planet earth - Mr. Shack`s Class
... 4. Coal beds are found on different continents in moderate to cold weather climates. However, coal forms in areas rich in plants that are normally found in warm climates. Therefore they must have been in warmer areas before and moved. ...
... 4. Coal beds are found on different continents in moderate to cold weather climates. However, coal forms in areas rich in plants that are normally found in warm climates. Therefore they must have been in warmer areas before and moved. ...
foreign language academy of global studies
... 11. Where are the youngest rocks in New York State? _____________ 12. Where are the oldest rocks in New York State? _____________ 13. Which region(s) of New York State would have little evidence of fossils? ________________ 14. Which city is located closest to 43˚N and 77˚38' W? ___________________ ...
... 11. Where are the youngest rocks in New York State? _____________ 12. Where are the oldest rocks in New York State? _____________ 13. Which region(s) of New York State would have little evidence of fossils? ________________ 14. Which city is located closest to 43˚N and 77˚38' W? ___________________ ...
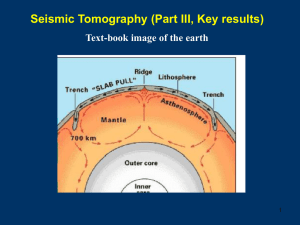
Seismic tomography - Italo Bovolenta Editore
... core-mantle boundary. Near the surface, you can clearly see the structure of plate tectonics. The low S-wave speeds caused by the upwelling of hot asthenosphere along the mid-ocean ridges are shown in warm colors; the high S-wave speeds from cold lithosphere in the old ocean basins and beneath the c ...
... core-mantle boundary. Near the surface, you can clearly see the structure of plate tectonics. The low S-wave speeds caused by the upwelling of hot asthenosphere along the mid-ocean ridges are shown in warm colors; the high S-wave speeds from cold lithosphere in the old ocean basins and beneath the c ...
Earth Science Introduction
... • 35 minutes to birth of Christ • 1 hour+ to pyramids • 3 hours to retreat of glaciers from Wisconsin • 12 days = 1 million years • 2 years to extinction of dinosaurs • 14 years to age of Niagara Escarpment • 31 years = 1 billion years ...
... • 35 minutes to birth of Christ • 1 hour+ to pyramids • 3 hours to retreat of glaciers from Wisconsin • 12 days = 1 million years • 2 years to extinction of dinosaurs • 14 years to age of Niagara Escarpment • 31 years = 1 billion years ...
3/15 Lesson 15 Investigating plate movement and faults pg
... is younger than parts of the sea floor located near trenches. This would suggest that as the sea floor spreads, magma rises forming new land where the plates separate. The older sea floor slides under continental crust forming ocean trenches. 3. What is the theory of Plate Tectonics? ...
... is younger than parts of the sea floor located near trenches. This would suggest that as the sea floor spreads, magma rises forming new land where the plates separate. The older sea floor slides under continental crust forming ocean trenches. 3. What is the theory of Plate Tectonics? ...
plate boundaries
... more dense with distance from mid-oceanic ridge • When sufficiently cool and dense, these rocks may sink back into the mantle at subduction zones – Downward plunge of cold rocks gives rise to oceanic trenches ...
... more dense with distance from mid-oceanic ridge • When sufficiently cool and dense, these rocks may sink back into the mantle at subduction zones – Downward plunge of cold rocks gives rise to oceanic trenches ...
exam_1
... 32. Which of the following is NOT true about passive continental margins? A. They have little seismic or volcanic activity. B. They form after continents are rifted apart. C. They tend to be wider than active margins. D. They occur away from plate boundaries. E. They are commonly at subduction zones ...
... 32. Which of the following is NOT true about passive continental margins? A. They have little seismic or volcanic activity. B. They form after continents are rifted apart. C. They tend to be wider than active margins. D. They occur away from plate boundaries. E. They are commonly at subduction zones ...
Plate Tectonics - Scoil Mhuire Geography
... • Draw the diagram of a constructive plate boundary ...
... • Draw the diagram of a constructive plate boundary ...
Name: Class: Date: Convergent Boundaries (All answers must be in
... The size of the Earth has not changed significantly during the past 600 million years, and very likely not since shortly after its formation 4.6 billion years ago. The Earth's unchanging size implies that the crust must be destroyed at about the same rate as it is being created, as Harry Hess surmis ...
... The size of the Earth has not changed significantly during the past 600 million years, and very likely not since shortly after its formation 4.6 billion years ago. The Earth's unchanging size implies that the crust must be destroyed at about the same rate as it is being created, as Harry Hess surmis ...
GEOL 2312 – Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology
... possible source areas for generating magmas in island arc systems. Which source is likely produce the most magma to the arc?; 2 Which is likely to produce the least? 4 or 5 (1 pt) ...
... possible source areas for generating magmas in island arc systems. Which source is likely produce the most magma to the arc?; 2 Which is likely to produce the least? 4 or 5 (1 pt) ...
NAME - Quia
... A. No, it is likely that any rocks older than a few hundred years are meteorites from outer space. B. No, this rock is probably just a sedimentary rock that was formed by much younger igneous rocks. C. Yes, most of the rocks on Earth can be dated back to the time when Earth was first formed. D. No, ...
