Chapter 4 Plate tectonics Review Game
... Pillow lava and other forms of hardened lava are scattered across the ocean floor, this is evidence that molten material constantly erupts from the mid-ocean ridge ...
... Pillow lava and other forms of hardened lava are scattered across the ocean floor, this is evidence that molten material constantly erupts from the mid-ocean ridge ...
Plate tectonics notes
... tectonics to the formation of crustal features; • TEKS 6.10C identify the major tectonic plates • TEKS 6.10D describe how plate tectonics causes major geological events such as ocean basins, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building ...
... tectonics to the formation of crustal features; • TEKS 6.10C identify the major tectonic plates • TEKS 6.10D describe how plate tectonics causes major geological events such as ocean basins, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building ...
Powerpoint template for scientific poster
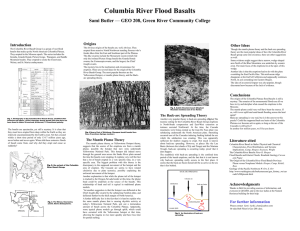
... deflected further by the thick margin of North America. A further difficulty lies in the fact that it is hard to explain why the same mantle plume that is causing rhyolitic activity at today’s Yellowstone National Park, spit out a tremendous amount of basalt across the Columbia Plateau. Apparently, ...
... deflected further by the thick margin of North America. A further difficulty lies in the fact that it is hard to explain why the same mantle plume that is causing rhyolitic activity at today’s Yellowstone National Park, spit out a tremendous amount of basalt across the Columbia Plateau. Apparently, ...
File - Coach Marker`s World of earth Science
... At some tectonic plate boundaries, an oceanic plate plunges beneath another plate and sinks into the Earth's interior. As it sinks, it releases water, which rises into the overriding plate. This causes parts of the overriding plate to melt and form magma. The magma rises up, squeezing through wideni ...
... At some tectonic plate boundaries, an oceanic plate plunges beneath another plate and sinks into the Earth's interior. As it sinks, it releases water, which rises into the overriding plate. This causes parts of the overriding plate to melt and form magma. The magma rises up, squeezing through wideni ...
Plate tectonics in a hotter Earth?
... * phase transitions: mantle (400-D, 670-D), crust (basalteclogite) * rheology: diffusion-, dislocation creep, yielding, material-dependent ...
... * phase transitions: mantle (400-D, 670-D), crust (basalteclogite) * rheology: diffusion-, dislocation creep, yielding, material-dependent ...
Physical Geology
... • The rest of the mantle is soft but solid (Asthenosphere) • The Continental Crust “floats” on the uppermost mantle • The denser, thinner Oceanic Crust comprises the ocean basins ...
... • The rest of the mantle is soft but solid (Asthenosphere) • The Continental Crust “floats” on the uppermost mantle • The denser, thinner Oceanic Crust comprises the ocean basins ...
Directed Reading A
... 9. According to the wave speeds shown in the table below, which two physical layers of the Earth are densest? Speed of Seismic Waves in Earth’s Interior ...
... 9. According to the wave speeds shown in the table below, which two physical layers of the Earth are densest? Speed of Seismic Waves in Earth’s Interior ...
The Birth of a Theory
... along the axis of the oceanic ridge system and are associated with seafloor spreading, which occurs at rates between about 2 and 15 centimeters per year. New divergent boundaries may form within a continent (for example, the East African rift valleys), where they may fragment a landmass and develop ...
... along the axis of the oceanic ridge system and are associated with seafloor spreading, which occurs at rates between about 2 and 15 centimeters per year. New divergent boundaries may form within a continent (for example, the East African rift valleys), where they may fragment a landmass and develop ...
Earth Surfaces Chapter 1 Study Guide The inner core is . (A
... 15. Mantle material rises in convection currents because heated materials N. conduction become ____________ dense. (U-Y) 16. When geologists study Earth’s interior, they rely on ________ methods O. indirect such as seismic waves to study layers. (K-O) 17. When sun warms your face it is a form of hea ...
