Classifying Matter and the Periodic Table
... • Between any two objects in the universe there is an attractive force proportional to the masses of the objects and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. ...
... • Between any two objects in the universe there is an attractive force proportional to the masses of the objects and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. ...
friction newton`s third law
... NON-CONSTANT F If F is not constant (eg. as when compressing a spring), then the work done can be found by calculating the area under the force-distance graph, no matter what the shape of the graph. For Example: Force (N) ...
... NON-CONSTANT F If F is not constant (eg. as when compressing a spring), then the work done can be found by calculating the area under the force-distance graph, no matter what the shape of the graph. For Example: Force (N) ...
10.2 Simple Harmonic Motion and the Reference Circle
... Determine the length of a simple pendulum that will swing back and forth in simple harmonic motion with a period of 1.00 s. ...
... Determine the length of a simple pendulum that will swing back and forth in simple harmonic motion with a period of 1.00 s. ...
South Pasadena AP Physics Hooke`s Law Sample Data Name
... We will begin our discussion with an investigation of the forces exerted by a spring on a hanging mass. Consider a spring system with a spring attached to a support. The spring hangs in a relaxed, un-stretched position. If you were to hold the bottom of the spring and pull downward, the spring would ...
... We will begin our discussion with an investigation of the forces exerted by a spring on a hanging mass. Consider a spring system with a spring attached to a support. The spring hangs in a relaxed, un-stretched position. If you were to hold the bottom of the spring and pull downward, the spring would ...
Simple Harmonic Motion
... pendulum is a particular kind of repetitive or periodic motion called simple harmonic motion, or SHM1 . The position of the oscillating object varies sinusoidally with time. Many objects oscillate back and forth. The motion of a child on a swing can be approximated to be sinusoidal and can therefore ...
... pendulum is a particular kind of repetitive or periodic motion called simple harmonic motion, or SHM1 . The position of the oscillating object varies sinusoidally with time. Many objects oscillate back and forth. The motion of a child on a swing can be approximated to be sinusoidal and can therefore ...
Chapter 12 Study guide
... 8) Figure 12-1 shows the motion of three balls. (12.1) The curved paths followed by balls B and C are examples of what type of motion? Each ball started moving at the same time. Ball A was dropped and balls B and C were thrown sideways. Compare the times for each ball to reach the ground. Explain. ...
... 8) Figure 12-1 shows the motion of three balls. (12.1) The curved paths followed by balls B and C are examples of what type of motion? Each ball started moving at the same time. Ball A was dropped and balls B and C were thrown sideways. Compare the times for each ball to reach the ground. Explain. ...
Practice Problems
... A. Plot the velocity as a function of time for an object shot straight up in the air to a maximum height . Use marker values in terms of to label the vertical and horizontal axes. B. There are many planets an other rocks orbiting the sum. Plot the average speed of such an orbiting body as a function ...
... A. Plot the velocity as a function of time for an object shot straight up in the air to a maximum height . Use marker values in terms of to label the vertical and horizontal axes. B. There are many planets an other rocks orbiting the sum. Plot the average speed of such an orbiting body as a function ...
Honors/CP Physics
... Questions 46-47 Two blocks of wood, each of mass 2 kg, are suspended from the ceiling by strings of negligible mass. 40. An object of mass, M, travels along a horizontal air track at a constant speed, v, and collides elastically with an object of identical mass that is initially at rest on the track ...
... Questions 46-47 Two blocks of wood, each of mass 2 kg, are suspended from the ceiling by strings of negligible mass. 40. An object of mass, M, travels along a horizontal air track at a constant speed, v, and collides elastically with an object of identical mass that is initially at rest on the track ...
Formulas velocity(speed) = distance/time a=vf
... 10. How is MASS different from WEIGHT? 11. In what unit is weight measured in science? 12. What does Newton’s 3rd Law state? 13. What are the action and reaction forces that allow a rocket to launch? Use the formulas to calculate the following: 14. What is the average speed of a car that travels 250 ...
... 10. How is MASS different from WEIGHT? 11. In what unit is weight measured in science? 12. What does Newton’s 3rd Law state? 13. What are the action and reaction forces that allow a rocket to launch? Use the formulas to calculate the following: 14. What is the average speed of a car that travels 250 ...
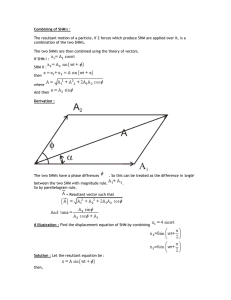
Combining of SHM`s
... so motion is a SHM. At Mean position Potential energy = minimum and Force = 0 So Mean position. Ans. Question - 2. Two particle move parellel to x axis about origin with same amplitude and frequency. At a certain instant, they both are found at a distance A/n from origin (y>1) and they are on opposi ...
... so motion is a SHM. At Mean position Potential energy = minimum and Force = 0 So Mean position. Ans. Question - 2. Two particle move parellel to x axis about origin with same amplitude and frequency. At a certain instant, they both are found at a distance A/n from origin (y>1) and they are on opposi ...