You get to explore the possible energy transitions for Hydrogen
... is a satellite of the more massive object. The two bodies orbit a common center of mass. For a much smaller satellite, the center of mass is inside the more massive body. ...
... is a satellite of the more massive object. The two bodies orbit a common center of mass. For a much smaller satellite, the center of mass is inside the more massive body. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Force, Mass and Acceleration More force on a constant mass causes more acceleration. Doubling the force, doubles the acceleration. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force acting on it ...
... Force, Mass and Acceleration More force on a constant mass causes more acceleration. Doubling the force, doubles the acceleration. The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force acting on it ...
Chapter 8 Motion and Forces - Mrs. Cavanaugh's PbWiki
... acceleration for this fall due to gravity is 9.8 m/s2. How long does it take for the pot to hit the sidewalk? ...
... acceleration for this fall due to gravity is 9.8 m/s2. How long does it take for the pot to hit the sidewalk? ...
9-Momentum and impulse
... Ex: a gun will recoil when fired b/c the momentum of the gun and bullet together before the shot should equal the total momentum of the bullet and the gun after ...
... Ex: a gun will recoil when fired b/c the momentum of the gun and bullet together before the shot should equal the total momentum of the bullet and the gun after ...
PDF
... α21 , are the acceleration of Q2, the angular velocity and acceleration vectors respectively, all of them measured by an observer located at 1. This equation was got by Euler by using a fixed system of principal axes with origin at C2. In that case we have Q = C, and therefore MC = IC α21 + ω 21 × ( ...
... α21 , are the acceleration of Q2, the angular velocity and acceleration vectors respectively, all of them measured by an observer located at 1. This equation was got by Euler by using a fixed system of principal axes with origin at C2. In that case we have Q = C, and therefore MC = IC α21 + ω 21 × ( ...
Newton`s Second Law
... Newton’s second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly related to the force on it, and inversely related to the mass of the object. You need more force to move or stop an object with a lot of mass (or inertia) than you need for an object with less mass. The formula for the sec ...
... Newton’s second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly related to the force on it, and inversely related to the mass of the object. You need more force to move or stop an object with a lot of mass (or inertia) than you need for an object with less mass. The formula for the sec ...
Review - Hingham Schools
... Be able to identify and diagram the forces on an object. Know what net force means and understand the direction it points relative to a and v for different types of motion. Know the differences between mass and weight. Be able to calculate weight given the mass and vice versa. Be able to apply Newto ...
... Be able to identify and diagram the forces on an object. Know what net force means and understand the direction it points relative to a and v for different types of motion. Know the differences between mass and weight. Be able to calculate weight given the mass and vice versa. Be able to apply Newto ...
02 Mechanical Energy
... Calculate the change in potential energy of a 94.7 kg man when he takes an elevator from the first floor to 20th floor, if the distance between floors is 3.81 m. ...
... Calculate the change in potential energy of a 94.7 kg man when he takes an elevator from the first floor to 20th floor, if the distance between floors is 3.81 m. ...
3.Momentum
... • The Total Momentum of a system equals the vector sum of the momenta of all the objects in the system: • PTotal System = P1 + P2 (for a system of two objects) • Also called the “Net Momentum”: PNET • EXAMPLES: – We have two cars, each with mass: m=6 kg. One travels at 20m/s East and the other at 20 ...
... • The Total Momentum of a system equals the vector sum of the momenta of all the objects in the system: • PTotal System = P1 + P2 (for a system of two objects) • Also called the “Net Momentum”: PNET • EXAMPLES: – We have two cars, each with mass: m=6 kg. One travels at 20m/s East and the other at 20 ...
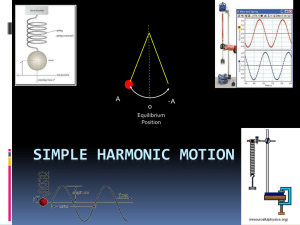
where 14-3 Energy in the Simple Harmonic Oscillator This graph
... 0.100 m, x = -(0.100 m) cos 8.08t, and v = (0.808 m/s) sin 8.08t), determine (a) the total energy, (b) the kinetic and potential energies as a function of time, (c) the velocity at half amplitude (x = ± A/2), and (d) the kinetic and potential energies when the mass is 0.050 m from equilibrium ...
... 0.100 m, x = -(0.100 m) cos 8.08t, and v = (0.808 m/s) sin 8.08t), determine (a) the total energy, (b) the kinetic and potential energies as a function of time, (c) the velocity at half amplitude (x = ± A/2), and (d) the kinetic and potential energies when the mass is 0.050 m from equilibrium ...
Kinetic Energy
... velocity of a fluid increases, the pressure exerted by the fluid decreases. In other words, the faster a fluid moves the less pressure it exerts. Bernoulli’s principle explains why planes can fly. The shape of the wing causes air to move faster across the top, resulting in higher pressure below the ...
... velocity of a fluid increases, the pressure exerted by the fluid decreases. In other words, the faster a fluid moves the less pressure it exerts. Bernoulli’s principle explains why planes can fly. The shape of the wing causes air to move faster across the top, resulting in higher pressure below the ...
Study Notes
... box is that they are accelerating with respect to each other. If the two observers are not accelerating with respect to each other then they will agree on the acceleration of the box. Galileo realized that fact and it is called Galilean Relativity: All frames in uniform motion are equivalent. This w ...
... box is that they are accelerating with respect to each other. If the two observers are not accelerating with respect to each other then they will agree on the acceleration of the box. Galileo realized that fact and it is called Galilean Relativity: All frames in uniform motion are equivalent. This w ...