Homework 8
... A beam of protons is moving along an accelerator pipe in the z-direction. The particles are uniformly distributed in a cylindrical volume of length L0 (in the z direction) and radius R0 . The particles have momenta uniformly distributed with pz in an interval p0 ± pz and the transverse (along x-y) m ...
... A beam of protons is moving along an accelerator pipe in the z-direction. The particles are uniformly distributed in a cylindrical volume of length L0 (in the z direction) and radius R0 . The particles have momenta uniformly distributed with pz in an interval p0 ± pz and the transverse (along x-y) m ...
template
... experience the greatest force of impact? FMack truck Geo = -FGeo M ack truck Which will experience the greatest change in momentum? Because the magnitude of the force and time of impact is identical for each object, the changes in momentum would also be equal. Which will experience the greatest a ...
... experience the greatest force of impact? FMack truck Geo = -FGeo M ack truck Which will experience the greatest change in momentum? Because the magnitude of the force and time of impact is identical for each object, the changes in momentum would also be equal. Which will experience the greatest a ...
Physics 105a-2008 Practice Problems for Exam 2 IMPORTANT: This
... Derive the law of conservation of momentum, i.e. dP Fnet ext (where P is the total momentum of a system), dt from Newton’s laws. 5. Many commercial satellites are in “geosynchronous” orbits, i.e. circular orbits above the equator for which the period is 24 hours, so that the satellite is always ab ...
... Derive the law of conservation of momentum, i.e. dP Fnet ext (where P is the total momentum of a system), dt from Newton’s laws. 5. Many commercial satellites are in “geosynchronous” orbits, i.e. circular orbits above the equator for which the period is 24 hours, so that the satellite is always ab ...
The Mechanical Energy of an object is the total of all kinetic energy
... m/s. The force of friction between the mass and the surface on which it is sliding is 0.240 N. If the mass compresses the spring 10.0 cm: (a) What is the kvalue for the spring? (b) How fast will the mass be moving as it leaves the spring? ...
... m/s. The force of friction between the mass and the surface on which it is sliding is 0.240 N. If the mass compresses the spring 10.0 cm: (a) What is the kvalue for the spring? (b) How fast will the mass be moving as it leaves the spring? ...
Momentum Notes
... m1v1 + m2v2 = mtotalvtotal m1=mass of 1st object (kg) v1=velocity of 1st object(m/s) m2= mass of 2nd object(kg) v2=velocity of 2nd object(m/s) ...
... m1v1 + m2v2 = mtotalvtotal m1=mass of 1st object (kg) v1=velocity of 1st object(m/s) m2= mass of 2nd object(kg) v2=velocity of 2nd object(m/s) ...
Chapter 3 Problem Set
... Before we can solve for power we have to convert the time (25 min) into seconds: t = 25 min X 60 sec/min = 1,500 sec Now solving for the power: P = W/t = 253,820 J/1500 sec = 169 w (watts) 24. A boy throws a 4-kg pumpkin at 8 m/sec to a 40-kg girl on roller skates, who catches it. At what speed does ...
... Before we can solve for power we have to convert the time (25 min) into seconds: t = 25 min X 60 sec/min = 1,500 sec Now solving for the power: P = W/t = 253,820 J/1500 sec = 169 w (watts) 24. A boy throws a 4-kg pumpkin at 8 m/sec to a 40-kg girl on roller skates, who catches it. At what speed does ...
2. energy and momentum
... 4. A field gun of mass 1000kg fires a shell of mass 5kg with a velocity of 100m/s. Calculate the recoil velocity of the gun. ...
... 4. A field gun of mass 1000kg fires a shell of mass 5kg with a velocity of 100m/s. Calculate the recoil velocity of the gun. ...
F - Sfu
... momentum of the system is conserved (even though the total momentum vector may or may not be conserved). Note 2: For a one-object system, the condition for momentum conservation is that the net force acting on the object is zero. ...
... momentum of the system is conserved (even though the total momentum vector may or may not be conserved). Note 2: For a one-object system, the condition for momentum conservation is that the net force acting on the object is zero. ...
File
... Elastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is equal to the total kinetic energy before the collision. Inelastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is not equal to the total kinetic energy before the c ...
... Elastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is equal to the total kinetic energy before the collision. Inelastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is not equal to the total kinetic energy before the c ...
Standard Physics Final Exam Review Guide
... a) They collide and destroy each other b) They pass through each other c) They tangle up d) They bounce off 3) When a wave enters a new medium and it bends this is: c) Diffraction c) Refraction d) Reflection 4) What is an example of sound diffracting and then reflecting? a) Hearing the teacher in th ...
... a) They collide and destroy each other b) They pass through each other c) They tangle up d) They bounce off 3) When a wave enters a new medium and it bends this is: c) Diffraction c) Refraction d) Reflection 4) What is an example of sound diffracting and then reflecting? a) Hearing the teacher in th ...
Ch 9 HW Day 1
... 62. Picture the Problem The earth’s rotational kinetic energy is given by K rot 12 I 2 where I is its moment of inertia with respect to its axis of rotation. The center of mass of the earth-sun system is so close to the center of the sun and the earthsun distance so large that we can use the eart ...
... 62. Picture the Problem The earth’s rotational kinetic energy is given by K rot 12 I 2 where I is its moment of inertia with respect to its axis of rotation. The center of mass of the earth-sun system is so close to the center of the sun and the earthsun distance so large that we can use the eart ...
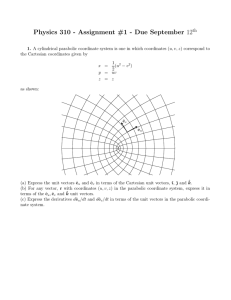
Physics 310 - Assignment #1 - Due September 12
... (c) Express the derivatives dêu /dt and dêv /dt in terms of the unit vectors in the parabolic coordinate system. ...
... (c) Express the derivatives dêu /dt and dêv /dt in terms of the unit vectors in the parabolic coordinate system. ...
Ch6 momentum and collision
... In a crash test, a car of mass 1.50 x 103 kg collides with a wall and rebounds. The initial and final velocities of the car are vi = -15.0m/s vf = 2.60m/s, A rocket has a total mass of 1.00 x 105 kg and a respectively. If the collision lasts for 0.150s, find burnout mass of 1.00 x104 kg, including ...
... In a crash test, a car of mass 1.50 x 103 kg collides with a wall and rebounds. The initial and final velocities of the car are vi = -15.0m/s vf = 2.60m/s, A rocket has a total mass of 1.00 x 105 kg and a respectively. If the collision lasts for 0.150s, find burnout mass of 1.00 x104 kg, including ...