Geology Module: Rock Cycle Lecture Outline
... d. Are used as time indicators e. Are used for matching rocks from different places VIII. Metamorphic rocks A. Rocks that have changed form B. Produced from preexisting 1. Igneous rocks 2. Sedimentary rocks 3. Other metamorphic rocks C. Metamorphism 1. Takes place where preexisting rock is subjected ...
... d. Are used as time indicators e. Are used for matching rocks from different places VIII. Metamorphic rocks A. Rocks that have changed form B. Produced from preexisting 1. Igneous rocks 2. Sedimentary rocks 3. Other metamorphic rocks C. Metamorphism 1. Takes place where preexisting rock is subjected ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... • Magma: melted rock that found beneath the surface of the earth (called lava when above earth’s surface) • Located near tectonic plate boundaries where plates are sliding or separating from one another. • May occur on the land or under sea. ...
... • Magma: melted rock that found beneath the surface of the earth (called lava when above earth’s surface) • Located near tectonic plate boundaries where plates are sliding or separating from one another. • May occur on the land or under sea. ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes - St. Louis Public Schools
... • Magma: melted rock that found beneath the surface of the earth (called lava when above earth’s surface) • Located near tectonic plate boundaries where plates are sliding or separating from one another. • May occur on the land or under sea. ...
... • Magma: melted rock that found beneath the surface of the earth (called lava when above earth’s surface) • Located near tectonic plate boundaries where plates are sliding or separating from one another. • May occur on the land or under sea. ...
Granite, Alkali Feldspar Granite, Granodiorite, Monzonite, and Quartz
... • These rocks are often collectively called “granite” • When used in this sense, granite means any lightcolored, medium to coarse grained intrusive rock containing quartz ...
... • These rocks are often collectively called “granite” • When used in this sense, granite means any lightcolored, medium to coarse grained intrusive rock containing quartz ...
Brainpop - Tsunami
... b. the destructiveness of natural disasters c. underwater energy d. seismic activity _____ 8. Which of the following statements is an opinion about tsunamis? a. The 2004 tsunami caused millions of ...
... b. the destructiveness of natural disasters c. underwater energy d. seismic activity _____ 8. Which of the following statements is an opinion about tsunamis? a. The 2004 tsunami caused millions of ...
Granite, Alkali Feldspar Granite, Granodiorite
... • These rocks are often collectively called “granite” • When used in this sense, granite means any lightcolored, medium to coarse grained intrusive rock containing quartz ...
... • These rocks are often collectively called “granite” • When used in this sense, granite means any lightcolored, medium to coarse grained intrusive rock containing quartz ...
Questions and answers
... 1.) At the end of the 2 week period study the map that you have produced displaying the recent earthquake events. See if you can answer these questions. ...
... 1.) At the end of the 2 week period study the map that you have produced displaying the recent earthquake events. See if you can answer these questions. ...
Introduction to Geology, Lab 2
... TEXTURE: relates to the size of the individual mineral grains in the final, solid rock, usually dependent on how quickly the magma cooled Groundmass – fine-grained crystalline base of porphyritic rock in which larger crystals are embedded Phaneritic – individual grains in an igneous rock are large e ...
... TEXTURE: relates to the size of the individual mineral grains in the final, solid rock, usually dependent on how quickly the magma cooled Groundmass – fine-grained crystalline base of porphyritic rock in which larger crystals are embedded Phaneritic – individual grains in an igneous rock are large e ...
The Geology of the Island of Newfoundland (adapted from Appendix
... Like the rocks of the Avalon Platform zone, those of the Western Platform are pre-Cambrian at the base with early Paleozoic rocks on top. Also, the Western Platform contains sedimentary rocks that were deposited in a shallow marine environment. These limestones and shales contain marine fossils that ...
... Like the rocks of the Avalon Platform zone, those of the Western Platform are pre-Cambrian at the base with early Paleozoic rocks on top. Also, the Western Platform contains sedimentary rocks that were deposited in a shallow marine environment. These limestones and shales contain marine fossils that ...
Intrusive Igneous Rocks, part 2
... • These rocks are often collectively called “granite” • When used in this sense, granite means any lightcolored, medium to coarse grained intrusive rock containing quartz ...
... • These rocks are often collectively called “granite” • When used in this sense, granite means any lightcolored, medium to coarse grained intrusive rock containing quartz ...
HOT SPOT! - Moanalua Gardens Foundation
... core is approximately 3,500 km (2,200 mi) thick and consists of a solid inner core and a fluid outer core. Surrounding the core is the solid rock of the mantle, about 2,900 km thick (1,800 mi), where molten material exists in hot spots, subduction zones and spreading centers. The thin crust of the Ea ...
... core is approximately 3,500 km (2,200 mi) thick and consists of a solid inner core and a fluid outer core. Surrounding the core is the solid rock of the mantle, about 2,900 km thick (1,800 mi), where molten material exists in hot spots, subduction zones and spreading centers. The thin crust of the Ea ...
geology-and-scenery-of-iceland-mikeadler
... • Maximum was 25,000 years ago • Also shown is the evolution of the rift system moving from the west in the Snaefellsnes peninsula to its current landfall in the Reykjanes peninsula • Stages of growth of a subglacial volcanic eruption • If the eruption stops well below the surface pillow lava is for ...
