Document
... 37. What is produced from magma formed from melted mantle rock? _______________________________________________________________ 38. An example of a feature that formed when two plates made of oceanic lithosphere collided is ______________________. 39. What causes earthquakes at transform boundaries? ...
... 37. What is produced from magma formed from melted mantle rock? _______________________________________________________________ 38. An example of a feature that formed when two plates made of oceanic lithosphere collided is ______________________. 39. What causes earthquakes at transform boundaries? ...
Land Unit: Plate Tectonics - Mrs. Tes de Luna`s Science Class
... What is the Theory of Plate Tectonics? -Pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in slow, constant motion -Movement is caused by convection currents in the mantle. -Plates move in three types of behavior -Tectonic plates are made of continental and oceanic crust ...
... What is the Theory of Plate Tectonics? -Pieces of Earth’s lithosphere are in slow, constant motion -Movement is caused by convection currents in the mantle. -Plates move in three types of behavior -Tectonic plates are made of continental and oceanic crust ...
Name - Duncanville ISD
... Alfred Wegner, Harry Hess & Robert Dietz, or Fred Vine & Drummond Matthews How has this person (or these persons) contributed to the theory of plate tectonics? ...
... Alfred Wegner, Harry Hess & Robert Dietz, or Fred Vine & Drummond Matthews How has this person (or these persons) contributed to the theory of plate tectonics? ...
journey 05 - Auburn High School
... The study of seismic waves allows scientists to “see” inside the earth. Scientists have discovered that seismic waves • refract • reflect • change velocity • and become absorbed by various parts of the Earth’s interior ...
... The study of seismic waves allows scientists to “see” inside the earth. Scientists have discovered that seismic waves • refract • reflect • change velocity • and become absorbed by various parts of the Earth’s interior ...
Slideshow
... The structure of the earth •The crust - the outer layer of the earth is relatively thin •The crust is not one single piece of skin, like that of an apple. •Instead, it is split into plates of varying size and at plate margins it is liable to move. •This is because the slabs of crust float on the se ...
... The structure of the earth •The crust - the outer layer of the earth is relatively thin •The crust is not one single piece of skin, like that of an apple. •Instead, it is split into plates of varying size and at plate margins it is liable to move. •This is because the slabs of crust float on the se ...
Notes_-_Earths_Layers
... Layers of the Earth Crust Outer layer; covers the whole earth; varies in thickness from 5 to 60 Km. Together with the upper mantle, is part of a zone called the lithosphere. There are 2 kinds of crust: continental crust and oceanic crust. Continental Crust Exists under continents Average thickne ...
... Layers of the Earth Crust Outer layer; covers the whole earth; varies in thickness from 5 to 60 Km. Together with the upper mantle, is part of a zone called the lithosphere. There are 2 kinds of crust: continental crust and oceanic crust. Continental Crust Exists under continents Average thickne ...
Practice 1 - WordPress.com
... 3two kinds of crust, a lower and denser oceanic crust and an upper, lighter continental 4crust found over only about 40 percent of the Earth's surface. The rocks of the crust are 5of very different ages. Some continental rocks are over 3,000 million years old, while 6those of the ocean flow are less ...
... 3two kinds of crust, a lower and denser oceanic crust and an upper, lighter continental 4crust found over only about 40 percent of the Earth's surface. The rocks of the crust are 5of very different ages. Some continental rocks are over 3,000 million years old, while 6those of the ocean flow are less ...
Minerals • Mineral is a substance that is: • Solid • Formed in Nature
... These plates are constantly moving because of convection currents Convection currents form in the mantle where hot dense magma rises, spreads out, cools down and then sinks These currents causes the plates to collide, separate or slide past each other There are 3 types of plate boundaries o ...
... These plates are constantly moving because of convection currents Convection currents form in the mantle where hot dense magma rises, spreads out, cools down and then sinks These currents causes the plates to collide, separate or slide past each other There are 3 types of plate boundaries o ...
Bundle 1 - Humble ISD
... plate boundaries. “Ring of Fire” is the name given to an area along the border of the Pacific Plate with a high concentration of volcanoes. Earthquakes happen randomly across the earth’s surface. Fact: As with volcanoes, most of the world’s seismic activity is associated with tectonic plate bounda ...
... plate boundaries. “Ring of Fire” is the name given to an area along the border of the Pacific Plate with a high concentration of volcanoes. Earthquakes happen randomly across the earth’s surface. Fact: As with volcanoes, most of the world’s seismic activity is associated with tectonic plate bounda ...
CHANGING EARTH NOTES
... - Underwater earthquakes are one cause of ________________. - Earthquake Waves are used to infer what the Earth’s ______________ are composed of. - P waves are primary waves and S waves are secondary waves - both produced during earthquakes. ___ __________ travel at slower speed. - Earthquake Safety ...
... - Underwater earthquakes are one cause of ________________. - Earthquake Waves are used to infer what the Earth’s ______________ are composed of. - P waves are primary waves and S waves are secondary waves - both produced during earthquakes. ___ __________ travel at slower speed. - Earthquake Safety ...
Directed Reading A
... POSSIBLE CAUSES OF TECTONIC PLATE MOTION ______11. When rock is heated, it becomes less dense and tends to a. rise. b. sink. c. move sideways. d. erupt. ______12. When rock cools, it becomes more dense and tends to a. rise to the surface. b. sink below the surface. c. move sideways. d. push against ...
