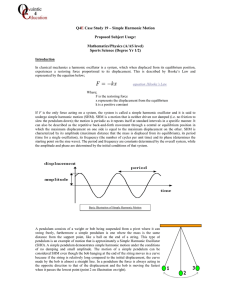
6) Simple Harmonic Motion
... A point on the end of a 440 Hz tuning fork vibrating with SHM moves a total distance of 1 mm from one extreme position to the other. What is the maximum speed and maximum acceleration of this point? We have = 2f = 880 Hz, and A= 0.5 mm = 5 x 10-4 m. v = (A2 - x2), vmax = A = 880 Hz x 5 x 1 ...
... A point on the end of a 440 Hz tuning fork vibrating with SHM moves a total distance of 1 mm from one extreme position to the other. What is the maximum speed and maximum acceleration of this point? We have = 2f = 880 Hz, and A= 0.5 mm = 5 x 10-4 m. v = (A2 - x2), vmax = A = 880 Hz x 5 x 1 ...
Class Exercise - Career Launcher
... Two motor cyclists start a race along a flat race track. Each track has two straight sections connected by a semicircular section, whose radii for track A and track B are 1 km and 2 km respectively. Friction coefficients of A and B are 0.1 and 0.2 respectively. The rules of the race requires that ea ...
... Two motor cyclists start a race along a flat race track. Each track has two straight sections connected by a semicircular section, whose radii for track A and track B are 1 km and 2 km respectively. Friction coefficients of A and B are 0.1 and 0.2 respectively. The rules of the race requires that ea ...
Physics 112/111 Exam Review – Problems
... 70. A 10.0 kg object is accelerated horizontally from rest to a velocity of 11.0 m/s in 5.00 s by a horizontal force. How much work is done on this object assuming the object is on a frictionless surface? (605 J) 71. A student wearing frictionless in-line skates on a horizontal surface is pushed by ...
... 70. A 10.0 kg object is accelerated horizontally from rest to a velocity of 11.0 m/s in 5.00 s by a horizontal force. How much work is done on this object assuming the object is on a frictionless surface? (605 J) 71. A student wearing frictionless in-line skates on a horizontal surface is pushed by ...
South Pasadena · AP Chemistry
... state the two situations where acceleration is zero (standing still & moving at a constant speed in a straight line) and relate these situations to net force (zero net force). 4-Newton’s First Law ...
... state the two situations where acceleration is zero (standing still & moving at a constant speed in a straight line) and relate these situations to net force (zero net force). 4-Newton’s First Law ...
Recitation Ch 4-1
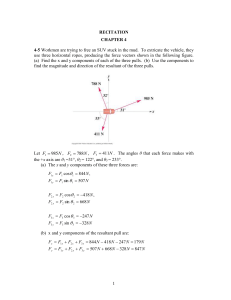
... 4-52. You leave the doctor’s office after your annual checkup and recall that you weighted 683 N in her office. You then get into an elevator that, conveniently, has a scale. Find the magnitude and direction of the elevator’s acceleration if the scale reads (a) 725 N, (b) 595 N. w 683 N is the for ...
... 4-52. You leave the doctor’s office after your annual checkup and recall that you weighted 683 N in her office. You then get into an elevator that, conveniently, has a scale. Find the magnitude and direction of the elevator’s acceleration if the scale reads (a) 725 N, (b) 595 N. w 683 N is the for ...
File
... Rotating objects (like a ball rolling) (these are moving in a circular path even though radius is very small) Orbits of planets Running back cutting up field ...
... Rotating objects (like a ball rolling) (these are moving in a circular path even though radius is very small) Orbits of planets Running back cutting up field ...
Physics
... You are standing in a bus that makes a sharp left turn. Which of the following is true? (A) you lean to the left because of centripetal force (B) you lean to the right because of inertia (C) you lean straight ahead because of the net force is ...
... You are standing in a bus that makes a sharp left turn. Which of the following is true? (A) you lean to the left because of centripetal force (B) you lean to the right because of inertia (C) you lean straight ahead because of the net force is ...