The stability of the continents and the tendency for old oceanic
... Problem set #3. Isostasy and Ridge Push (Due in class on May 6) A. Why do only oceans get subducted? ...
... Problem set #3. Isostasy and Ridge Push (Due in class on May 6) A. Why do only oceans get subducted? ...
Lesson 1 - Earth`s Interior
... evidence to learn about Earth’s interior: direct evidence from rock samples and indirect evidence from seismic waves. Rocks from inside Earth give geologists clues about Earth’s structure. To study Earth’s interior, geologists also study seismic waves. When earthquakes occur, they produce seismic wa ...
... evidence to learn about Earth’s interior: direct evidence from rock samples and indirect evidence from seismic waves. Rocks from inside Earth give geologists clues about Earth’s structure. To study Earth’s interior, geologists also study seismic waves. When earthquakes occur, they produce seismic wa ...
ContinentalDrift
... Some of the plates are pushing together – these are called converging plates Some of the plates are pulling apart – these are called diverging plates Some plates slide past one another – transform plate boundary ...
... Some of the plates are pushing together – these are called converging plates Some of the plates are pulling apart – these are called diverging plates Some plates slide past one another – transform plate boundary ...
Quiz: Volcanoes Study Guide
... viscosity =the resistance of a liquid to flowing; low viscosity flows freely, high viscosity resist flowing silica = a compound made up of oxygen and silicon particles Where Volcanoes Form convergent boundary = two plates moving together; one plate subducts causing a volcano to form divergent bounda ...
... viscosity =the resistance of a liquid to flowing; low viscosity flows freely, high viscosity resist flowing silica = a compound made up of oxygen and silicon particles Where Volcanoes Form convergent boundary = two plates moving together; one plate subducts causing a volcano to form divergent bounda ...
Martin - Think Geography
... would not be living on earth.) There are three main different types of rocks there is igneous ,sedimentary and the last type of rock is metamorphic. Rocks are very interesting and my power point presentation will tell you more interesting points about rocks. ...
... would not be living on earth.) There are three main different types of rocks there is igneous ,sedimentary and the last type of rock is metamorphic. Rocks are very interesting and my power point presentation will tell you more interesting points about rocks. ...
The Earth`s structure
... solid layer; the asthenosphere, which behaves plastically and flows slowly; and a solid upper layer. Partial melting within the asthenosphere generates magma (molten material), some of which rises to the surface because it is less dense than the surrounding material. The upper mantle and the crust m ...
... solid layer; the asthenosphere, which behaves plastically and flows slowly; and a solid upper layer. Partial melting within the asthenosphere generates magma (molten material), some of which rises to the surface because it is less dense than the surrounding material. The upper mantle and the crust m ...
Plate Boundaries - Clinton Public Schools
... • As they collide, the less dense • Characteristics: continental plate overrides the – Coastal Mountain Ranges oceanic plate. – Continental Volcanic Arcs – Oceanic plate is forced down; temperature increases; plate becomes magma in convection ...
... • As they collide, the less dense • Characteristics: continental plate overrides the – Coastal Mountain Ranges oceanic plate. – Continental Volcanic Arcs – Oceanic plate is forced down; temperature increases; plate becomes magma in convection ...
1. Recent volcanic activity in different parts
... below, which shows the location of the Peru-Chile Trench. ...
... below, which shows the location of the Peru-Chile Trench. ...
Notes
... 2. Divergent plate boundaries are those that _____________________________________. As plates spread apart __________________ material is ______________________ to fill the gap. Divergent boundaries on the ocean floor form ________________________________. Divergent boundaries on continental c ...
... 2. Divergent plate boundaries are those that _____________________________________. As plates spread apart __________________ material is ______________________ to fill the gap. Divergent boundaries on the ocean floor form ________________________________. Divergent boundaries on continental c ...
