1 Plate Tectonics Review w
... Concept caused revelation. Yes, revelation. Earth’s many features were all caused by the same process. Subduction Zone same process as Andes ...
... Concept caused revelation. Yes, revelation. Earth’s many features were all caused by the same process. Subduction Zone same process as Andes ...
here - GeoCoops
... temperature and pressure at depth cause the fluids to “sweat” from the sinking plate. The fluids sweated out percolate upward, helping to locally melt the overlying solid mantle above the subducting plate to form pockets of liquid rock (magma). 13. The newly generated molten mantle (magma) is less d ...
... temperature and pressure at depth cause the fluids to “sweat” from the sinking plate. The fluids sweated out percolate upward, helping to locally melt the overlying solid mantle above the subducting plate to form pockets of liquid rock (magma). 13. The newly generated molten mantle (magma) is less d ...
Alkaline rocks
... • Contain feldspathoids, alkali amphibole, alkali pyroxene and many unusual minerals • High concentrations of incompatible trace elements (Zr, Nb, Rb, Ti, P, etc.) ...
... • Contain feldspathoids, alkali amphibole, alkali pyroxene and many unusual minerals • High concentrations of incompatible trace elements (Zr, Nb, Rb, Ti, P, etc.) ...
Unit Three Review Guide: Plate Tectonics
... 1. What is a mid-ocean ridge and what is produced here? 2. How does the age of oceanic crust change the further it gets from the mid-ocean ridge? 3. Explain the relationship between normal polarity, reversed polarity, magnetic reversal, and the evidence for seafloor spreading. 4. What theory does ‘s ...
... 1. What is a mid-ocean ridge and what is produced here? 2. How does the age of oceanic crust change the further it gets from the mid-ocean ridge? 3. Explain the relationship between normal polarity, reversed polarity, magnetic reversal, and the evidence for seafloor spreading. 4. What theory does ‘s ...
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonic
... earthquakes occur within trench/where descending plate interacts with lithosphere 2. Deep focused earthquakes occur toward mainland/ when oceanic lithosphere plunges into mantle ...
... earthquakes occur within trench/where descending plate interacts with lithosphere 2. Deep focused earthquakes occur toward mainland/ when oceanic lithosphere plunges into mantle ...
Tectonic Impacts #3
... Summary of features: Rarely volcanism, shallow focus earthquakes, opposite and parallel movement on either side of the boundary, builds elastic potential energy until it releases in seismic waves Example – San Andreas fault ...
... Summary of features: Rarely volcanism, shallow focus earthquakes, opposite and parallel movement on either side of the boundary, builds elastic potential energy until it releases in seismic waves Example – San Andreas fault ...
Powerpoint
... Plate Tectonic Theory Earth’s outer layer is comprised of several large, rigid but mobile chunks called tectonic plates There are 12 tectonic plates that make up the crust Divided into: Continental plates Oceanic plates ...
... Plate Tectonic Theory Earth’s outer layer is comprised of several large, rigid but mobile chunks called tectonic plates There are 12 tectonic plates that make up the crust Divided into: Continental plates Oceanic plates ...
Deep Earth Volatiles Cycle: processes, fluxes and deep mantle
... On the other hand, the distribution of volatiles within the Earth’s mantle – Figure 1 – Numerical modelling of slab hydration at the trench the largest volatiles reservoir – has outer-‐rise due to bending-‐related faulting and subsequent ...
... On the other hand, the distribution of volatiles within the Earth’s mantle – Figure 1 – Numerical modelling of slab hydration at the trench the largest volatiles reservoir – has outer-‐rise due to bending-‐related faulting and subsequent ...
Grade 6 Chapter 1 Study Guide
... Know that scientist use sonar devices that bounce sound waves off underwater objects to map the bottom of the ocean. Know that Henry Hess proposed the idea of sea-floor spreading to provide a mechanism to Alfred Wegner’s continental drift hypothesis. Understand that in the sea-floor spreading ...
... Know that scientist use sonar devices that bounce sound waves off underwater objects to map the bottom of the ocean. Know that Henry Hess proposed the idea of sea-floor spreading to provide a mechanism to Alfred Wegner’s continental drift hypothesis. Understand that in the sea-floor spreading ...
Earth System - Rock Cycle
... b. They're metamorphic rocks c. They're igneous rocks d. They're formed by erosion 4. What is the difference between magma and lava? a. Magma is very hot, lava is cool b. Magma is molten rock within the earth; lava is molten rock on the earth's surface c. Magma is molten rock on the earth's surface; ...
... b. They're metamorphic rocks c. They're igneous rocks d. They're formed by erosion 4. What is the difference between magma and lava? a. Magma is very hot, lava is cool b. Magma is molten rock within the earth; lava is molten rock on the earth's surface c. Magma is molten rock on the earth's surface; ...
