Plate Tectonics
... isostatic equilibrium: the concept that the oceanic crust and the continental crust float buoyantly in the denser mantle beneath. • Earth’s internal layers are studied by observing how earthquake waves change as they pass through the earth. • In plate tectonic theory the Earth’s outer rigid surface ...
... isostatic equilibrium: the concept that the oceanic crust and the continental crust float buoyantly in the denser mantle beneath. • Earth’s internal layers are studied by observing how earthquake waves change as they pass through the earth. • In plate tectonic theory the Earth’s outer rigid surface ...
How the Earth Works
... -One of the most distinctive features of the earth's interior is how it seems to be layered by density, with the heaviest stuff in the center, and the lightest material at the surface. The earth probably looks a lot like a hard boiled egg if you could cut it open. - The yellow stuff in the center (t ...
... -One of the most distinctive features of the earth's interior is how it seems to be layered by density, with the heaviest stuff in the center, and the lightest material at the surface. The earth probably looks a lot like a hard boiled egg if you could cut it open. - The yellow stuff in the center (t ...
Plate-Boundaries-Notes
... Tectonic Lithospheric Plate Boundaries You have learned that lithospheric plates move due to convection, slab pulling and ridge pushing –basically gravity and heat. You have also categorized many different mountains according to their shape. Let’s find out how these shapes came to be. ...
... Tectonic Lithospheric Plate Boundaries You have learned that lithospheric plates move due to convection, slab pulling and ridge pushing –basically gravity and heat. You have also categorized many different mountains according to their shape. Let’s find out how these shapes came to be. ...
8-Plate_Tectonics short
... In cross-section, tectonic plate = lithosphere - ~cool, outer rigid layer where rocks can break, ~100 km thick, includes entire crust + outer part of mantle; below lithosphere is asthenosphere - layer of ~hot, weak rock that flows, from ~100 - ~300 km in depth, only mantle rock . ...
... In cross-section, tectonic plate = lithosphere - ~cool, outer rigid layer where rocks can break, ~100 km thick, includes entire crust + outer part of mantle; below lithosphere is asthenosphere - layer of ~hot, weak rock that flows, from ~100 - ~300 km in depth, only mantle rock . ...
Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics
... Gondwanaland began to separate into continents 65 million years ago the continents move even further apart ...
... Gondwanaland began to separate into continents 65 million years ago the continents move even further apart ...
Portfolio Assessment Sheet - Unit 1 Nature of Science
... the world. Demonstrates knowledge of the differences between mass, weight, density & volume and the metric units used to measure them. Compare and contrast the Earth's crust, mantle, and core including temperature, density, and composition. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the ...
... the world. Demonstrates knowledge of the differences between mass, weight, density & volume and the metric units used to measure them. Compare and contrast the Earth's crust, mantle, and core including temperature, density, and composition. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the ...
continental drift
... both are similar density. Typically, the colder, older, more dense ocean crust subducts. The subducting ocean slab melts at about 100 km depth and forms an underwater volcano. When this volcano reaches a height above sea level, a volcanic island arc forms. ...
... both are similar density. Typically, the colder, older, more dense ocean crust subducts. The subducting ocean slab melts at about 100 km depth and forms an underwater volcano. When this volcano reaches a height above sea level, a volcanic island arc forms. ...
Inside the Earth
... Next, calculate the time it would take the object to get 240 miles if it traveled at that same speed. Show your work!!!! ...
... Next, calculate the time it would take the object to get 240 miles if it traveled at that same speed. Show your work!!!! ...
Effects of Volcanic Eruptions
... • The effects of lower temperatures led to the deaths of about 82,000 people. • Therefore, an estimated total of 92,000 people around the world lost their lives as a result of the Tambora eruption. ...
... • The effects of lower temperatures led to the deaths of about 82,000 people. • Therefore, an estimated total of 92,000 people around the world lost their lives as a result of the Tambora eruption. ...
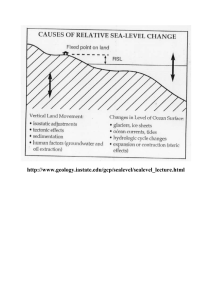
Eustatic Sea Level Change Mechanisms
... Crustal movements may be local or global in scale. For example, tectonic activity along mid-ocean ridges will cause eustatic sea-level changes that are expressed worldwide. The most common tectonic mechanism to impact global sea-level change is the movement of the earth's lithospheric plates. This i ...
... Crustal movements may be local or global in scale. For example, tectonic activity along mid-ocean ridges will cause eustatic sea-level changes that are expressed worldwide. The most common tectonic mechanism to impact global sea-level change is the movement of the earth's lithospheric plates. This i ...
What have earthquakes to do with the Earth`s climate?
... The subduction described above sometimes creates a volcanic arc. As an example, the Pacific Rim is characterized by active volcanoes and earthquakes. Volcanic arcs are present in places such as Japan, the Philippines, the Aleutian Islands, and the western coasts of the Americas. The subduction me ...
... The subduction described above sometimes creates a volcanic arc. As an example, the Pacific Rim is characterized by active volcanoes and earthquakes. Volcanic arcs are present in places such as Japan, the Philippines, the Aleutian Islands, and the western coasts of the Americas. The subduction me ...