Igneous Rocks
... Igneous rock chart. Found in text book page 107 Found in the ESRT’s page 6 The environment of formation is found on the left side of the chart. This corresponds to the texture on the right side. The deeper in the ground a rock forms, the slower it cools and the bigger the crystal (grain size) is. ...
... Igneous rock chart. Found in text book page 107 Found in the ESRT’s page 6 The environment of formation is found on the left side of the chart. This corresponds to the texture on the right side. The deeper in the ground a rock forms, the slower it cools and the bigger the crystal (grain size) is. ...
Lesson 7.1: Volcanoes and Plate Boundaries
... has to give and bend and move underneath. • If the one that bends goes deep enough, the heat from Earth’s interior will melt the rocks and it will float back up again, pushing cooler rocks down. • Volcanoes form on surface and an opening on the earth’s surface, where the magma comes out as lava. ...
... has to give and bend and move underneath. • If the one that bends goes deep enough, the heat from Earth’s interior will melt the rocks and it will float back up again, pushing cooler rocks down. • Volcanoes form on surface and an opening on the earth’s surface, where the magma comes out as lava. ...
Section 1: Earth`s Interior (pages 16 – 24)
... from an earthquake. The speed and paths the seismic waves take tell geologists how the planet is put together. Three main layers make up Earth’s interior: (Be able to label layers!) 1. Crust – layer of rock that forms Earths OUTER surface. - It includes both dry land and the ocean floor. - The crust ...
... from an earthquake. The speed and paths the seismic waves take tell geologists how the planet is put together. Three main layers make up Earth’s interior: (Be able to label layers!) 1. Crust – layer of rock that forms Earths OUTER surface. - It includes both dry land and the ocean floor. - The crust ...
The Geosphere
... Why can Earth’s tectonic plates move? Most tectonic activity occurs along Earth’s _____________________. Mountain ranges are formed when tectonic plates _________________. Is it possible to never notice an earthquake? Describe one way than an earthquake can cause damage. ...
... Why can Earth’s tectonic plates move? Most tectonic activity occurs along Earth’s _____________________. Mountain ranges are formed when tectonic plates _________________. Is it possible to never notice an earthquake? Describe one way than an earthquake can cause damage. ...
Project #1: Inversion of multiple geophysical data for composition
... Project #3: Imaging of small-scale chemical anomalies within the continental lithospheric mantle The seismological structure of the Earth's upper mantle is known to be highly heterogeneous, and much of this heterogeneity is associated with the lithosphere's thermal and compositional structure. Lith ...
... Project #3: Imaging of small-scale chemical anomalies within the continental lithospheric mantle The seismological structure of the Earth's upper mantle is known to be highly heterogeneous, and much of this heterogeneity is associated with the lithosphere's thermal and compositional structure. Lith ...
Plate Tectonics II
... The Grand Canyon catches the eye for its tremendous depth, but the North Rim is also over 8000 feet (2400 m) above sea level! Note how FLAT the upland surface is! ...
... The Grand Canyon catches the eye for its tremendous depth, but the North Rim is also over 8000 feet (2400 m) above sea level! Note how FLAT the upland surface is! ...
A Review of the Earth Notes
... mountain formation) takes place at the boundaries between tectonic plates. There are three different types of boundaries: 1. Divergent boundaries 2. Transform boundaries 3. Convergent boundaries Divergent Boundaries Divergent plates are where two plates move apart. This is also known as floor ...
... mountain formation) takes place at the boundaries between tectonic plates. There are three different types of boundaries: 1. Divergent boundaries 2. Transform boundaries 3. Convergent boundaries Divergent Boundaries Divergent plates are where two plates move apart. This is also known as floor ...
Chapter 3 - Igneous Rocks
... oceanic crust - relatively thin (3-5 miles thick) relatively dense, iron rich continental crust - relatively thick (up to 50 miles thick) less dense than oceanic crust Alfred Wegener and Continental Drift o fit of the continents o similarities in rock type and structure o fossil evidence o pal ...
