File
... – Crust (~3-70 km thick) • Very thin outer rocky shell of Earth – Continental crust - thicker and less dense – Oceanic crust - thinner and more dense ...
... – Crust (~3-70 km thick) • Very thin outer rocky shell of Earth – Continental crust - thicker and less dense – Oceanic crust - thinner and more dense ...
Scientists contribution to early Ideas of Plate Tectonics
... basins and continents were fixed. During the past 70 years these ideas have brought about a scientific revolution in which new evidence and data support a slowly but continually moving planet. It was not until 1968 that a theory called Plate Tectonics provided reliable evidence supporting a mobile ...
... basins and continents were fixed. During the past 70 years these ideas have brought about a scientific revolution in which new evidence and data support a slowly but continually moving planet. It was not until 1968 that a theory called Plate Tectonics provided reliable evidence supporting a mobile ...
the layers of the earth - NATSCI-A7
... • The outer core of Earth is a scorching hot, electrically conductive liquid in which convection takes place. • The outer core is in the range of 200 to 300 kilometers (125 to 188 miles) thick and represents about 4% of the mantle-crust mass. • This layer is sometimes identified as part of the lowe ...
... • The outer core of Earth is a scorching hot, electrically conductive liquid in which convection takes place. • The outer core is in the range of 200 to 300 kilometers (125 to 188 miles) thick and represents about 4% of the mantle-crust mass. • This layer is sometimes identified as part of the lowe ...
It`s easy! Each plate is named after the major land mass
... 6 Major Tectonic Plates on Earth Earth has many tectonic plates - like a giant jigsaw puzzle. The largest 6 plates are called the major plates. Your job is to know the names and locations of the 6 major plates. (It's easy! You will see how the names of the plates match up to the names of Earth's co ...
... 6 Major Tectonic Plates on Earth Earth has many tectonic plates - like a giant jigsaw puzzle. The largest 6 plates are called the major plates. Your job is to know the names and locations of the 6 major plates. (It's easy! You will see how the names of the plates match up to the names of Earth's co ...
Slide 1
... Small crystals form when the molten rock cools quickly- this happens when the lava flows over the Earth’s surface Larger crystals are formed when the molten rock cools slowly- this happens when the magma is trapped underground. From the rocks you have seen today, which do you think came from undergr ...
... Small crystals form when the molten rock cools quickly- this happens when the lava flows over the Earth’s surface Larger crystals are formed when the molten rock cools slowly- this happens when the magma is trapped underground. From the rocks you have seen today, which do you think came from undergr ...
How Does Earth Work?
... • Location of economically important minerals, ore deposits associated with igneous intrusions • Gives us insight into Earth’s dynamic internal processes • Helps us understand volcanic hazards • Continents built largely by addition of igneous rocks ...
... • Location of economically important minerals, ore deposits associated with igneous intrusions • Gives us insight into Earth’s dynamic internal processes • Helps us understand volcanic hazards • Continents built largely by addition of igneous rocks ...
File - Etna FFA Agriculture
... convergent plate boundaries may also develop where slabs of oceanic lithosphere are subducted under lithosphere to produce a continental volcanic arc. ...
... convergent plate boundaries may also develop where slabs of oceanic lithosphere are subducted under lithosphere to produce a continental volcanic arc. ...
Section 1: Earth`s Interior (pages 16 – 24)
... - Scientist mapped the mid-ocean ridge using Sonar. Sonar is a device that bounces sound waves off underwater objects and then records the echoes of these sound waves. (The time it takes for the echo to arrive indicates the distance to the ...
... - Scientist mapped the mid-ocean ridge using Sonar. Sonar is a device that bounces sound waves off underwater objects and then records the echoes of these sound waves. (The time it takes for the echo to arrive indicates the distance to the ...
Integrated Science Chapter 19 Notes Section 1: Earth`s Interior and
... → In subduction zones, when the oceanic plate dives into the hotter mantle, the materials in the plate reach their boiling point and start to melt, forming magma. → Because the magma is less dense than the rock above it, it rises toward the surface; this rising magma pushes the continental crust upw ...
... → In subduction zones, when the oceanic plate dives into the hotter mantle, the materials in the plate reach their boiling point and start to melt, forming magma. → Because the magma is less dense than the rock above it, it rises toward the surface; this rising magma pushes the continental crust upw ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... volcanic glass or other materials. 2. Quartz is a ______ ________________ granite is a __________________. 3. The model that show how one rock changes into another is called ______________. 4. Each type of rock can a) __ ________________________________________________________________________ b) ___ ...
... volcanic glass or other materials. 2. Quartz is a ______ ________________ granite is a __________________. 3. The model that show how one rock changes into another is called ______________. 4. Each type of rock can a) __ ________________________________________________________________________ b) ___ ...
"Inside Earth" Chapter 1 Section 5
... oceanic crust sinks, through subduction beneath the lessdense continental crust. * Two continental plates collide: Neither is dense enough to sink far, so the crust is squeezed and broken in “mighty mountain ranges” include the Himalayas, the tallest mountains on Earth. *** Transform Boundaries occu ...
