Document
... Seafloor Recycling • Since new material is created at the midocean ridges and Earth is not expanding, somewhere material must be removed from the surface. • It turns out that old ocean floor is “subducted” into the mantle at subduction zones. ...
... Seafloor Recycling • Since new material is created at the midocean ridges and Earth is not expanding, somewhere material must be removed from the surface. • It turns out that old ocean floor is “subducted” into the mantle at subduction zones. ...
NCEA Level 3 Science (90731) 2012 Assessment Schedule
... South Island is also subducting but the Australian Plate subducts under the Pacific Plate. The middle of the South Island is a transform fault with the two plates sliding past each other. The diagram shows the earthquakes getting deeper the further they occur from the plate boundary. This is because ...
... South Island is also subducting but the Australian Plate subducts under the Pacific Plate. The middle of the South Island is a transform fault with the two plates sliding past each other. The diagram shows the earthquakes getting deeper the further they occur from the plate boundary. This is because ...
LAYERS OF THE EARTH
... CRUST The crust is the thin, outermost layer of the Earth It is similar to the peel of an apple in the sense that it is thin and covers the outside of the Earth ...
... CRUST The crust is the thin, outermost layer of the Earth It is similar to the peel of an apple in the sense that it is thin and covers the outside of the Earth ...
Earth Processes Part 1: Lithosphere
... Erosion -the process by which Earth materials are moved from one place to another. •Wind (rain, waves), water, gravity, ice, organisms ...
... Erosion -the process by which Earth materials are moved from one place to another. •Wind (rain, waves), water, gravity, ice, organisms ...
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Part 1 Multiple Choice
... d. where Earth’s magnetic field changes polarity ...
... d. where Earth’s magnetic field changes polarity ...
ESCI 107 Earth Science STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY
... a. Sketch and describe the major layers of the Earth. b. List and explain the lines of evidence that indicate that the continents have moved through time. c. Summarize the major types of plate boundaries and the processes that occur at each. d. Use Bowen’s Reaction Series as a conceptual framework f ...
... a. Sketch and describe the major layers of the Earth. b. List and explain the lines of evidence that indicate that the continents have moved through time. c. Summarize the major types of plate boundaries and the processes that occur at each. d. Use Bowen’s Reaction Series as a conceptual framework f ...
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics Virtual Lab http://earthguide
... Feel free to click through the other tabs to learn more about different types of sonar technology. ...
... Feel free to click through the other tabs to learn more about different types of sonar technology. ...
Elaborating on a Preexisting Concept
... 19. If plates are moving apart two centimeters per year, that distance is so insignificant that it could never be noticed. ...
... 19. If plates are moving apart two centimeters per year, that distance is so insignificant that it could never be noticed. ...
Geology and Nonrenewable Mineral Resources G. Tyler Miller`s
... occurs at the subduction zone. The third type of boundary is a transform fault and occurs where plates slide/grind past one another. ...
... occurs at the subduction zone. The third type of boundary is a transform fault and occurs where plates slide/grind past one another. ...
Sample Questions for Mrs. Igo`s Earth Science Final
... 28. Matching ____ on different continents are evidence for continental drift. a. river systems c. weather patterns b. rock structures d. wind systems 29. ____ currents inside Earth might drive plate motion. a. Vertical c. Horizontal b. Convection d. none of the above 30. In which of the following cl ...
... 28. Matching ____ on different continents are evidence for continental drift. a. river systems c. weather patterns b. rock structures d. wind systems 29. ____ currents inside Earth might drive plate motion. a. Vertical c. Horizontal b. Convection d. none of the above 30. In which of the following cl ...
Part A The Rock Cycle
... 22. Geologists use THIN SECTIONS to examine the minerals in rocks with a special polarized-light microscope. 23. Magmas with high VISCOSITY have great difficulty flowing through narrow cracks or other openings in country rock. 24. If the contacts of a pluton are parallel to the structure of the cou ...
... 22. Geologists use THIN SECTIONS to examine the minerals in rocks with a special polarized-light microscope. 23. Magmas with high VISCOSITY have great difficulty flowing through narrow cracks or other openings in country rock. 24. If the contacts of a pluton are parallel to the structure of the cou ...
View powerpoint - Deyes High School
... earthquake proof buildings. Since 1981 all new buildings in Japan have had to be earthquake proof. It is also common to have disaster plans to tell people in an emergency ...
... earthquake proof buildings. Since 1981 all new buildings in Japan have had to be earthquake proof. It is also common to have disaster plans to tell people in an emergency ...
Notes: Plate Tectonics - Riverdale Middle School
... top. The hot rock eventually cools and sinks back through the mantle. Over and over the cycle of rising and sinking takes place. • Convection currents like these have been moving inside Earth for more than four billion years! ...
... top. The hot rock eventually cools and sinks back through the mantle. Over and over the cycle of rising and sinking takes place. • Convection currents like these have been moving inside Earth for more than four billion years! ...
Intrusive Igneous
... Dikes and Batholiths • Dikes – plutons that form when magma is injected into fractures, cutting across preexisting rock layers • Many dikes form when magma from a large magma chamber invades fractures in the ...