12.710 – Problem Set 4 solutions 1. What is “the geothermal
... Volcanism occurs at divergent margins (spreading ridges), convergent margins (subduction zones or arcs), and intraplate settings (“hot spots”). Melts at spreading centers form by decompression melting of upwelling solids in the convecting mantle; most of the lavas erupted on earth erupt at ridges, t ...
... Volcanism occurs at divergent margins (spreading ridges), convergent margins (subduction zones or arcs), and intraplate settings (“hot spots”). Melts at spreading centers form by decompression melting of upwelling solids in the convecting mantle; most of the lavas erupted on earth erupt at ridges, t ...
File
... 28. In a strike-slip fault, the rocks on either side of the fault slip past each other sideways with little up-or-down motion. 29. The ___________________ would most likely be used to tell how much earthquake damage was done to homes and other buildings. 30. A fold in rock that bends upward into an ...
... 28. In a strike-slip fault, the rocks on either side of the fault slip past each other sideways with little up-or-down motion. 29. The ___________________ would most likely be used to tell how much earthquake damage was done to homes and other buildings. 30. A fold in rock that bends upward into an ...
Earth Space Science
... The composition and properties of Earth’s interior are identified by the behavior of seismic waves. Earth’s crust consists of major and minor tectonic plates that move relative to each other. A combination of constructive and destructive geologic processes formed Earth’s surface. Evidence of the dyn ...
... The composition and properties of Earth’s interior are identified by the behavior of seismic waves. Earth’s crust consists of major and minor tectonic plates that move relative to each other. A combination of constructive and destructive geologic processes formed Earth’s surface. Evidence of the dyn ...
Sample
... 5. Why has the study of paleomagnetism and magnetic reversals been important in understanding plate tectonics? (p. 39) Earth’s magnetic field is sufficient to permanently magnetize some surface rocks. For example, volcanic rock that erupts and cools at mid-oceanic ridges becomes magnetized at the ti ...
... 5. Why has the study of paleomagnetism and magnetic reversals been important in understanding plate tectonics? (p. 39) Earth’s magnetic field is sufficient to permanently magnetize some surface rocks. For example, volcanic rock that erupts and cools at mid-oceanic ridges becomes magnetized at the ti ...
Earth`s Crust
... Continental drift – idea that continents have moved slowly to their current positions due to convection currents in the mantel. Pangea – the idea that the all land masses on earth were once a single large land mass. ...
... Continental drift – idea that continents have moved slowly to their current positions due to convection currents in the mantel. Pangea – the idea that the all land masses on earth were once a single large land mass. ...
Earth_sCrust2
... Continental drift – idea that continents have moved slowly to their current positions due to convection currents in the mantel. Pangea – the idea that the all land masses on earth were once a single large land mass. ...
... Continental drift – idea that continents have moved slowly to their current positions due to convection currents in the mantel. Pangea – the idea that the all land masses on earth were once a single large land mass. ...
internal resistance to flow of a liquid
... particles to move at right angles to the direction of the wave ...
... particles to move at right angles to the direction of the wave ...
Rocks and Minerals Webquest
... Mount Nyiragongo is an active volcano in central Africa. Not much is known about how long the volcano has been erupting, but since 1882, it has erupted at least 34 times (once every 4 years), including many periods where activity was continuous for years at a time, often in the form of a churning la ...
... Mount Nyiragongo is an active volcano in central Africa. Not much is known about how long the volcano has been erupting, but since 1882, it has erupted at least 34 times (once every 4 years), including many periods where activity was continuous for years at a time, often in the form of a churning la ...
Chapter-8 Metamorphic Rocks
... 102. Extensive pyroclastic flow deposits are associated with which volcanic structure? 103. How to the eruptions that created the Columbia Plateau differ from eruptions that create large composite cones? 104. What is Shiprock, New Mexico, and how did it form? 105. Draw a diagram of various intrusive ...
... 102. Extensive pyroclastic flow deposits are associated with which volcanic structure? 103. How to the eruptions that created the Columbia Plateau differ from eruptions that create large composite cones? 104. What is Shiprock, New Mexico, and how did it form? 105. Draw a diagram of various intrusive ...
From: http://www.meteo.mcgill.ca/195
... The cinders are generally of basaltic composition The eruptive activity typically lasts a few months or years ...
... The cinders are generally of basaltic composition The eruptive activity typically lasts a few months or years ...
The Islands of Blowtorches
... Common Sense: If a small area in the mantle distorts the crust that passes above it, the distortion in the crust will form a trail, which gets younger in the direction OPPOSITE to the crust’s movement. Observation: The Hawaiian Islands and other Pacific island chains are trails of volcanic islands, ...
... Common Sense: If a small area in the mantle distorts the crust that passes above it, the distortion in the crust will form a trail, which gets younger in the direction OPPOSITE to the crust’s movement. Observation: The Hawaiian Islands and other Pacific island chains are trails of volcanic islands, ...
Convergent Boundaries
... called a deep-sea trench that forms along the boundary. Such trenches are the deepest parts of the ocean floor. Subduction boundaries can occur at the convergence of two oceanic plates or at the convergence of an oceanic plate with a continental plate. When two oceanic plates converge, the deep-sea ...
... called a deep-sea trench that forms along the boundary. Such trenches are the deepest parts of the ocean floor. Subduction boundaries can occur at the convergence of two oceanic plates or at the convergence of an oceanic plate with a continental plate. When two oceanic plates converge, the deep-sea ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.