... 15. Mantle material rises in convection currents because heated materials N. conduction become ____________ dense. (U-Y) 16. When geologists study Earth’s interior, they rely on ________ methods O. indirect such as seismic waves to study layers. (K-O) 17. When sun warms your face it is a form of hea ...
Tertiary Igneous Chronology of the Great Basin of Western United
... TECTONIC SETTING The older igneous rocks (high-K andesites and rhyolite ash-flow tuffs) were extruded on an erosion surface of low to moderate relief in a region that had been tectonically stable for many millions of years. Eruption was not accompanied by any marked increase in tectonism, except in ...
... TECTONIC SETTING The older igneous rocks (high-K andesites and rhyolite ash-flow tuffs) were extruded on an erosion surface of low to moderate relief in a region that had been tectonically stable for many millions of years. Eruption was not accompanied by any marked increase in tectonism, except in ...
Plate Tectonics Theory.
... The seafloor spreads apart along both sides of a mid ocean ridge like a conveyer belt. ...
... The seafloor spreads apart along both sides of a mid ocean ridge like a conveyer belt. ...
File
... South American, Eurasian Australian, Antarctic, and pacific plates. Several minor plates also exist. These plates fit together like a jigsaw puzzle. • The plates consist of two types of crust: continental crust and oceanic crust. • The theory explains the movement of the earth’s plates and the cause ...
... South American, Eurasian Australian, Antarctic, and pacific plates. Several minor plates also exist. These plates fit together like a jigsaw puzzle. • The plates consist of two types of crust: continental crust and oceanic crust. • The theory explains the movement of the earth’s plates and the cause ...
Chapter 4 Plate tectonics Review Game
... Pillow lava and other forms of hardened lava are scattered across the ocean floor, this is evidence that molten material constantly erupts from the mid-ocean ridge ...
... Pillow lava and other forms of hardened lava are scattered across the ocean floor, this is evidence that molten material constantly erupts from the mid-ocean ridge ...
Plate Movement
... Convection is the movement caused within a fluid by the tendency of hotter, less dense material to rise, and colder, denser material to sink under the influence of gravity, which results in transfer of heat. ...
... Convection is the movement caused within a fluid by the tendency of hotter, less dense material to rise, and colder, denser material to sink under the influence of gravity, which results in transfer of heat. ...
Volcano: Creator or Destroyer?
... Philippines, Japan, El Salvador Explosive/pyroclastic flow Hot Spot Hawaii ...
... Philippines, Japan, El Salvador Explosive/pyroclastic flow Hot Spot Hawaii ...
$doc.title
... • Both oceanic and continental crust are less dense (lighter) than the mantle below, causing them to float on it (and ...
... • Both oceanic and continental crust are less dense (lighter) than the mantle below, causing them to float on it (and ...
Text Action - ESOL Online
... Volcanoes Text and Actions The Earth's crust, its hard top layer, is made of several pieces, called tectonic plates. The plates float on top of the mantle. They are always moving, because of convection currents. Where the plates collide or rub together they cause earthquakes and fold the crust into ...
... Volcanoes Text and Actions The Earth's crust, its hard top layer, is made of several pieces, called tectonic plates. The plates float on top of the mantle. They are always moving, because of convection currents. Where the plates collide or rub together they cause earthquakes and fold the crust into ...
Unit 3: Plate Tectonics: Test Review
... 5. What was the Glossopteris? A fern-like plant which only grows in warm climates. Found in Antarctica. 6. Where was it found? Antarctica, South America, India, Africa and Australia. 7. How did it prove the existence of Pangaea? The continents which are now in cooler climates, could not have support ...
... 5. What was the Glossopteris? A fern-like plant which only grows in warm climates. Found in Antarctica. 6. Where was it found? Antarctica, South America, India, Africa and Australia. 7. How did it prove the existence of Pangaea? The continents which are now in cooler climates, could not have support ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.