Congestion in the Earth`s Mantle Mineralogists explain in the
... changing. In the space of a year Africa and America are drifting apart at the back of the Middle Atlantic for some centimeters while the floor of the Pacific Ocean is subducted underneath the South American Continent. "In 100 million years' time Africa will be pulled apart and North Australia will b ...
... changing. In the space of a year Africa and America are drifting apart at the back of the Middle Atlantic for some centimeters while the floor of the Pacific Ocean is subducted underneath the South American Continent. "In 100 million years' time Africa will be pulled apart and North Australia will b ...
Plate Tectonics
... During the 20th Century, scientists developed Wegener’s ideas and came up with the theory of Plate Tectonics. The theory of plate tectonics suggested that the crust of the Earth is split up into seven large plates (or ‘slabs’ of rock) and a few smaller ones, all of which are able to slowly move arou ...
... During the 20th Century, scientists developed Wegener’s ideas and came up with the theory of Plate Tectonics. The theory of plate tectonics suggested that the crust of the Earth is split up into seven large plates (or ‘slabs’ of rock) and a few smaller ones, all of which are able to slowly move arou ...
controls (practical/laboratory) work, abstract
... 2. The grain size of igneous rocks does not depend on their occurrence. 3. The intrusive rocks generally cool more slowly than the extrusive rocks. 4. Extrusive igneous rocks have been formed from lava flows 5. Basalt is not the principal rock type of the ocean floor. Activity 3. Match the beginning ...
... 2. The grain size of igneous rocks does not depend on their occurrence. 3. The intrusive rocks generally cool more slowly than the extrusive rocks. 4. Extrusive igneous rocks have been formed from lava flows 5. Basalt is not the principal rock type of the ocean floor. Activity 3. Match the beginning ...
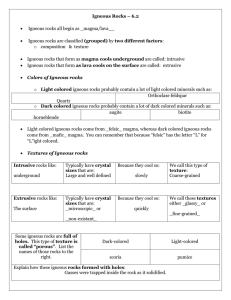
Igneous Rocks – 6.2
... Igneous rocks that form as magma cools underground are called: intrusive Igneous rocks that form as lava cools on the surface are called: extrusive ...
... Igneous rocks that form as magma cools underground are called: intrusive Igneous rocks that form as lava cools on the surface are called: extrusive ...
Different Kinds of Volcanoes
... Hotspots • "Hotspots" is the name given to volcanic provinces postulated to be formed by mantle plumes. These are postulated to comprise columns of hot material that rise from the core-mantle boundary. They are suggested to be hot, causing large-volume melting, and to be fixed in space. Because the ...
... Hotspots • "Hotspots" is the name given to volcanic provinces postulated to be formed by mantle plumes. These are postulated to comprise columns of hot material that rise from the core-mantle boundary. They are suggested to be hot, causing large-volume melting, and to be fixed in space. Because the ...
Chapter 8 Volcanoes Section 1, Why Volcanoes Form
... • When magma reaches the surface, it erupts to form a volcano. • Volcanoes can form at divergent boundaries, convergent boundaries, or hot spots. ...
... • When magma reaches the surface, it erupts to form a volcano. • Volcanoes can form at divergent boundaries, convergent boundaries, or hot spots. ...
Geosphere PowerPoint
... Parts of the Earth's crust slowly drift atop a liquid core. This theory is supported by fossil records. ...
... Parts of the Earth's crust slowly drift atop a liquid core. This theory is supported by fossil records. ...
Physical Geography Chapter 9
... Overall, volcanoes are not the death and destruction machines that we often make them out to be: (1) volcanoes frequently give us warning of their actions (2) many volcanoes are located in rural uninhabited places (3) if the eruption produces lava flows rather than poisonous gas or flaming projecti ...
... Overall, volcanoes are not the death and destruction machines that we often make them out to be: (1) volcanoes frequently give us warning of their actions (2) many volcanoes are located in rural uninhabited places (3) if the eruption produces lava flows rather than poisonous gas or flaming projecti ...
SuperScience TE Template
... Scientists measure an earthquake’s strength using a unit of measure called magnitude. Each one-unit increase in magnitude means that the earthquake is 10 times as powerful as the number below it. Earlier this year, a major earthquake struck Haiti. This quake had a magnitude of 7. Earthquakes measuri ...
... Scientists measure an earthquake’s strength using a unit of measure called magnitude. Each one-unit increase in magnitude means that the earthquake is 10 times as powerful as the number below it. Earlier this year, a major earthquake struck Haiti. This quake had a magnitude of 7. Earthquakes measuri ...
Plate Tectonics - dhsearthandspacescience
... What is a mobilist? What is an antimobilist? • People (geologists) that believe the features of the Earth is a result of massive global contraction and expansion are called ANTIMOBILISTS • People (geologists) that believe the Earth is made of moving pieces are MOBILISTS ...
... What is a mobilist? What is an antimobilist? • People (geologists) that believe the features of the Earth is a result of massive global contraction and expansion are called ANTIMOBILISTS • People (geologists) that believe the Earth is made of moving pieces are MOBILISTS ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.