... oceanic crust - relatively thin (3-5 miles thick) relatively dense, iron rich continental crust - relatively thick (up to 50 miles thick) less dense than oceanic crust Alfred Wegener and Continental Drift o fit of the continents o similarities in rock type and structure o fossil evidence o pal ...
8th Grade Earth Science Study Guide Where`s is most of Earth`s
... 17. Why would a volcanic island arc be a landform most likely created when two oceanic plates converge? When plates are converging they are moving toward each other. When this happens, on plate can be pushed under the other. The plate pushed underground will melt back into magma and a volcano can be ...
... 17. Why would a volcanic island arc be a landform most likely created when two oceanic plates converge? When plates are converging they are moving toward each other. When this happens, on plate can be pushed under the other. The plate pushed underground will melt back into magma and a volcano can be ...
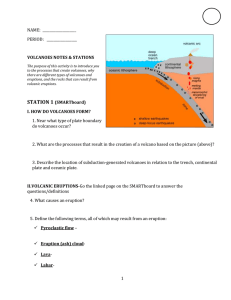
volcanoes stations
... 13. After looking at the samples, sketch the crystal sizes of each in the boxes below. Based on the picture of where each of these formed, fill in the blanks below for each sample with (cooled) quickly or slowly or quickly and slowly, large or small or large and small (crystals). Texture information ...
... 13. After looking at the samples, sketch the crystal sizes of each in the boxes below. Based on the picture of where each of these formed, fill in the blanks below for each sample with (cooled) quickly or slowly or quickly and slowly, large or small or large and small (crystals). Texture information ...
Plate Tectonic Theory
... Mantle. About 1860 miles thick, the mantle is made of iron and magnesium-rich silicate rocks and has a density of about 4.5 g/cm3. The mantle is hot, but mostly solid because the minerals are under pressure. Outer Core. About 1240 miles thick, the outer core is also made mostly of iron with a densit ...
... Mantle. About 1860 miles thick, the mantle is made of iron and magnesium-rich silicate rocks and has a density of about 4.5 g/cm3. The mantle is hot, but mostly solid because the minerals are under pressure. Outer Core. About 1240 miles thick, the outer core is also made mostly of iron with a densit ...
Plate Tectonics
... • Antonio Snyder published a sketch in 1655 showing S.A. and Africa together • Benjamin Franklin in 1782 said – “The crust of the Earth must be a shell floating on a fluid interior. Thus, the surface of the globe would be capable of being broken and disordered by the violent movements of the fluids ...
... • Antonio Snyder published a sketch in 1655 showing S.A. and Africa together • Benjamin Franklin in 1782 said – “The crust of the Earth must be a shell floating on a fluid interior. Thus, the surface of the globe would be capable of being broken and disordered by the violent movements of the fluids ...
Lesson Plan - GeographyPods
... What is underneath where we are sat right now? What would you find if you drilled down? What or where would you come to? * Explain the earth is structured into four layers. (Boardworks KS3 Plate Tectonics Slide 7) Name each layer – Crust, Mantle, Outer Core, Inner Core. Explain that the crust is lik ...
... What is underneath where we are sat right now? What would you find if you drilled down? What or where would you come to? * Explain the earth is structured into four layers. (Boardworks KS3 Plate Tectonics Slide 7) Name each layer – Crust, Mantle, Outer Core, Inner Core. Explain that the crust is lik ...
Document
... • Antonio Snyder published a sketch in 1655 showing S.A. and Africa together • Benjamin Franklin in 1782 said – “The crust of the Earth must be a shell floating on a fluid interior. Thus, the surface of the globe would be capable of being broken and disordered by the violent movements of the fluids ...
... • Antonio Snyder published a sketch in 1655 showing S.A. and Africa together • Benjamin Franklin in 1782 said – “The crust of the Earth must be a shell floating on a fluid interior. Thus, the surface of the globe would be capable of being broken and disordered by the violent movements of the fluids ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.