... • Maximum was 25,000 years ago • Also shown is the evolution of the rift system moving from the west in the Snaefellsnes peninsula to its current landfall in the Reykjanes peninsula • Stages of growth of a subglacial volcanic eruption • If the eruption stops well below the surface pillow lava is for ...
ISNS 4359 EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES Spring 2005
... Hazard Maps incorporating soil & bedrock data (do not suggest/permit development in hazard zones). Step 2. Retrofit existing structures, build seismically isolated buildings and specially engineered structures. Step 3. Monitor activity with advanced instruments (seismometers, strain-meters, etc.). S ...
... Hazard Maps incorporating soil & bedrock data (do not suggest/permit development in hazard zones). Step 2. Retrofit existing structures, build seismically isolated buildings and specially engineered structures. Step 3. Monitor activity with advanced instruments (seismometers, strain-meters, etc.). S ...
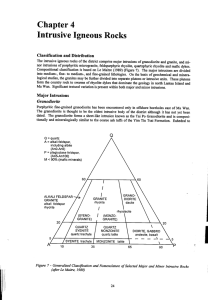
Chapter 4 Intrusive Igneous Rocks
... Mafic dykes are mostly of basaltic andesite composition but range from basalt to andesite. On Ma Wan and at Tsing Chau Tsai, melanocratic enclaves within quartzphyric rhyolite dykes are dacitic in composition and similar to the melanocratic margins of composite dykes. Whereas these dacitic dykes are ...
... Mafic dykes are mostly of basaltic andesite composition but range from basalt to andesite. On Ma Wan and at Tsing Chau Tsai, melanocratic enclaves within quartzphyric rhyolite dykes are dacitic in composition and similar to the melanocratic margins of composite dykes. Whereas these dacitic dykes are ...
The Boggulakonda Gabbros, Prakasam District, Andhra Pradesh
... materials at construction sites to polished stone counter tops and floor tiles. Gabbros are known to contain economic mineral deposits. Gabbros containing significant amounts of the mineral ilmenite are mined for their titanium content. Elsewhere, gabbros are mined to yield nickel, chromium and plat ...
... materials at construction sites to polished stone counter tops and floor tiles. Gabbros are known to contain economic mineral deposits. Gabbros containing significant amounts of the mineral ilmenite are mined for their titanium content. Elsewhere, gabbros are mined to yield nickel, chromium and plat ...
GRANITOID ROCKS
... dominated by amphibole and plagioclase. Magma mixing between the granitoids and basalts intruded into them is common. 2) Continental collision - The most prevalent granitoids are S-type. They form by partial melting of shales and graywackes. Some magmas bring up large amount of restite, pieces of th ...
... dominated by amphibole and plagioclase. Magma mixing between the granitoids and basalts intruded into them is common. 2) Continental collision - The most prevalent granitoids are S-type. They form by partial melting of shales and graywackes. Some magmas bring up large amount of restite, pieces of th ...
Early cretaceous subduction-related adakite
... The Late Jurassic–Early Cretaceous volcano-sedimentary sequences of the Sangri Group, which consists of the underlying Mamuxia Formation (the focus of the present study) and overlying Bima Formation, are sporadically exposed in the southern Gangdese Belt from Yawa in the west to Sangri County in the ...
... The Late Jurassic–Early Cretaceous volcano-sedimentary sequences of the Sangri Group, which consists of the underlying Mamuxia Formation (the focus of the present study) and overlying Bima Formation, are sporadically exposed in the southern Gangdese Belt from Yawa in the west to Sangri County in the ...
19.1 Earthquakes
... • A fracture or system of fractures along which Earth moves – Reverse faults form as a result compression. • This causes rock on one side of a reverse fault to be pushed up relative to the other side. ...
... • A fracture or system of fractures along which Earth moves – Reverse faults form as a result compression. • This causes rock on one side of a reverse fault to be pushed up relative to the other side. ...
PLATE TECTONICS Plate tectonics: Earth`s major tectonic plates
... PLATE TECTONICS Plate tectonics: Earth’s major tectonic plates make up 14 plates. Drifting Continents: Reasons: 1) Similarities of types of rock 2) Distribution of fossil species 3) Other lines of evidence 225 Million Years ago, all continents were in one: Pangea moving 6 cm per year: steady slow mo ...
... PLATE TECTONICS Plate tectonics: Earth’s major tectonic plates make up 14 plates. Drifting Continents: Reasons: 1) Similarities of types of rock 2) Distribution of fossil species 3) Other lines of evidence 225 Million Years ago, all continents were in one: Pangea moving 6 cm per year: steady slow mo ...
9.2 Plate Tectonics
... Pacific Ocean. Notice that several of the large plates include an entire continent plus a large area of the seafloor. This is a major departure from Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis, which proposed that the continents moved through the ocean floor, not with it. Note also that none of the plates i ...
... Pacific Ocean. Notice that several of the large plates include an entire continent plus a large area of the seafloor. This is a major departure from Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis, which proposed that the continents moved through the ocean floor, not with it. Note also that none of the plates i ...
Use of Remote Sensing and GIS in Volcanic Eruption
... always erupting. Sometime they lie quietly for thousands of years in between eruptions. Some volcanoes have areas around them that experience earthquakes and release gases, but they do not erupt with magma. ...
... always erupting. Sometime they lie quietly for thousands of years in between eruptions. Some volcanoes have areas around them that experience earthquakes and release gases, but they do not erupt with magma. ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.