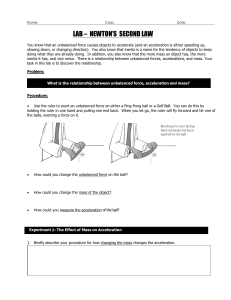
Force and it laws (Basics)
... Section 2: Measuring Waves Any point on a transverse wave moves up and down in a repeating pattern. The shortest time that a point takes to return to the initial position (one vibration) is called period, T. In this example, every vibration is marked with a short pause. ...
... Section 2: Measuring Waves Any point on a transverse wave moves up and down in a repeating pattern. The shortest time that a point takes to return to the initial position (one vibration) is called period, T. In this example, every vibration is marked with a short pause. ...
Ch 7 Impulse and Momentum
... same direction as the average net force. Impulse is very useful when dealing with forces that act over a short time and/or time varying forces—hitting a baseball with a bat, for instance (graph below). ...
... same direction as the average net force. Impulse is very useful when dealing with forces that act over a short time and/or time varying forces—hitting a baseball with a bat, for instance (graph below). ...
1 - Newton`s laws - Ms. Gamm
... Newton’s third law simply says that forces come in pairs. You push on a wall and the wall pushes on you. We call these action/reaction force pairs. One of the skills most people master is walking. We rarely think about the act of walking – you don’t have to concentrate on it, it’s just something tha ...
... Newton’s third law simply says that forces come in pairs. You push on a wall and the wall pushes on you. We call these action/reaction force pairs. One of the skills most people master is walking. We rarely think about the act of walking – you don’t have to concentrate on it, it’s just something tha ...
3, 4, 6, 9, 14 / 5, 8, 13, 18, 23, 27, 32, 52
... acceleration must be zero. On the other hand, if the speed of the object is constant, the object could be accelerating if the direction of the velocity is changing. ...
... acceleration must be zero. On the other hand, if the speed of the object is constant, the object could be accelerating if the direction of the velocity is changing. ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... the initial location to be the origin. Thus the displacement is given by x = at 2 2 or, solving for acceleration: a = 2x t 2 ...
... the initial location to be the origin. Thus the displacement is given by x = at 2 2 or, solving for acceleration: a = 2x t 2 ...
Word version of Episode 302
... We need to get to a point where we can develop the equation F = - kx to a = -2x, where a is the acceleration and is the angular velocity associated with the SHM. To do this, we develop the graphical representation of SHM. Consider first the tethered trolley at its maximum displacement. Its veloci ...
... We need to get to a point where we can develop the equation F = - kx to a = -2x, where a is the acceleration and is the angular velocity associated with the SHM. To do this, we develop the graphical representation of SHM. Consider first the tethered trolley at its maximum displacement. Its veloci ...