Year 9: Global Hazards and the Restless Earth
... Can use a map to Can describe the Can describe the Can describe Can explain how Can compare and identify the basic structure of structure of a some volcanoes some volcanoes contrast the What are are formed by location of major a volcano. structure of volcano using the as active, vo ...
... Can use a map to Can describe the Can describe the Can describe Can explain how Can compare and identify the basic structure of structure of a some volcanoes some volcanoes contrast the What are are formed by location of major a volcano. structure of volcano using the as active, vo ...
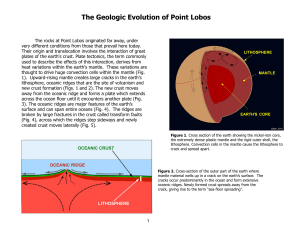
Geologic Evolution of Point Lobos
... Figure 7 shows the distribution transform and subducting margins on the western sides of North and South American continents. Central and southern California lie on a transform margin on which the Pacific Plate is sliding to the northwest relative to the North American Plate. Much of Northern Califo ...
... Figure 7 shows the distribution transform and subducting margins on the western sides of North and South American continents. Central and southern California lie on a transform margin on which the Pacific Plate is sliding to the northwest relative to the North American Plate. Much of Northern Califo ...
Classifying Rocks
... • The grains can be round (Conglomerate), jagged (Breccia), star-shaped, look like small seeds, etc… • They can be formed from other rocks Conglomerate ...
... • The grains can be round (Conglomerate), jagged (Breccia), star-shaped, look like small seeds, etc… • They can be formed from other rocks Conglomerate ...
Sea Floor Spreading - Smyth County Schools
... Proposed answer: Sea Floor Spreading • New sea floor created by insertion of lava in rift valley • Pushes ridge apart in center ...
... Proposed answer: Sea Floor Spreading • New sea floor created by insertion of lava in rift valley • Pushes ridge apart in center ...
Chapter 2 - MrJardina
... Types of Sedimentary Rocks Clastic: pieces of rocks, minerals, and organic ...
... Types of Sedimentary Rocks Clastic: pieces of rocks, minerals, and organic ...
Petrological models of magma evolution and deep crustal structure
... discrepancy between the composition of the erupted lavas, predominantly tholeiitic basal@ and the expected picritic composition of the parental mantle melts. In our model the initial liquid compositions are taken from melting experiments on spine1 lherzolites at lo-30 kbar pressure and span reasonab ...
... discrepancy between the composition of the erupted lavas, predominantly tholeiitic basal@ and the expected picritic composition of the parental mantle melts. In our model the initial liquid compositions are taken from melting experiments on spine1 lherzolites at lo-30 kbar pressure and span reasonab ...
Density of Oceanic Crust
... Certain properties of a substance are both distinctive and relatively easy to determine. Density, the ratio between a sample’s mass and volume at a specific temperature and pressure (like standard ambient temperature and pressure), is one such property. Regardless of the size of a sample, the densit ...
... Certain properties of a substance are both distinctive and relatively easy to determine. Density, the ratio between a sample’s mass and volume at a specific temperature and pressure (like standard ambient temperature and pressure), is one such property. Regardless of the size of a sample, the densit ...
Media Release
... Scientists say the presence of a magma body does not mean an eruption might be imminent and it has not changed the volcanic hazard of the Bay of Plenty region. The research has just been published in the science journal Science Advances. It is titled 'Offaxis magmatism along a subaerial back-arc rif ...
... Scientists say the presence of a magma body does not mean an eruption might be imminent and it has not changed the volcanic hazard of the Bay of Plenty region. The research has just been published in the science journal Science Advances. It is titled 'Offaxis magmatism along a subaerial back-arc rif ...
AlexanderT
... I have received your request for information on earthquake activity. These questions that you have asked are definitely some very important ones. Once I have answered them, I might be saving many lives. People all around the world, who live in earthquake zones, will need to know this information. It ...
... I have received your request for information on earthquake activity. These questions that you have asked are definitely some very important ones. Once I have answered them, I might be saving many lives. People all around the world, who live in earthquake zones, will need to know this information. It ...
Plate Tectonics
... outer shell is divided into several plates that glide over the mantle, plate tectonics national geographic society - in much the same way that geographic borders have separated collided and been redrawn throughout human history tectonic plate boundaries have diverged converged, plate tectonics geolo ...
... outer shell is divided into several plates that glide over the mantle, plate tectonics national geographic society - in much the same way that geographic borders have separated collided and been redrawn throughout human history tectonic plate boundaries have diverged converged, plate tectonics geolo ...
How Do Geologists Classify Rocks?
... What is the Mineral Composition of an Igneous Rock? • Igneous Rocks differ in mineral composition depending on how much silica and other minerals are present in magma and lava • Higher silica forms lightcolored rocks like granite • Lower silica forms dark-colored ...
... What is the Mineral Composition of an Igneous Rock? • Igneous Rocks differ in mineral composition depending on how much silica and other minerals are present in magma and lava • Higher silica forms lightcolored rocks like granite • Lower silica forms dark-colored ...
RELICS OF MOZAMBIQUE OCEAN IN EASTERN AFRICA OROGEN
... formation of which is related to the assembly of the Gondwana supercontinent. It is dominated by metabasic rocks, which have chemical compositions similar to those of recent basalts from a mid-ocean ridge, back-arc setting and island-arc setting. The age of formation of proto lith basalts has been d ...