... A. No, it is likely that any rocks older than a few hundred years are meteorites from outer space. B. No, this rock is probably just a sedimentary rock that was formed by much younger igneous rocks. C. Yes, most of the rocks on Earth can be dated back to the time when Earth was first formed. D. No, ...
Plate Tectonics and Geology
... To date, humans have never drilled through the crust of the Earth. Scientists study where waves from earthquakes end up around the globe. The waves move differently through different densities of material. ...
... To date, humans have never drilled through the crust of the Earth. Scientists study where waves from earthquakes end up around the globe. The waves move differently through different densities of material. ...
Unit 8 ~ Learning Guide Name
... Information About Each layer Crust: Thin layer of solid rock, Broken into may parts called plates Mantle: Largest layer on the earth, mostly solid rock but has some melted material at the bottom Outer Core: Allot of pressure, temperature over 4000 degrees, liquid and flows like the bottom of the man ...
... Information About Each layer Crust: Thin layer of solid rock, Broken into may parts called plates Mantle: Largest layer on the earth, mostly solid rock but has some melted material at the bottom Outer Core: Allot of pressure, temperature over 4000 degrees, liquid and flows like the bottom of the man ...
Instructions: Earth`s Layers Questions
... Information About Each layer Crust: Thin layer of solid rock, Broken into may parts called plates Mantle: Largest layer on the earth, mostly solid rock but has some melted material at the bottom Outer Core: Allot of pressure, temperature over 4000 degrees, liquid and flows like the bottom of the man ...
... Information About Each layer Crust: Thin layer of solid rock, Broken into may parts called plates Mantle: Largest layer on the earth, mostly solid rock but has some melted material at the bottom Outer Core: Allot of pressure, temperature over 4000 degrees, liquid and flows like the bottom of the man ...
Plate Tectonics*what is it?
... Evidence of these landmass collisions and splits comes from fossils, landform shape, features, and rock structures, and climate change. Landmass changes can occur at hot spots within ______Lithospheric____ plates; Earth’s landmasses_ will continue to move and change during the geologic time of the f ...
... Evidence of these landmass collisions and splits comes from fossils, landform shape, features, and rock structures, and climate change. Landmass changes can occur at hot spots within ______Lithospheric____ plates; Earth’s landmasses_ will continue to move and change during the geologic time of the f ...
here
... Plate tectonics cause earthquakes and volcanoes(38). The point where two plates meet is called a plate boundary(39). Earthquakes and volcanoes are most likely to occur either on or near plate boundaries(40). There are three types of boundaries that we can observe. These plate boundaries are: Diverg ...
... Plate tectonics cause earthquakes and volcanoes(38). The point where two plates meet is called a plate boundary(39). Earthquakes and volcanoes are most likely to occur either on or near plate boundaries(40). There are three types of boundaries that we can observe. These plate boundaries are: Diverg ...
Exam 2 review Earth Science 2 Exam on April 8th
... C. Tensional. compressional. and shearing D. Normal, reverse, and plunging E. None of the choices is correct. 33 Which type of seismic wave causes changes in volume of material? A. P Wave B. S wave C. Rayleigh wave D. Love wave E. None of the choices is correct. 34. Finding an epicenter requires: A. ...
... C. Tensional. compressional. and shearing D. Normal, reverse, and plunging E. None of the choices is correct. 33 Which type of seismic wave causes changes in volume of material? A. P Wave B. S wave C. Rayleigh wave D. Love wave E. None of the choices is correct. 34. Finding an epicenter requires: A. ...
Year 8: Tectonics: Revision worksheet SS2017 1. Constructive plate
... melted plate is now hot, liquid rock (magma). The magma rises through the gaps in the continental plate. If it reaches the surface, the liquid rock forms a volcano. 3. Collision plate margin Collision boundaries occur when two plates of similar densities move together (i.e. a continental plate and a ...
... melted plate is now hot, liquid rock (magma). The magma rises through the gaps in the continental plate. If it reaches the surface, the liquid rock forms a volcano. 3. Collision plate margin Collision boundaries occur when two plates of similar densities move together (i.e. a continental plate and a ...
CP EnvSci Geosphere Review Name ______KEY______ Period
... Part I. Match the following terms in column II with the descriptions and examples in column I. Terms in column II may be used once, more than once, or not at all. ...
... Part I. Match the following terms in column II with the descriptions and examples in column I. Terms in column II may be used once, more than once, or not at all. ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... – As plate descends, partial melting of mantle rock makes basaltic or andesitic magmas – Volcanic mountains associated with subduction of oceanic lithosphere are called continental volcanic arcs (Andes and Cascades) ...
... – As plate descends, partial melting of mantle rock makes basaltic or andesitic magmas – Volcanic mountains associated with subduction of oceanic lithosphere are called continental volcanic arcs (Andes and Cascades) ...
lecture7_tomo
... 1. New Britain, Marianas, Aleutians, and South Sandwich show restricted range close to MORB (mid-ocean ridge basalt) ...
... 1. New Britain, Marianas, Aleutians, and South Sandwich show restricted range close to MORB (mid-ocean ridge basalt) ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.