... Dikes and Batholiths • Dikes – plutons that form when magma is injected into fractures, cutting across preexisting rock layers • Many dikes form when magma from a large magma chamber invades fractures in the ...
Journey_to_the_surface_of_the_earth_pt2
... asthenosphere is part of the upper mantle – It is consider a “plastic” zone – not complete molten, but not really rigid – Rocks in the asthenosphere are very close to their melting points and so deform easily – Convection in this region is thought to be the driving force of plate tectonics ...
... asthenosphere is part of the upper mantle – It is consider a “plastic” zone – not complete molten, but not really rigid – Rocks in the asthenosphere are very close to their melting points and so deform easily – Convection in this region is thought to be the driving force of plate tectonics ...
Inside Earth Worksheet
... c. layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer surface d. the “middle” part of the Earth e. layer that is composed of both the crust and the upper part of the mantle that behaves like a brittle, rigid solid f. the layer made up of liquid iron and nickel g. hot, ultramafic rock layer that makes up 68% of ...
... c. layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer surface d. the “middle” part of the Earth e. layer that is composed of both the crust and the upper part of the mantle that behaves like a brittle, rigid solid f. the layer made up of liquid iron and nickel g. hot, ultramafic rock layer that makes up 68% of ...
Planetary Accretion and the Origin of Crust
... crust to float to surface as “scum” • Subduction returned more dense material to interior • Less dense components were scraped off or returned to surface via volcanism • Plate interactions added continental crust to margins of continents • Quantity of continental crust has increased ...
... crust to float to surface as “scum” • Subduction returned more dense material to interior • Less dense components were scraped off or returned to surface via volcanism • Plate interactions added continental crust to margins of continents • Quantity of continental crust has increased ...
The Rock Cycle - Geevor Tin Mine
... Throughout the Devonian and Carboniferous Periods there were times of volcanic activity. These periods of volcanism produced mainly basic (basalt) lavas, often erupted beneath the sea to form pillow lavas, or as sills and dykes intruded into the surrounding rock. These basic extrusive and intrusive ...
... Throughout the Devonian and Carboniferous Periods there were times of volcanic activity. These periods of volcanism produced mainly basic (basalt) lavas, often erupted beneath the sea to form pillow lavas, or as sills and dykes intruded into the surrounding rock. These basic extrusive and intrusive ...
Nugget
... volcanic successions. Ongoing Ar-Ar geochronology of lavas will further constrain depositional ages. ...
... volcanic successions. Ongoing Ar-Ar geochronology of lavas will further constrain depositional ages. ...
Plate Tectonics
... 1. Hand-out guided note sheets to students. 2. Instruct students to follow along with the ppt. and fill in the appropriate blanks. 3. Show ppt. on Plate Tectonics. 4. Incorporate questions into the ppt. as we go along. 5. Discuss how the theory of continental drift came to be. 6. Discuss Alfred Wege ...
... 1. Hand-out guided note sheets to students. 2. Instruct students to follow along with the ppt. and fill in the appropriate blanks. 3. Show ppt. on Plate Tectonics. 4. Incorporate questions into the ppt. as we go along. 5. Discuss how the theory of continental drift came to be. 6. Discuss Alfred Wege ...
How The Earth Works
... 35 minutes to birth of Christ 1 hour+ to pyramids 3 hours to retreat of glaciers from Wisconsin 12 days = 1 million years 2 years to extinction of dinosaurs 14 years to age of Niagara Escarpment 31 years = 1 billion years ...
... 35 minutes to birth of Christ 1 hour+ to pyramids 3 hours to retreat of glaciers from Wisconsin 12 days = 1 million years 2 years to extinction of dinosaurs 14 years to age of Niagara Escarpment 31 years = 1 billion years ...
Geology - Lone Star College
... When hot mantle material pushes upward it “uplifts” the lithosphere. Where the lithosphere is cool and dense it sinks downward into the deeper mantle. Tectonic Forces cause deformation of rocks as well as vertical and horizontal movement of portions of the earth’s crust. Model for Mantle Convections ...
... When hot mantle material pushes upward it “uplifts” the lithosphere. Where the lithosphere is cool and dense it sinks downward into the deeper mantle. Tectonic Forces cause deformation of rocks as well as vertical and horizontal movement of portions of the earth’s crust. Model for Mantle Convections ...
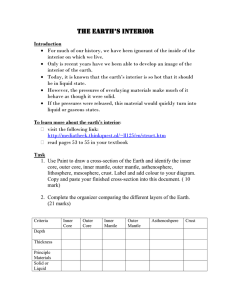
The Earth`s Interior
... The Earth’s Interior Introduction For much of our history, we have been ignorant of the inside of the interior on which we live. Only is recent years have we been able to develop an image of the interior of the earth. Today, it is known that the earth’s interior is so hot that it should be in ...
... The Earth’s Interior Introduction For much of our history, we have been ignorant of the inside of the interior on which we live. Only is recent years have we been able to develop an image of the interior of the earth. Today, it is known that the earth’s interior is so hot that it should be in ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.