... POSSIBLE CAUSES OF TECTONIC PLATE MOTION ______11. When rock is heated, it becomes less dense and tends to a. rise. b. sink. c. move sideways. d. erupt. ______12. When rock cools, it becomes more dense and tends to a. rise to the surface. b. sink below the surface. c. move sideways. d. push against ...
Seismic structure of the European crust and upper mantle based on
... We present a new crust and upper mantle model for the European continent and the North Atlantic Ocean, named EU60.It is constructed based on an adjoint-state method and involves 3D variations in elastic wavespeeds, anelastic attenuation, and radial & azimuthal anisotropy. Longwavelength elastic wave ...
... We present a new crust and upper mantle model for the European continent and the North Atlantic Ocean, named EU60.It is constructed based on an adjoint-state method and involves 3D variations in elastic wavespeeds, anelastic attenuation, and radial & azimuthal anisotropy. Longwavelength elastic wave ...
Document
... •What do you think the inside of Earth is like? ____________________________________________________ II. Composition of the Earth A.Earth is divided into ___________ layers- the crust, mantle, and core. 1. Earth’s layers are arranged by their ___________________________ III. The Crust A.Crust- Earth ...
... •What do you think the inside of Earth is like? ____________________________________________________ II. Composition of the Earth A.Earth is divided into ___________ layers- the crust, mantle, and core. 1. Earth’s layers are arranged by their ___________________________ III. The Crust A.Crust- Earth ...
PwrPt - University of Minnesota Duluth
... Map Attributes of Volcanic and Volcaniclastic Rocks Volcanic Rocks- crystallized from lava flows Volcaniclastic Rocks – air-fall accumulations of lava, ash and preexisting volcanic rock ; Rock types: tuff, lahar, agglomerates) ...
... Map Attributes of Volcanic and Volcaniclastic Rocks Volcanic Rocks- crystallized from lava flows Volcaniclastic Rocks – air-fall accumulations of lava, ash and preexisting volcanic rock ; Rock types: tuff, lahar, agglomerates) ...
Marine Geology
... CRUST – thin outer layer • less dense, rocks that floated to the surface when the Earth was formed • between 35km and 70km thick. – not a continuous layer of rock • Split into plates, which are free to drift slowly across the surface of the planet. ...
... CRUST – thin outer layer • less dense, rocks that floated to the surface when the Earth was formed • between 35km and 70km thick. – not a continuous layer of rock • Split into plates, which are free to drift slowly across the surface of the planet. ...
The Structure of the Earth
... • Two types: –Continental Crust (thicker) –Oceanic Crust (thin and more dense) ...
... • Two types: –Continental Crust (thicker) –Oceanic Crust (thin and more dense) ...
Name___________________________ Date______________
... 6.E.2.2 Explain how crustal plates and ocean basins are formed, move and interact using earthquakes, heat flow and volcanoes to reflect forces within the earth. The earth's plates sit on a dense, hot, somewhat melted layer of the earth. The plates move very slowly, pressing against one another in so ...
... 6.E.2.2 Explain how crustal plates and ocean basins are formed, move and interact using earthquakes, heat flow and volcanoes to reflect forces within the earth. The earth's plates sit on a dense, hot, somewhat melted layer of the earth. The plates move very slowly, pressing against one another in so ...
Dynamic Earth Review Sheet
... Layers of the Earth o Be able to use the chart on page 10 to determine the different properties of the layers of the Earth. o Describe the major differences between continental and oceanic crust? ...
... Layers of the Earth o Be able to use the chart on page 10 to determine the different properties of the layers of the Earth. o Describe the major differences between continental and oceanic crust? ...
EARTH-2
... (6-11 km) thick and mainly consists of heavy rocks, like basalt. The Continental crust is thicker than the Oceanic crust, about 19 miles(30 km) thick. It is mainly made up of light material like granite. T ...
... (6-11 km) thick and mainly consists of heavy rocks, like basalt. The Continental crust is thicker than the Oceanic crust, about 19 miles(30 km) thick. It is mainly made up of light material like granite. T ...
Characteristic and Uncharacteristic Earthquakes as Possible
... Concepts of hot spots and plumes are attractive and widely used, but the relation between the persistent volcanism and possible deep mantle plumes is under active investigation because of many deviations from what would be expected: Some hot spots move significantly ...
... Concepts of hot spots and plumes are attractive and widely used, but the relation between the persistent volcanism and possible deep mantle plumes is under active investigation because of many deviations from what would be expected: Some hot spots move significantly ...
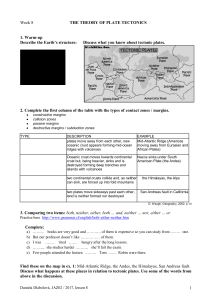
1 Week 8 THE THEORY OF PLATE TECTONICS 1. Warm
... The Andes Mountains run the length of the West Coast of South America, rising in the north in Colombia and finishing in Chile and Argentina in the south. They are the world's longest mountain range running for over 7,000 km and covering 6 countries. The mountains have been formed as a result of the ...
... The Andes Mountains run the length of the West Coast of South America, rising in the north in Colombia and finishing in Chile and Argentina in the south. They are the world's longest mountain range running for over 7,000 km and covering 6 countries. The mountains have been formed as a result of the ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.