File
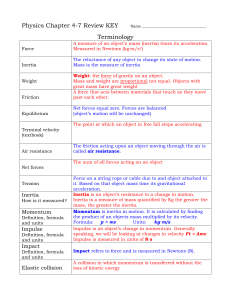
... One type of PE is called gravitational PE depends on the mass and height of object (GPE = m*9.8*h OR GPE = w * h) Ex: A skydiver has more GPE on the plane than ...
... One type of PE is called gravitational PE depends on the mass and height of object (GPE = m*9.8*h OR GPE = w * h) Ex: A skydiver has more GPE on the plane than ...
Energy And SHM
... mass is hung from it. The spring is stretched and additional .100m from its equilibrium point then released. Determine a) k b) the amplitude c) the max velocity d) the velocity when .050 m from equilibrium e) the max acceleration f) the total energy ...
... mass is hung from it. The spring is stretched and additional .100m from its equilibrium point then released. Determine a) k b) the amplitude c) the max velocity d) the velocity when .050 m from equilibrium e) the max acceleration f) the total energy ...
Astronomy
... Determine the average effective force using graphical representation. Calculate average force and impulse given mass, velocity, and time. Car Crash Video 8.3. Conservation of Momentum Describe the principle of conservation of momentum. Derive an expression for the conservation of momentum. ...
... Determine the average effective force using graphical representation. Calculate average force and impulse given mass, velocity, and time. Car Crash Video 8.3. Conservation of Momentum Describe the principle of conservation of momentum. Derive an expression for the conservation of momentum. ...
Chapter13_4-8_FA05
... Strategy: First use conservation of momentum to find the speed of the bullet-block just after collision. Use this to find the intial kinetic energy. Use conservation of energy to find A. Then figure out the period of oscillation, and take ¼ of that to find the time to compress the spring. (You have ...
... Strategy: First use conservation of momentum to find the speed of the bullet-block just after collision. Use this to find the intial kinetic energy. Use conservation of energy to find A. Then figure out the period of oscillation, and take ¼ of that to find the time to compress the spring. (You have ...
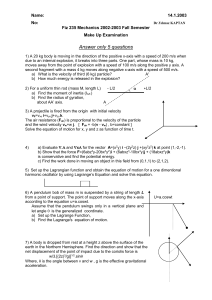
Fiz 235 Mechanics 2002
... a) Evaluate and xfor the vector A=(x2y) i –(2y2z) j +(xy2z2) k at point (1,-2,-1). b) Show that the force F=(6abz3y-20bx3y2)i + (6abxz3-10bx4y)j + (18abxz2y)k is conservative and find the potential energy. c) Find the work done in moving an object in this field from (0,1,1) to (2,1,2). ...
... a) Evaluate and xfor the vector A=(x2y) i –(2y2z) j +(xy2z2) k at point (1,-2,-1). b) Show that the force F=(6abz3y-20bx3y2)i + (6abxz3-10bx4y)j + (18abxz2y)k is conservative and find the potential energy. c) Find the work done in moving an object in this field from (0,1,1) to (2,1,2). ...
Unit 1
... • Every mass exerts a force of attraction on every other mass. The strength of the force is proportional to the product of the masses divided by the square of the distance between them – Simply put, everything pulls on ...
... • Every mass exerts a force of attraction on every other mass. The strength of the force is proportional to the product of the masses divided by the square of the distance between them – Simply put, everything pulls on ...
8.1: Linear Momentum and Force By: Chris, Jakub, Luis
... Impulse changes the momentum of an object. Impulse is defined as the integral of a force acting on an object, with respect to time. This means that impulse contains the product of force and time. As a result, a large force applied for a short period of time can produce the same momentum change as a ...
... Impulse changes the momentum of an object. Impulse is defined as the integral of a force acting on an object, with respect to time. This means that impulse contains the product of force and time. As a result, a large force applied for a short period of time can produce the same momentum change as a ...
Chris, Jakub, Luis PDF
... Impulse changes the momentum of an object. Impulse is defined as the integral of a force acting on an object, with respect to time. This means that impulse contains the product of force and time. As a result, a large force applied for a short period of time can produce the same momentum change as a ...
... Impulse changes the momentum of an object. Impulse is defined as the integral of a force acting on an object, with respect to time. This means that impulse contains the product of force and time. As a result, a large force applied for a short period of time can produce the same momentum change as a ...