Motion - RowesPhysicalScience
... Change of Velocity Delta V = gravity(g) x time(t); where Acceleration of gravity = 9.8 m/s2 and time it takes to fall. 5. What is a force? Push, pull, gravity, friction, balanced and unbalanced forces, net force, vector You can change an objects motion by pushing it, pulling it, nudging it, or by an ...
... Change of Velocity Delta V = gravity(g) x time(t); where Acceleration of gravity = 9.8 m/s2 and time it takes to fall. 5. What is a force? Push, pull, gravity, friction, balanced and unbalanced forces, net force, vector You can change an objects motion by pushing it, pulling it, nudging it, or by an ...
T3F2008
... II. The vector sum of all external torques that act on the body, measured about any possible point, must also be zero. III. The linear momentum of the body must be zero. Which of the above conditions must be met for equilibrium? a. I b. II c. I and II d. II and III e. I, II, and III ...
... II. The vector sum of all external torques that act on the body, measured about any possible point, must also be zero. III. The linear momentum of the body must be zero. Which of the above conditions must be met for equilibrium? a. I b. II c. I and II d. II and III e. I, II, and III ...
Solution - Georgia Tech
... 4. [25] A ball of mass m suspended on the end of a wire is released from height h and colides elastically with a block of mass 2m at rest on a frictionless surface. What is the maximum height that the ball reaches after the collision? Solution: Use V as the block’s velocity, and m, vi , vf as the ba ...
... 4. [25] A ball of mass m suspended on the end of a wire is released from height h and colides elastically with a block of mass 2m at rest on a frictionless surface. What is the maximum height that the ball reaches after the collision? Solution: Use V as the block’s velocity, and m, vi , vf as the ba ...
in m/s - Wildern VLE
... are no external forces have an effect). Example question: Two cars are racing around Teville Gate. Car A collides with the back of car B and the cars stick together. What speed do they move at after the collision? Speed = 50m/s Mass = 1000kg ...
... are no external forces have an effect). Example question: Two cars are racing around Teville Gate. Car A collides with the back of car B and the cars stick together. What speed do they move at after the collision? Speed = 50m/s Mass = 1000kg ...
Problems
... 1.50 m/s. The pulling force is 100 N parallel to the incline, which makes an angle of 20.0° with the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.400, and the crate is pulled 5.00 m. (a) How much work is done by the gravitational force on the crate? (b) Determine the increase in internal energ ...
... 1.50 m/s. The pulling force is 100 N parallel to the incline, which makes an angle of 20.0° with the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.400, and the crate is pulled 5.00 m. (a) How much work is done by the gravitational force on the crate? (b) Determine the increase in internal energ ...
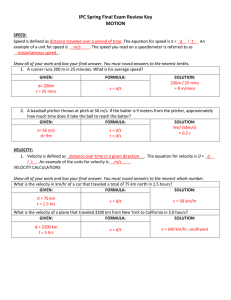
IPC Spring Final Exam Review Key MOTION
... Newton’s 1st law is also referred to as the law of inertia. According to this law, an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force. Mass is related to inertia. The more of it an object has, the more inertia it has. In the ima ...
... Newton’s 1st law is also referred to as the law of inertia. According to this law, an object at rest will remain at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion unless acted on by an unbalanced force. Mass is related to inertia. The more of it an object has, the more inertia it has. In the ima ...
Harmonic notes
... horizontally on a smooth surface. You give the block an initial displacement of 7.00 cm. What is (a) the maximum force and (b) the maximum acceleration acting on the block? ...
... horizontally on a smooth surface. You give the block an initial displacement of 7.00 cm. What is (a) the maximum force and (b) the maximum acceleration acting on the block? ...
Final Exam Spring 2001 Phy 231 Form 1
... --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Note on significant figures: If your answer is close to one of the choices offered, within the significant figure specified for the latter (with possible round-off), it should be considered as the ...
... --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Note on significant figures: If your answer is close to one of the choices offered, within the significant figure specified for the latter (with possible round-off), it should be considered as the ...
Title: Springs, Spring Constants, and Changes in Potential Energy
... between kinetic and potential energy. Suppose a spring is hung vertically with a mass attached to its lower end. The force exerted on the spring by the mass will cause the spring to stretch and the mass will come to rest at its equilibrium position. If the mass is lifted a few centimeters above its ...
... between kinetic and potential energy. Suppose a spring is hung vertically with a mass attached to its lower end. The force exerted on the spring by the mass will cause the spring to stretch and the mass will come to rest at its equilibrium position. If the mass is lifted a few centimeters above its ...