... oceanic crust sinks, through subduction beneath the lessdense continental crust. * Two continental plates collide: Neither is dense enough to sink far, so the crust is squeezed and broken in “mighty mountain ranges” include the Himalayas, the tallest mountains on Earth. *** Transform Boundaries occu ...
The Dynamic Crust
... correlation also provides evidence that the continents were once joined together. ...
... correlation also provides evidence that the continents were once joined together. ...
Plate Tectonics 2 ppt
... Observe plate boundaries near the west coast of North America (green lines are transform boundaries) ...
... Observe plate boundaries near the west coast of North America (green lines are transform boundaries) ...
Section 17.3 Theory of Plate Tectonics
... 10. Explain the process of convection. 11. Summarize how convection in the mantle is related to the movements of tectonic plates. 12. Compare & contrast the processes of ridge push & slab pull. 13. Miscellaneous: Pangea, early mapmakers, Wegener Sec 17.1 Drifting Continents 1. Early mapmakers noted ...
... 10. Explain the process of convection. 11. Summarize how convection in the mantle is related to the movements of tectonic plates. 12. Compare & contrast the processes of ridge push & slab pull. 13. Miscellaneous: Pangea, early mapmakers, Wegener Sec 17.1 Drifting Continents 1. Early mapmakers noted ...
EarthquakesandVolcan..
... of seismic wave. Will pass through solid, quid and gas.(fastest of the three) 2. Secondary Waves (S-waves) – arrive at a given point after the P wave. second fastest) Will only travel thru solids. Will NOT pass through liquids and gases thus creating a shadow zone. ...
... of seismic wave. Will pass through solid, quid and gas.(fastest of the three) 2. Secondary Waves (S-waves) – arrive at a given point after the P wave. second fastest) Will only travel thru solids. Will NOT pass through liquids and gases thus creating a shadow zone. ...
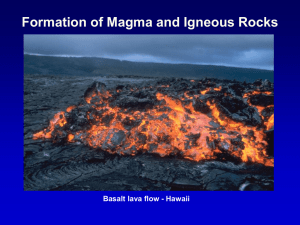
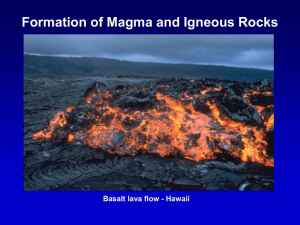
Formation of Magma and Igneous Rocks Basalt
... • Location of economically important minerals - ore deposits associated with igneous intrusions • Gives us insight into Earth’s dynamic internal processes • Helps us understand volcanic hazards • Continents built largely by addition of igneous rocks ...
... • Location of economically important minerals - ore deposits associated with igneous intrusions • Gives us insight into Earth’s dynamic internal processes • Helps us understand volcanic hazards • Continents built largely by addition of igneous rocks ...
Ocean Floor Characteristics
... formed where tectonic plates pull apart from one another. • Pulling creates cracks or rift zones. Magma will fill open spaces causing the sides to expand and create ridges ...
... formed where tectonic plates pull apart from one another. • Pulling creates cracks or rift zones. Magma will fill open spaces causing the sides to expand and create ridges ...
Objectives 6 E Review- TEST FRIDAY, JANUARY 4th Part A: Read
... type of crustal plate boundary. What theory is used to explain the movement of crustal ...
... type of crustal plate boundary. What theory is used to explain the movement of crustal ...
Unit 1B Natural hazards
... plates – you do not need to know them! But take a few minutes to colour in examples of each type on your grey map. ...
... plates – you do not need to know them! But take a few minutes to colour in examples of each type on your grey map. ...
Know the pulling force that acts on tectonic plates, causing the
... What is a transform boundary and what would its diagram be drawn like? When two tectonic plates slide past each other The San Andreas Fault is a strike-slip fault that is located on a transform boundary. The Gorda and Juan de Fuca plates are two small lithospheric plates forced between the Californi ...
... What is a transform boundary and what would its diagram be drawn like? When two tectonic plates slide past each other The San Andreas Fault is a strike-slip fault that is located on a transform boundary. The Gorda and Juan de Fuca plates are two small lithospheric plates forced between the Californi ...
Hawaii Crustal Plate Lab
... The idea behind plate tectonics is that the crustal plates are moving with respect to one another over geologic time. The rates of movement of crustal plates can be determined by using data from the plate margins along the mid-ocean ridges, or at regions known as “HOTSPOTS” where the distance and ag ...
... The idea behind plate tectonics is that the crustal plates are moving with respect to one another over geologic time. The rates of movement of crustal plates can be determined by using data from the plate margins along the mid-ocean ridges, or at regions known as “HOTSPOTS” where the distance and ag ...
Year 9: Volcanoes and Earthquakes
... (liquid) rock. This layer is warmer than the crust. The liquid rock moves in convection currents. These move the plates around the crust. ...
... (liquid) rock. This layer is warmer than the crust. The liquid rock moves in convection currents. These move the plates around the crust. ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.




![Plate_tectonics[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002008574_1-75611a1f04cab56ed6d6f0dd254e9b31-300x300.png)