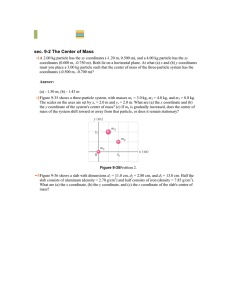
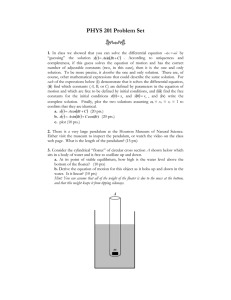
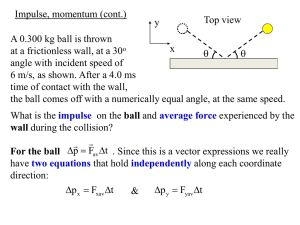
Newton`s Laws
... c. any forces acting on the object are paired, with one force equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction to the other. d. any forces acting on the object are paired, with one perpendicular to the other. e. there is only one force acting on the object, and that force is a frictional force. ANS: a ...
... c. any forces acting on the object are paired, with one force equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction to the other. d. any forces acting on the object are paired, with one perpendicular to the other. e. there is only one force acting on the object, and that force is a frictional force. ANS: a ...
additional assignments
... 38. A ball of mass 175 g is attached to a string and it is twirled around in a horizontal circle of radius 75.0 cm at a frequency of 2.00 Hz. It revolves clockwise as seen from above. (a) Find the magnitude of its linear momentum. (b) Find its angular momentum vector about the center of the circle. ...
... 38. A ball of mass 175 g is attached to a string and it is twirled around in a horizontal circle of radius 75.0 cm at a frequency of 2.00 Hz. It revolves clockwise as seen from above. (a) Find the magnitude of its linear momentum. (b) Find its angular momentum vector about the center of the circle. ...
Ch#8 - KFUPM Faculty List
... Q4: A 200 kg box is pulled along a horizontal surface by an engine. The coefficient of friction between the box and the surface is 0.400. The power the engine delivers to move the box at constant speed of 5.00 m/s is: (Ans: 3920 W) Q5. A 2.0 kg object is connected to one end of an unstretched spring ...
... Q4: A 200 kg box is pulled along a horizontal surface by an engine. The coefficient of friction between the box and the surface is 0.400. The power the engine delivers to move the box at constant speed of 5.00 m/s is: (Ans: 3920 W) Q5. A 2.0 kg object is connected to one end of an unstretched spring ...
s - Nuffield Foundation
... You have used the model F ≤ μR to solve a range of problems involving friction. What factors determine whether you can use F = μR? You have seen that friction can be the force causing a body to move, or it can be opposing motion. Can you think of any other situations in which friction is either caus ...
... You have used the model F ≤ μR to solve a range of problems involving friction. What factors determine whether you can use F = μR? You have seen that friction can be the force causing a body to move, or it can be opposing motion. Can you think of any other situations in which friction is either caus ...