our book states that in isolated systems momentum is conserved. Another way to state this is that we can account for all the parts involved in the problem. ΣF ...
... 9.1: Linear Momentum and Its Conservation Our book states that in isolated systems momentum is conserved. Another way to state this is that we can account for all the parts involved in the problem. ΣF ...