... formation of which is related to the assembly of the Gondwana supercontinent. It is dominated by metabasic rocks, which have chemical compositions similar to those of recent basalts from a mid-ocean ridge, back-arc setting and island-arc setting. The age of formation of proto lith basalts has been d ...
How Do Geologists Classify Rocks?
... What is the Mineral Composition of an Igneous Rock? • Igneous Rocks differ in mineral composition depending on how much silica and other minerals are present in magma and lava • Higher silica forms lightcolored rocks like granite • Lower silica forms dark-colored ...
... What is the Mineral Composition of an Igneous Rock? • Igneous Rocks differ in mineral composition depending on how much silica and other minerals are present in magma and lava • Higher silica forms lightcolored rocks like granite • Lower silica forms dark-colored ...
Genesis of the Supercontinent Cycle Geological Society of America
... Even in 1984, we were by no means the first to suggest that supercontinents had formed prior to Pangea. Indeed, the existence of a Neoproterozoic supercontinent had been implied by Valentine and Moores as early as 1970 and, in the mid-70s, Piper was arguing for the existence of a single supercontine ...
... Even in 1984, we were by no means the first to suggest that supercontinents had formed prior to Pangea. Indeed, the existence of a Neoproterozoic supercontinent had been implied by Valentine and Moores as early as 1970 and, in the mid-70s, Piper was arguing for the existence of a single supercontine ...
here - ScienceA2Z.com
... The D" layer of Earth is about 3% of Earth's mass, is 125 to 188 miles (200 to 300 kilometers) thick and covers about 4% of the mantle-crust mass. This layer, in terms of whether it is part of the lower mantle or an independent layer is still somewhat unclear. Based on evidence collected from seismi ...
... The D" layer of Earth is about 3% of Earth's mass, is 125 to 188 miles (200 to 300 kilometers) thick and covers about 4% of the mantle-crust mass. This layer, in terms of whether it is part of the lower mantle or an independent layer is still somewhat unclear. Based on evidence collected from seismi ...
Chapter 7 Lecture 1
... plenty of internal heat because of its relatively large size for a terrestrial world. This heat causes mantle convection and keeps Earth’s lithosphere thin, ensuring active surface geology. It also keeps part of Earth’s core melted, and the circulation of this molten metal creates Earth’s magnetic f ...
... plenty of internal heat because of its relatively large size for a terrestrial world. This heat causes mantle convection and keeps Earth’s lithosphere thin, ensuring active surface geology. It also keeps part of Earth’s core melted, and the circulation of this molten metal creates Earth’s magnetic f ...
Course overview – full
... 1) The cycle of geological processes. Internal and external geological factors, their significance for the evolution of the Earth. 2) The Earth’s body. Earth formation hypothesis and geotectonic hypotheses. Geophysical evidence of the structure and composition of the Earth. The shape and movements o ...
... 1) The cycle of geological processes. Internal and external geological factors, their significance for the evolution of the Earth. 2) The Earth’s body. Earth formation hypothesis and geotectonic hypotheses. Geophysical evidence of the structure and composition of the Earth. The shape and movements o ...
Midterm Exam - Heritage Collegiate
... (D) trace 38. In which rock will fossils most likely form? (A) basalt (B) gneiss (C) granite (D) limestone 39. Which factor is most important for the formation of a fossil? (A) burial in coarse sediment (B) high rates of mechanical weathering (C) presence of hard body parts (D) slow burial in a deep ...
... (D) trace 38. In which rock will fossils most likely form? (A) basalt (B) gneiss (C) granite (D) limestone 39. Which factor is most important for the formation of a fossil? (A) burial in coarse sediment (B) high rates of mechanical weathering (C) presence of hard body parts (D) slow burial in a deep ...
Unit 3 Physical Oceanography
... • Evidence to support Continental Drift: – Fossils of the same animals and plants have been found on continents that are not currently connected but would have been in Pangaea. ...
... • Evidence to support Continental Drift: – Fossils of the same animals and plants have been found on continents that are not currently connected but would have been in Pangaea. ...
Plate Tectonic Map of Geoworld
... 1. Absolute motion of the Aragorn Ocean and the Bilbo Continent Notice the Gandalf Islands. They are analogous to the Hawaiian Islands on Earth. They form a linear chain that originated by the migration of the plate over a mantle hot spot. Mantle hot spots are assumed to be fixed relative to the cen ...
... 1. Absolute motion of the Aragorn Ocean and the Bilbo Continent Notice the Gandalf Islands. They are analogous to the Hawaiian Islands on Earth. They form a linear chain that originated by the migration of the plate over a mantle hot spot. Mantle hot spots are assumed to be fixed relative to the cen ...
Large igneous province

A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including liquid rock (intrusive) or volcanic rock formations (extrusive), when hot magma extrudes from inside the Earth and flows out. The source of many or all LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with plate tectonics. Types of LIPs can include large volcanic provinces (LVP), created through flood basalt and large plutonic provinces (LPP). Eleven distinct flood basalt episodes occurred in the past 250 million years, creating volcanic provinces, which coincided with mass extinctions in prehistoric times. Formation depends on a range of factors, such as continental configuration, latitude, volume, rate, duration of eruption, style and setting (continental vs. oceanic), the preexisting climate state, and the biota resilience to change.