Plate Tectonics
... Plate tectonics causes movement in the plates and crust, resulting in cracks being formed. These cracks allows the pressure underneath the crust to push the magma, or sometimes water and steam, up the crust. ...
... Plate tectonics causes movement in the plates and crust, resulting in cracks being formed. These cracks allows the pressure underneath the crust to push the magma, or sometimes water and steam, up the crust. ...
Document
... When do mountain chains form? • Mountain chains form when continental landmasses that have the same rock density converge. Since they have similar density, one plate can’t be subducted under the other. The pressure of the impinging plates can only be relieved by thrusting skyward forming mountain p ...
... When do mountain chains form? • Mountain chains form when continental landmasses that have the same rock density converge. Since they have similar density, one plate can’t be subducted under the other. The pressure of the impinging plates can only be relieved by thrusting skyward forming mountain p ...
Orogenesis: Folding, Faulting, and Volcanism
... Landforms: Effusive • Shield volcanoes – large, rounded volcanoes with a gentle slope – central vent – flat terrain (or can not build up dome) – constructed by a series of basalt flows over time. ...
... Landforms: Effusive • Shield volcanoes – large, rounded volcanoes with a gentle slope – central vent – flat terrain (or can not build up dome) – constructed by a series of basalt flows over time. ...
Ch 17 Plate Tectonics
... Antarctica must have been closer to the _______________ to have a ____ enough climate to grow the fern d. Climate data i. _________deposits have been found in Antarctica It forms from dead swamp plants. Swamps only occur in an area that is _________ This indicates that Antarctica was once _________ ...
... Antarctica must have been closer to the _______________ to have a ____ enough climate to grow the fern d. Climate data i. _________deposits have been found in Antarctica It forms from dead swamp plants. Swamps only occur in an area that is _________ This indicates that Antarctica was once _________ ...
Maria – Clorinda LUCK – Durham High School
... outlet glacier. Amazingly, we were able to actually walk inside this glacier’s crevasses and touch the icy waters of the glacier’s river. Our second stop was at Seljalandsfoss waterfall, which we climbed to the top. Lunch was eaten on the famous South Shore Black Beach, home to its basalt columns an ...
... outlet glacier. Amazingly, we were able to actually walk inside this glacier’s crevasses and touch the icy waters of the glacier’s river. Our second stop was at Seljalandsfoss waterfall, which we climbed to the top. Lunch was eaten on the famous South Shore Black Beach, home to its basalt columns an ...
Lithosphere and Asthenosphere
... The mantle is Earth’s thickest layer, measuring nearly 2900 kilometers (1700 mi). It is made of hot rock that is less dense than the metallic core. The very top part of the mantle is cool and rigid. Just below that, the rock is hot and soft enough to move like a thick paste. The crust is a thin laye ...
... The mantle is Earth’s thickest layer, measuring nearly 2900 kilometers (1700 mi). It is made of hot rock that is less dense than the metallic core. The very top part of the mantle is cool and rigid. Just below that, the rock is hot and soft enough to move like a thick paste. The crust is a thin laye ...
Comparison of the volcanic geology of the Tacambaro
... Michoacan-Guanajuato Volcanic Field (MGVF), hosts more than 1000 monogenetic volcanoes and vents, and the only two of the MVB born in historical times: Jorullo and Paricutin. The 690 km2 Tacambaro-Puruaran area (TAC) is located at the volcanic front while the 2310 km2 Zacapu area (ZAC) lies more inl ...
... Michoacan-Guanajuato Volcanic Field (MGVF), hosts more than 1000 monogenetic volcanoes and vents, and the only two of the MVB born in historical times: Jorullo and Paricutin. The 690 km2 Tacambaro-Puruaran area (TAC) is located at the volcanic front while the 2310 km2 Zacapu area (ZAC) lies more inl ...
KArl quilligan plate tectonics powerpoint
... away from each other, occurs above rising convection currents -Hazards include volcanic “leaks.” A volcanic leak is when lava runs down hills; it doesn’t erupt, it just leaks. You also have to be careful of rifts and rift valleys; they form from two faults pulling apart -Iceland is splitting right d ...
