further questions
... (b) Find the change in kinetic energy. (c) Explain why there is a change in kinetic energy. 13. A skater is spinning at 3.0 rad s-1 with her arms and one leg outstretched. The angular speed is increased to 25 rad s-1 when she draws her arms and leg in. (a) Explain why this movement of her arms and l ...
... (b) Find the change in kinetic energy. (c) Explain why there is a change in kinetic energy. 13. A skater is spinning at 3.0 rad s-1 with her arms and one leg outstretched. The angular speed is increased to 25 rad s-1 when she draws her arms and leg in. (a) Explain why this movement of her arms and l ...
The omnipresent impact force formula for a climbing rope
... In the following we will derive the well-known impact force formula as simply as possible and show its importance for more complex fall models and situations. It turns out that the same form of the impact force formula can also describe falls with internal and external friction, with slack rope and ...
... In the following we will derive the well-known impact force formula as simply as possible and show its importance for more complex fall models and situations. It turns out that the same form of the impact force formula can also describe falls with internal and external friction, with slack rope and ...
12.4 Momentum and Impulse
... product of mass and velocity is equivalent to the product of mass and change in velocity. Specifically: J = Δp = mΔv So we're talking about changes in velocity... but what do we call changes in velocity? Of course, acceleration! And what causes acceleration? A force! And does it matter if the force ...
... product of mass and velocity is equivalent to the product of mass and change in velocity. Specifically: J = Δp = mΔv So we're talking about changes in velocity... but what do we call changes in velocity? Of course, acceleration! And what causes acceleration? A force! And does it matter if the force ...
13_InstructorSolutions
... IDENTIFY and SET UP: Calculate x using Eq.(13.13). Use T to calculate ω and x0 to calculate φ . EXECUTE: x = 0 at t = 0 implies that φ = ±π /2 rad Thus x = A cos(ωt ± π /2). T = 2π /ω so ω = 2π /T = 2π /1.20 s = 5.236 rad/s x = (0.600 m)cos([5.236 rad/s][0.480 s] ± π /2)= ∓ 0.353 m. The distance of ...
... IDENTIFY and SET UP: Calculate x using Eq.(13.13). Use T to calculate ω and x0 to calculate φ . EXECUTE: x = 0 at t = 0 implies that φ = ±π /2 rad Thus x = A cos(ωt ± π /2). T = 2π /ω so ω = 2π /T = 2π /1.20 s = 5.236 rad/s x = (0.600 m)cos([5.236 rad/s][0.480 s] ± π /2)= ∓ 0.353 m. The distance of ...
The added mass of a spherical projectile
... When a large, light, spherical ball (such as an inflatable beach ball) is gently tossed into the air, it appears to move in slow motion. It is obvious that the surrounding air has a profound effect on the motion of the ball, reducing its acceleration. One reason for the reduced acceleration is the b ...
... When a large, light, spherical ball (such as an inflatable beach ball) is gently tossed into the air, it appears to move in slow motion. It is obvious that the surrounding air has a profound effect on the motion of the ball, reducing its acceleration. One reason for the reduced acceleration is the b ...
Experiment P25: Kinetic Friction (Smart Pulley)
... For this activity, the Smart Pulley measures the motion of a block sliding on a horizontal surface. The block is connected by a string to a hanging mass. You will vary the mass and surface area of the block, type of material between the block and the surface, and the amount of hanging mass to change ...
... For this activity, the Smart Pulley measures the motion of a block sliding on a horizontal surface. The block is connected by a string to a hanging mass. You will vary the mass and surface area of the block, type of material between the block and the surface, and the amount of hanging mass to change ...
AP Physics B Lesson Plans
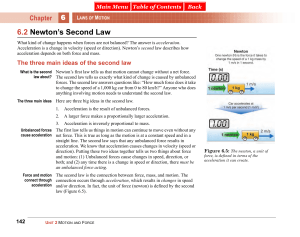
... Define “Projectile Motion” Discuss shadows (on ground and on a screen) of balls thrown across a field. (X- and y-motions are independent.) What’s happening with x (or y), v, and a? Explain equations 3.13 & 3.14 (Discuss symbols and subscripts.) Show problem solving setup: horizontal variables and 1 ...
... Define “Projectile Motion” Discuss shadows (on ground and on a screen) of balls thrown across a field. (X- and y-motions are independent.) What’s happening with x (or y), v, and a? Explain equations 3.13 & 3.14 (Discuss symbols and subscripts.) Show problem solving setup: horizontal variables and 1 ...