Plate Tectonics, Layers, and Continental Drift Mini
... D. Multiple Choice- Choose the best answer that completes the statement or answers the question. 19. The plate boundary where two plates collide is called a. divergent b. convergent c. transform 20. If a diverging boundary took place on land what would form over time? a. mountain b. seafloor spreadi ...
... D. Multiple Choice- Choose the best answer that completes the statement or answers the question. 19. The plate boundary where two plates collide is called a. divergent b. convergent c. transform 20. If a diverging boundary took place on land what would form over time? a. mountain b. seafloor spreadi ...
No Slide Title
... Large igneous intrusion, similar to batholith, but area is less than 100 km2. ...
... Large igneous intrusion, similar to batholith, but area is less than 100 km2. ...
key
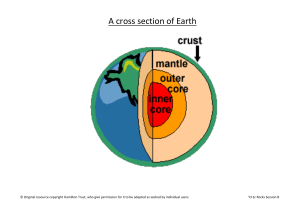
... 1. 200 million years ago, all the continents were one called Pangaea. Evidence is continents fitting together, fossils of same organism on two different continents, similar mountain ranges on diff. continents. 2. Seismic waves tell us that the inside of the Earth is made up of layers. 3. Continental ...
... 1. 200 million years ago, all the continents were one called Pangaea. Evidence is continents fitting together, fossils of same organism on two different continents, similar mountain ranges on diff. continents. 2. Seismic waves tell us that the inside of the Earth is made up of layers. 3. Continental ...
A combination of related parts that interact in an
... The part of the mantle that lies below the lithosphere; it behaves plastically and flows slowly. ...
... The part of the mantle that lies below the lithosphere; it behaves plastically and flows slowly. ...
Layers of Earth Notes On-Level
... LAYERS OF THE EARTH • GEOLOGY – STUDY OF PLANET EARTH • INCLUDING SURFACE & INTERIOR • GEOLOGISTS – A PERSON WHO STUDIES INSIDE THE EARTH, TEMP, PRESSURE, HOW THEY AFFECT THE SURFACE OF THE EARTH. ...
... LAYERS OF THE EARTH • GEOLOGY – STUDY OF PLANET EARTH • INCLUDING SURFACE & INTERIOR • GEOLOGISTS – A PERSON WHO STUDIES INSIDE THE EARTH, TEMP, PRESSURE, HOW THEY AFFECT THE SURFACE OF THE EARTH. ...
Plate Tectonics Review Answers
... 25. What happens when two oceanic plates separate? New seafloor will be added. 26. What happens when an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate? The more dense oceanic plate will subduct under the less dense continental plate. Volcanoes or deep ocean trenches can form at this type of boundar ...
... 25. What happens when two oceanic plates separate? New seafloor will be added. 26. What happens when an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate? The more dense oceanic plate will subduct under the less dense continental plate. Volcanoes or deep ocean trenches can form at this type of boundar ...
Opposition to Continental Drift
... This is a major departure from Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis, which proposed that the continents move through the ocean floor, not with it. ...
... This is a major departure from Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis, which proposed that the continents move through the ocean floor, not with it. ...
The Layers of the Earth
... Earth. The Mantle is made up of minerals rich in the elements iron, magnesium, silica, and oxygen. The Mantle makes up approximately ~85% of the Earth's volume. It is seperated from the crust by a sharp change to higher density and seismic velocity, and more mafic composition. The Earth's outer laye ...
... Earth. The Mantle is made up of minerals rich in the elements iron, magnesium, silica, and oxygen. The Mantle makes up approximately ~85% of the Earth's volume. It is seperated from the crust by a sharp change to higher density and seismic velocity, and more mafic composition. The Earth's outer laye ...
revision-tectonic-landscapes-gcse
... RECAP: Understanding hotspots Some volcanoes do not occur on plate boundaries. These volcanoes are formed over hotspots. These are fixed points in the mantle that generate intense heat. Small, long lasting, exceptionally hot areas of magma exist under the Earth's surface which in turn sustains long ...
... RECAP: Understanding hotspots Some volcanoes do not occur on plate boundaries. These volcanoes are formed over hotspots. These are fixed points in the mantle that generate intense heat. Small, long lasting, exceptionally hot areas of magma exist under the Earth's surface which in turn sustains long ...
Assessing the nature of crust in the central Red Sea using potential
... The Red Sea is considered an important example of a rifted continental shield proceeding to a seafloor spreading stage of development, and the transition of crustal types there from stretched continental to oceanic should mark the onset of significant mantle melting. However, whether the crust in th ...
... The Red Sea is considered an important example of a rifted continental shield proceeding to a seafloor spreading stage of development, and the transition of crustal types there from stretched continental to oceanic should mark the onset of significant mantle melting. However, whether the crust in th ...
Earth Structure
... (asthenes=____): The top hot layer that is partially melted slowly flowing below the lithosphere extending to a depth of 350-650km ...
... (asthenes=____): The top hot layer that is partially melted slowly flowing below the lithosphere extending to a depth of 350-650km ...
types of plate boundaries 2014-2015
... plate motion in which cool, dense oceanic crust sinks into the mantle and “pulls” the trailing lithosphere along. It is thought to be the primary downward arm of convective flow in the mantle. • Ridge-push causes oceanic lithosphere to slide down the sides of the oceanic ridge under the pull of grav ...