... away from each other, occurs above rising convection currents -Hazards include volcanic “leaks.” A volcanic leak is when lava runs down hills; it doesn’t erupt, it just leaks. You also have to be careful of rifts and rift valleys; they form from two faults pulling apart -Iceland is splitting right d ...
Background information Year 9, unit 2: Plate tectonics
... fragmented into a dozen or more large and small solid slabs called tectonic (lithospheric) plates. These plates move relative to one another as they float on more mobile material (the asthenosphere) of the mantle. The average rates of motion range from less than 1 cm to more than 15 cm per year. Nea ...
... fragmented into a dozen or more large and small solid slabs called tectonic (lithospheric) plates. These plates move relative to one another as they float on more mobile material (the asthenosphere) of the mantle. The average rates of motion range from less than 1 cm to more than 15 cm per year. Nea ...
TennMaps_PlateTectonics
... These isolated areas of volcanic activity are not associated with plate boundaries These volcanoes are found both on continents and out in the ocean ...
... These isolated areas of volcanic activity are not associated with plate boundaries These volcanoes are found both on continents and out in the ocean ...
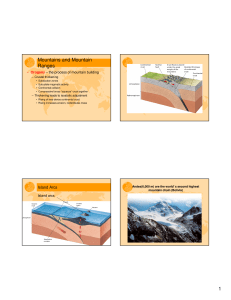
1 Mountains and Mountain Ranges
... • Orogeny – the process of mountain building – Crustal thickening ...
... • Orogeny – the process of mountain building – Crustal thickening ...
Earth`s Lithosphere Study Guide
... • glacial deposits are found in tropical areas suggests some continents now in tropical areas were once near the poles No possible force could move something as large as a continent. ...
... • glacial deposits are found in tropical areas suggests some continents now in tropical areas were once near the poles No possible force could move something as large as a continent. ...
Intro to Plate Tectoncis
... • Like we said, there was no mechanism for moving continents. • This was changed when we began mapping the ocean floor and developed the theory of seafloor spreading. – We will discuss seafloor spreading later. • As evidence began to accumulate and a mechanism had been proposed for how the continent ...
... • Like we said, there was no mechanism for moving continents. • This was changed when we began mapping the ocean floor and developed the theory of seafloor spreading. – We will discuss seafloor spreading later. • As evidence began to accumulate and a mechanism had been proposed for how the continent ...
Continental Drift: The Beginning of Plate Tectonics
... Idea that all continents were all pieced together 245 million years ago Pangaea = “All Earth” ...
... Idea that all continents were all pieced together 245 million years ago Pangaea = “All Earth” ...
Chapter Review - Oakman School News
... crust slowly springs back to its original elevation. Rift zones are a set of deep cracks in the Earth’s crust that form when two tectonic plates are pulling away from each other. As tectonic plates pull apart, stress builds up between the plates. This stress causes strain in the Earth’s crust, and a ...
... crust slowly springs back to its original elevation. Rift zones are a set of deep cracks in the Earth’s crust that form when two tectonic plates are pulling away from each other. As tectonic plates pull apart, stress builds up between the plates. This stress causes strain in the Earth’s crust, and a ...
Slide 1
... Density • Density = mass/volume • Heating an object causes it’s molecules to spread out causing it’s volume to change. • Examples liquid, solid, gas phases • Door key • Marbles in bag ...
... Density • Density = mass/volume • Heating an object causes it’s molecules to spread out causing it’s volume to change. • Examples liquid, solid, gas phases • Door key • Marbles in bag ...
Document
... crust squeezes or pull causing it to crack or break along a fault = stress in crust. ...
... crust squeezes or pull causing it to crack or break along a fault = stress in crust. ...
Theory of Plate Tectonics II
... boundaries evolving over time, because the time scale is too great, but: ...
... boundaries evolving over time, because the time scale is too great, but: ...
Study Guide Chapter 5 – Volcanoes GPS: S6E5. Students will
... S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth’s surface is formed. d. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the Earth. e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of ph ...
... S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of how the earth’s surface is formed. d. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the Earth. e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of ph ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.