File
... Q 21 A block is resting on a piston which is moving vertically with simple harmonic motion of period 1.0s. At what amplitude of motion will the block and piston separate? What is the maximum velocity of the piston at this amplitude? Marks (3) View Answer Q 22 A simple harmonic motion is represented ...
... Q 21 A block is resting on a piston which is moving vertically with simple harmonic motion of period 1.0s. At what amplitude of motion will the block and piston separate? What is the maximum velocity of the piston at this amplitude? Marks (3) View Answer Q 22 A simple harmonic motion is represented ...
Test Problems for Oscillatory motion (L9). Make sure you
... 31. Simple harmonic oscillations can be modeled by the projection of circular motion at constant angular velocity onto a diameter of the circle. When this is done, the analog along the diameter of the acceleration of the particle executing simple harmonic motion is a. the displacement from the cente ...
... 31. Simple harmonic oscillations can be modeled by the projection of circular motion at constant angular velocity onto a diameter of the circle. When this is done, the analog along the diameter of the acceleration of the particle executing simple harmonic motion is a. the displacement from the cente ...
Document
... If a force F is applied to an object of mass m it can accelerate it and increase its speed v and kinetic energy K. Similarly F can decelerate m and decrease its kinetic energy. We account for these changes in K by saying that F has transferred energy W to or from the object. If energy it transferred ...
... If a force F is applied to an object of mass m it can accelerate it and increase its speed v and kinetic energy K. Similarly F can decelerate m and decrease its kinetic energy. We account for these changes in K by saying that F has transferred energy W to or from the object. If energy it transferred ...
Lecture 10
... stop pushing an object, does it stop moving? Only if there is friction! In the absence of any net external force, an object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line, or remain at rest. This is Newton’s 1st Law, and it is also known as the Law of Inertia. ...
... stop pushing an object, does it stop moving? Only if there is friction! In the absence of any net external force, an object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line, or remain at rest. This is Newton’s 1st Law, and it is also known as the Law of Inertia. ...
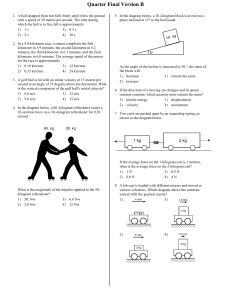
Quarter Final Version B
... 19. A train sounds a whistle of constant frequency as it leaves the train station. Compared to the sound emitted by the whistle, the sound that the passengers standing on the platform hear has a frequency that is 1) higher, because the sound-wave fronts reach the platform at a frequency higher than ...
... 19. A train sounds a whistle of constant frequency as it leaves the train station. Compared to the sound emitted by the whistle, the sound that the passengers standing on the platform hear has a frequency that is 1) higher, because the sound-wave fronts reach the platform at a frequency higher than ...
2. Work, Energy and Conservation of Energy
... To clean a floor, a cleaner pushes on a mop handle with a force of 50.0 N. (a) If the mop handle is at an angle of 55° above the horizontal, how much work is required to push the mop 0.50 m? (b) If the angle the mop handle makes with the horizontal is increased to 65°, does the work done by the clea ...
... To clean a floor, a cleaner pushes on a mop handle with a force of 50.0 N. (a) If the mop handle is at an angle of 55° above the horizontal, how much work is required to push the mop 0.50 m? (b) If the angle the mop handle makes with the horizontal is increased to 65°, does the work done by the clea ...
Study Guide for Physics Final Exam—1st semester
... 26. Suppose a car is moving in a straight line and steadily increases its speed. It moves from 45 km/h to 50 km/h in the first second and from 50 km/h to 55 km/h in the next second. What is the car’s acceleration? ...
... 26. Suppose a car is moving in a straight line and steadily increases its speed. It moves from 45 km/h to 50 km/h in the first second and from 50 km/h to 55 km/h in the next second. What is the car’s acceleration? ...
The Galaxy Education System S. N. Kansagra School Sub: Physics
... 15) Prove that F = ma. State the condition when it holds true. 16) Define (i) balanced forces (ii) unbalanced forces. 17) Name the SI unit of (i) linear momentum (ii) rate of change of momentum. 18) State the relationship between Force, mass and acceleration. Draw graphs showing the relationship bet ...
... 15) Prove that F = ma. State the condition when it holds true. 16) Define (i) balanced forces (ii) unbalanced forces. 17) Name the SI unit of (i) linear momentum (ii) rate of change of momentum. 18) State the relationship between Force, mass and acceleration. Draw graphs showing the relationship bet ...
Lecture17-10
... oscillating and in minimum time; an overdamped system will also not oscillate but is damped so heavily that it takes longer to reach equilibrium. ...
... oscillating and in minimum time; an overdamped system will also not oscillate but is damped so heavily that it takes longer to reach equilibrium. ...