fall04-term2-exercise
... the horizontal) and connected to a spring fastened at the top of the plane. The spring has spring constant 50 N/m. The mass is released from rest with the spring initially unstretched. The block moves a distance 25 cm before coming to rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and t ...
... the horizontal) and connected to a spring fastened at the top of the plane. The spring has spring constant 50 N/m. The mass is released from rest with the spring initially unstretched. The block moves a distance 25 cm before coming to rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and t ...
Stacey Carpenter - University of Hawaii
... Cavendish's and von Jolly's experiments to determine G are fun to discuss. Cavendish used a delicate torsion balance to measure the pull between two pieces of lead. von Jolly used a beam balance with a flask of mercury on one side, then rolled a 6 ton ball of lead (about 1 m diameter) under the merc ...
... Cavendish's and von Jolly's experiments to determine G are fun to discuss. Cavendish used a delicate torsion balance to measure the pull between two pieces of lead. von Jolly used a beam balance with a flask of mercury on one side, then rolled a 6 ton ball of lead (about 1 m diameter) under the merc ...
Motion in Two Dimensions
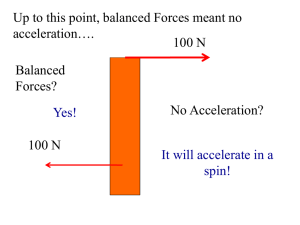
... A net force will cause and object to accelerate in one dimension, but what about rotational acceleration? Would a Force exerted at .5r from the center produce the same rotational acceleration around the center as……. ….. the same force exerted at r from the center? ...
... A net force will cause and object to accelerate in one dimension, but what about rotational acceleration? Would a Force exerted at .5r from the center produce the same rotational acceleration around the center as……. ….. the same force exerted at r from the center? ...
Dynamics-cause of motion
... Why don’t things move on their own on a frictionless surface? Something keeps them from moving That “something” must be universal ...
... Why don’t things move on their own on a frictionless surface? Something keeps them from moving That “something” must be universal ...
The Physics of Renewable Energy
... a force of 3,000 N for 0.005 seconds. What is its final velocity? 1. Use force and mass to find acceleration through the second law. 2. Use the acceleration to find the change in velocity or position. ...
... a force of 3,000 N for 0.005 seconds. What is its final velocity? 1. Use force and mass to find acceleration through the second law. 2. Use the acceleration to find the change in velocity or position. ...
Chapter 5
... vector equation, so we can write it as three component equations. 3. Identify the forces acting on each of the bodies and draw free body diagrams. ...
... vector equation, so we can write it as three component equations. 3. Identify the forces acting on each of the bodies and draw free body diagrams. ...
Monday, Oct. 6, 2008
... People have been very curious about the stars in the sky, making observations for a long time. The data people collected, however, have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly pr ...
... People have been very curious about the stars in the sky, making observations for a long time. The data people collected, however, have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly pr ...
ch6h
... then the weight to support the T = 2.54 seconds weight. 1 rev / 2.54 sec * (60 s / 1 min) sma = mg 23.6 rpm ...
... then the weight to support the T = 2.54 seconds weight. 1 rev / 2.54 sec * (60 s / 1 min) sma = mg 23.6 rpm ...
Unit 2
... see a truck parked next to a tree. A few hours later, you look out the window and that the truck is parked further down the street about 200 yards away from the tree. ...
... see a truck parked next to a tree. A few hours later, you look out the window and that the truck is parked further down the street about 200 yards away from the tree. ...
Gravity, Projectiles, and Satellites
... • If an satellite stays the same distance from the center of its motion, it is said to be undergoing uniform circular motion. • An object in uniform circular motion moves at a constant speed. • However, an object undergoing uniform circular motion is accelerating because it is constantly changing d ...
... • If an satellite stays the same distance from the center of its motion, it is said to be undergoing uniform circular motion. • An object in uniform circular motion moves at a constant speed. • However, an object undergoing uniform circular motion is accelerating because it is constantly changing d ...
AP Physics – The Physics Little AP Test Review Helper
... Galaxy.) Draw a picture. Visualize what is happening. Write down all the things that are given using proper symbols. Ask yourself these questions: What is going on in the problem? What do you have to find out? What kind of problem is it? Is it an electric problem? Is it a projectile motion problem? ...
... Galaxy.) Draw a picture. Visualize what is happening. Write down all the things that are given using proper symbols. Ask yourself these questions: What is going on in the problem? What do you have to find out? What kind of problem is it? Is it an electric problem? Is it a projectile motion problem? ...
Sir Isaac Newton
... Momentum is defined as the quantity of motion of a body. According to Newton, momentum causes an object in motion to remain in motion unless it’s acted on by some other force. So the momentum of a moving object is related to its mass and its velocity. For example, if you were driving a car, and want ...
... Momentum is defined as the quantity of motion of a body. According to Newton, momentum causes an object in motion to remain in motion unless it’s acted on by some other force. So the momentum of a moving object is related to its mass and its velocity. For example, if you were driving a car, and want ...
The ball rolls up the ramp, then back down. Let +x direction be up
... pairs and relations between accelerations (keeping consistent signs). 6. Check # of equations = # of unknowns 7. Solve. 8. Do a reality check. Things to remember: • If a = 0 (v = constant or zero) then2 Fnet = 0. ...
... pairs and relations between accelerations (keeping consistent signs). 6. Check # of equations = # of unknowns 7. Solve. 8. Do a reality check. Things to remember: • If a = 0 (v = constant or zero) then2 Fnet = 0. ...
Microsoft Word - Phy.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 8. Why is the stopping distance of a truck much shorter than for a train going the same speed? The stopping distance for a truck is much shorter than that of a train going the same speed because, even though the rate of slowing down, i.e. acceleration, is the same, the truck’s mass is significantly ...
... 8. Why is the stopping distance of a truck much shorter than for a train going the same speed? The stopping distance for a truck is much shorter than that of a train going the same speed because, even though the rate of slowing down, i.e. acceleration, is the same, the truck’s mass is significantly ...