... plate motion in which cool, dense oceanic crust sinks into the mantle and “pulls” the trailing lithosphere along. It is thought to be the primary downward arm of convective flow in the mantle. • Ridge-push causes oceanic lithosphere to slide down the sides of the oceanic ridge under the pull of grav ...
1 Plate Tectonics Review Homework w
... metamorphic rocks. (d) The shields and platforms are tectonically less active than the coastal ...
... metamorphic rocks. (d) The shields and platforms are tectonically less active than the coastal ...
Rock Types - Volcanoes Alive!
... Igneous rock is formed directly from magma. There are two types of igneous rocks, intrusive and extrusive. Intrusive igneous rocks are formed when magma is trapped within Earth. granite pumice obsidian The magma cools slowly because of the surrounding rock. These rocks are coarse grained. An example ...
... Igneous rock is formed directly from magma. There are two types of igneous rocks, intrusive and extrusive. Intrusive igneous rocks are formed when magma is trapped within Earth. granite pumice obsidian The magma cools slowly because of the surrounding rock. These rocks are coarse grained. An example ...
doc Igneous Rocks Notes
... are typically about 1/20th of their widths. The lower slopes are often gentle (3-5 degrees), but the middle slopes become steeper (10-12 degrees) and then flatten at the summit. This gives shield volcanoes a flank morphology that is convex in an upward direction. Their overall broad shapes result fr ...
... are typically about 1/20th of their widths. The lower slopes are often gentle (3-5 degrees), but the middle slopes become steeper (10-12 degrees) and then flatten at the summit. This gives shield volcanoes a flank morphology that is convex in an upward direction. Their overall broad shapes result fr ...
6th Grade Vocabulary 6, test on Wednesday, 1/11/17
... asthenosphere - the upper portion of the mantle below the lithosphere possessing the property of plasticity continental crust - the relatively thick part of the earth's crust that forms the large landmasses; it is generally older, more complex, and less dense than oceanic crust convection - the tran ...
... asthenosphere - the upper portion of the mantle below the lithosphere possessing the property of plasticity continental crust - the relatively thick part of the earth's crust that forms the large landmasses; it is generally older, more complex, and less dense than oceanic crust convection - the tran ...
Dynamic Ocean Floor
... • Two plates move away from one another. • This is a zone of weakness. • As two plates move apart at the mid-ocean ridges, magma from the mantle up wells through a crack in the oceanic crust and cooled by the sea creating new ocean floor. • Energy is released in the form of earthquakes. • Shallow fo ...
... • Two plates move away from one another. • This is a zone of weakness. • As two plates move apart at the mid-ocean ridges, magma from the mantle up wells through a crack in the oceanic crust and cooled by the sea creating new ocean floor. • Energy is released in the form of earthquakes. • Shallow fo ...
document
... • Earth’s continents were once joined in a single large landmass (Pangaea) that broke apart and drifted to their current locations (and are still moving) ...
... • Earth’s continents were once joined in a single large landmass (Pangaea) that broke apart and drifted to their current locations (and are still moving) ...
Geology Final Exam Review 1st Semester What drives Earth`s rock
... Geology Final Exam Review 1st Semester 1. What drives Earth’s rock cycle? 2. What are the textures of igneous rocks? a. Describe what causes the different textures. 3. Tell the differences between gabbro and granite. 4. List the 3 main compositional types of igneous rocks. a. Describe the mineral di ...
... Geology Final Exam Review 1st Semester 1. What drives Earth’s rock cycle? 2. What are the textures of igneous rocks? a. Describe what causes the different textures. 3. Tell the differences between gabbro and granite. 4. List the 3 main compositional types of igneous rocks. a. Describe the mineral di ...
1-1 Plate Tectonics
... Tension can cause rock layers to break or fault. Normal Fault – one block of rock drops down lower than the other. ...
... Tension can cause rock layers to break or fault. Normal Fault – one block of rock drops down lower than the other. ...
Quiz Maker - Geneva 304
... floor. This volcanic rock was found to be much younger than continental rock. Harry Hess reasoned that new volcanic mountains were being formed as the sea floor was moving away from each side of the midocean ridge. What is this movement called? (0.25 pts) Paleomagnetism is another piece of evidence ...
... floor. This volcanic rock was found to be much younger than continental rock. Harry Hess reasoned that new volcanic mountains were being formed as the sea floor was moving away from each side of the midocean ridge. What is this movement called? (0.25 pts) Paleomagnetism is another piece of evidence ...
File
... a. intrusive igneous rock b. sedimentary rock c. extrusive igneous rock d. fissures 13. Intrusive igneous rock usually has what kind of texture? a. coarse-grained b. medium-grained c. small-grained d. fine-grained 14. What is a sheetlike intrusion that is oriented parallel to previous rock layers ca ...
... a. intrusive igneous rock b. sedimentary rock c. extrusive igneous rock d. fissures 13. Intrusive igneous rock usually has what kind of texture? a. coarse-grained b. medium-grained c. small-grained d. fine-grained 14. What is a sheetlike intrusion that is oriented parallel to previous rock layers ca ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.