Old Exam - KFUPM Faculty List
... T062: Q9. An impulsive force Fx as a function of time (in ms) is shown in the Fig. 3 as applied to an object (m = 5.0 kg) at rest. What will be its final speed? A) 2.0 m/s. Q10. Each object in Fig. 4 has a mass of 2.0 kg. The mass m1 is at rest, m2 has a speed of 3.0 m/s in the direction of +ve x-ax ...
... T062: Q9. An impulsive force Fx as a function of time (in ms) is shown in the Fig. 3 as applied to an object (m = 5.0 kg) at rest. What will be its final speed? A) 2.0 m/s. Q10. Each object in Fig. 4 has a mass of 2.0 kg. The mass m1 is at rest, m2 has a speed of 3.0 m/s in the direction of +ve x-ax ...
Ch# 9 - KFUPM Faculty List
... T062: Q9. An impulsive force Fx as a function of time (in ms) is shown in the Fig. 3 as applied to an object (m = 5.0 kg) at rest. What will be its final speed? A) 2.0 m/s. Q10. Each object in Fig. 4 has a mass of 2.0 kg. The mass m1 is at rest, m2 has a speed of 3.0 m/s in the direction of +ve x-ax ...
... T062: Q9. An impulsive force Fx as a function of time (in ms) is shown in the Fig. 3 as applied to an object (m = 5.0 kg) at rest. What will be its final speed? A) 2.0 m/s. Q10. Each object in Fig. 4 has a mass of 2.0 kg. The mass m1 is at rest, m2 has a speed of 3.0 m/s in the direction of +ve x-ax ...
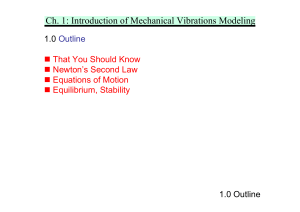
Ch. 1: Introduction of Mechanical Vibrations Modeling
... Apply the Taylor’s series expansion to any nonlinear expressions around xe . Assume small motion, which allows one to ignore the nonlinear terms in the series. In other words, only the constant and linear terms are remained. d 1 d2 ...
... Apply the Taylor’s series expansion to any nonlinear expressions around xe . Assume small motion, which allows one to ignore the nonlinear terms in the series. In other words, only the constant and linear terms are remained. d 1 d2 ...
James M. Hill Physics 122 Problem Set
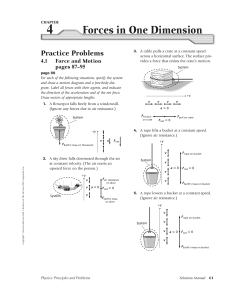
... 12. A 14.7 kg box is pressed up against the wall using an applied force of 600 N. For the box not to fall, calculate the minimum coefficient of static friction necessary between the wall and the box. (0.24) 13. A 22 kg box held up against a wall. The coefficients of friction are µs = 0.39 and µk = 0 ...
... 12. A 14.7 kg box is pressed up against the wall using an applied force of 600 N. For the box not to fall, calculate the minimum coefficient of static friction necessary between the wall and the box. (0.24) 13. A 22 kg box held up against a wall. The coefficients of friction are µs = 0.39 and µk = 0 ...
Rotational Motion
... Once the translational motion of an object is accounted for, all the other motions of the object can best be described in the stationary reference frame of the center of mass. A reasonable image to keep in mind is to imagine following a seagull in a helicopter that tracks its translational motion. I ...
... Once the translational motion of an object is accounted for, all the other motions of the object can best be described in the stationary reference frame of the center of mass. A reasonable image to keep in mind is to imagine following a seagull in a helicopter that tracks its translational motion. I ...
CP7e: Ch. 8 Problems
... is tethered by a wire so that it flies in a circle 30.0 m in radius. The airplane engine provides a net thrust of 0.800 N perpendicular to the tethering wire. (a) Find the torque the net thrust produces about the center of the circle. (b) Find the angular acceleration of the airplane when it is in l ...
... is tethered by a wire so that it flies in a circle 30.0 m in radius. The airplane engine provides a net thrust of 0.800 N perpendicular to the tethering wire. (a) Find the torque the net thrust produces about the center of the circle. (b) Find the angular acceleration of the airplane when it is in l ...
Physics 2010 Summer 2011 REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM
... 25° with the horizontal. The initial speed of the skier is 6.6 m/s. After coasting a distance of 1.9 m up the slope, the speed of the skier is 4.4 m/s. Find the work done by the kinetic frictional force that acts on the ...
... 25° with the horizontal. The initial speed of the skier is 6.6 m/s. After coasting a distance of 1.9 m up the slope, the speed of the skier is 4.4 m/s. Find the work done by the kinetic frictional force that acts on the ...
1. Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on (a) a
... The particle, if unrestrained by the string, will continue to move in a straight line without any change in velocity. The inertia force is internal to the particle. The weight of the particle = mg and the corresponding reaction of the table are balancing each other and do not figure in the net force ...
... The particle, if unrestrained by the string, will continue to move in a straight line without any change in velocity. The inertia force is internal to the particle. The weight of the particle = mg and the corresponding reaction of the table are balancing each other and do not figure in the net force ...
newton`s laws
... This is because static friction can vary, precisely counteracting weaker forces that attemp t to move an object. For example, suppose an object feels a normal force of FN = 100 Nand the coefficient of static friction between it and the surface it's on is 0.5. Then, the maximum force that static fric ...
... This is because static friction can vary, precisely counteracting weaker forces that attemp t to move an object. For example, suppose an object feels a normal force of FN = 100 Nand the coefficient of static friction between it and the surface it's on is 0.5. Then, the maximum force that static fric ...
Chapter 7: KINETIC ENERGY AND WORK
... 27. The velocity of a particle moving along the x axis changes from vi to vf . For which values of vi and vf is the total work done on the particle positive? A. vi = 5 m=s, vf = 2 m=s B. vi = 5 m=s, vf = ¡2 m=s C. vi = ¡5 m=s, vf = ¡2 m=s D. vi = ¡5 m=s, vf = 2 m=s E. vi = 2 m=s, vf = ¡5 m=s ans: E ...
... 27. The velocity of a particle moving along the x axis changes from vi to vf . For which values of vi and vf is the total work done on the particle positive? A. vi = 5 m=s, vf = 2 m=s B. vi = 5 m=s, vf = ¡2 m=s C. vi = ¡5 m=s, vf = ¡2 m=s D. vi = ¡5 m=s, vf = 2 m=s E. vi = 2 m=s, vf = ¡5 m=s ans: E ...
F - Uplift North Hills Prep
... PRACTICE: A 25-kg mass is hanging via three cords as shown. Find the tension in each of the three cords, in Newtons. SOLUTION: Since all of the angles are the same use the formulas we just derived: T3 = mg = 25(10) = 250 n T1 = mg / 1.366 = 25(10) / 1.366 = 180 n T2 = 0.897mg = 0.897(25)(10) = 2 ...
... PRACTICE: A 25-kg mass is hanging via three cords as shown. Find the tension in each of the three cords, in Newtons. SOLUTION: Since all of the angles are the same use the formulas we just derived: T3 = mg = 25(10) = 250 n T1 = mg / 1.366 = 25(10) / 1.366 = 180 n T2 = 0.897mg = 0.897(25)(10) = 2 ...